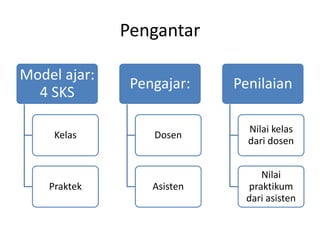
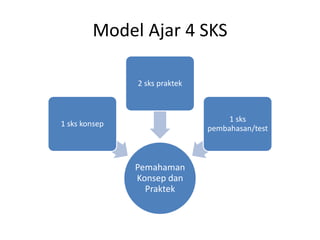
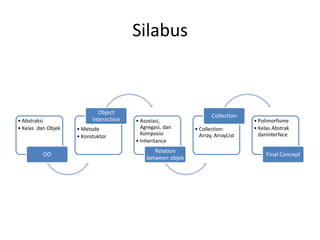
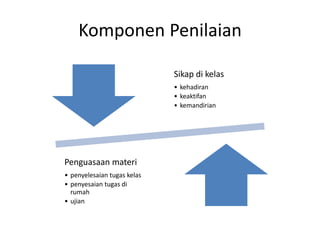
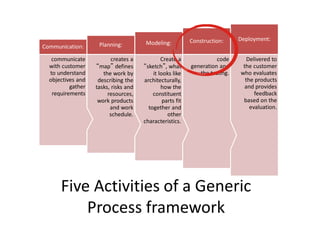
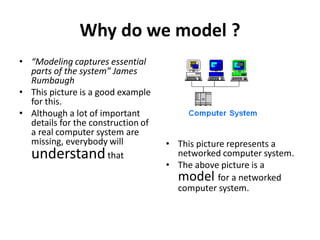
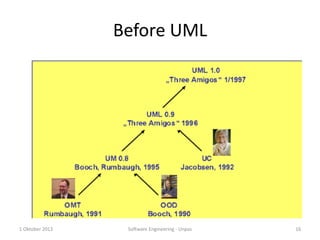
This document outlines the syllabus for the IT 405: Object-Oriented Software Construction course. It provides information about the course structure, instructors, learning objectives, topics to be covered, and assessment components. The course is a 4 credit class divided between conceptual learning and practical application. Students will learn object-oriented programming concepts in Java through lectures, assignments, and labs. Topics include abstraction, classes and objects, methods, constructors, object interaction, inheritance, polymorphism, collections, and more. Assessment will consider attitude, class participation, homework, and exams. The first session will cover modeling concepts and abstraction.