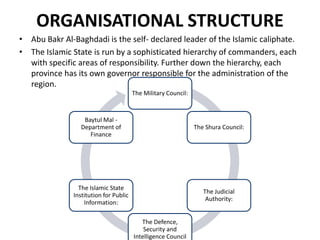
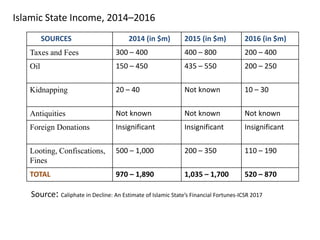
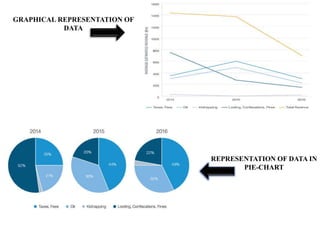
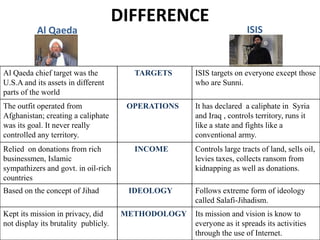
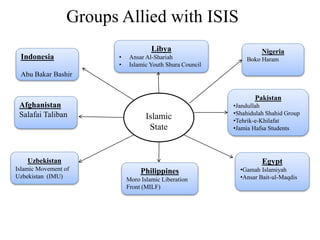
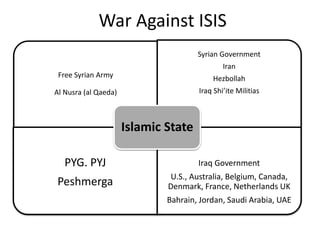
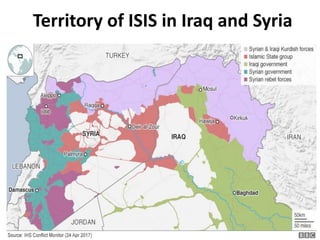
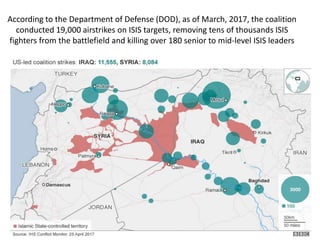
The document discusses the rise of ISIS, tracing its origins to the U.S. invasion of Iraq in 2003 and detailing its leadership under Abu Bakr al-Baghdadi. It outlines ISIS's ideologies, organizational structure, and methods of recruitment, as well as its military operations in Iraq and Syria. Additionally, it highlights the coalition's efforts to combat ISIS, noting significant territorial losses for the group and the need for comprehensive strategies to counteract its influence.