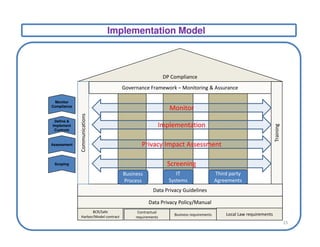
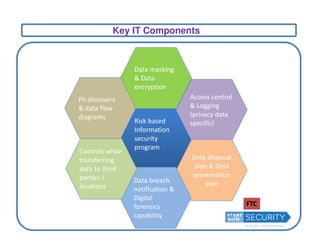
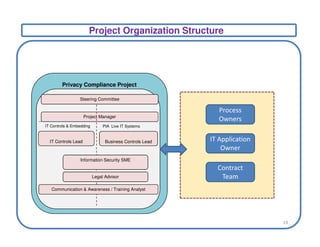
This document discusses privacy frameworks and their implementation. It begins by distinguishing privacy from security, then outlines several common privacy principles like notice, choice, and consent. It also reviews some key privacy standards and regulations. The document then presents an approach for implementing privacy that involves conducting privacy impact assessments, defining business and technical controls, and establishing an implementation project structure. It identifies some common challenges to privacy implementation like evolving rules and technical limitations.