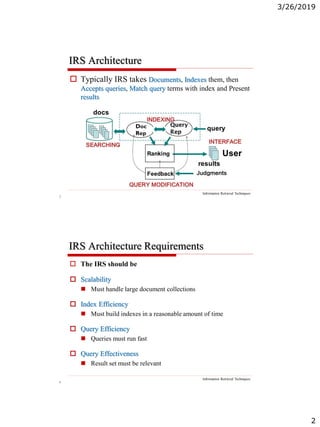
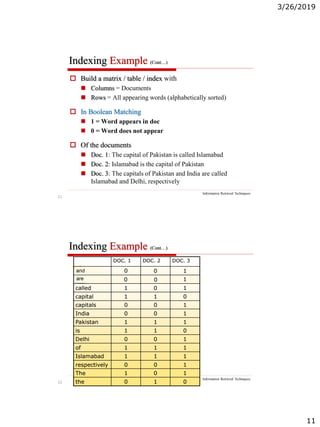
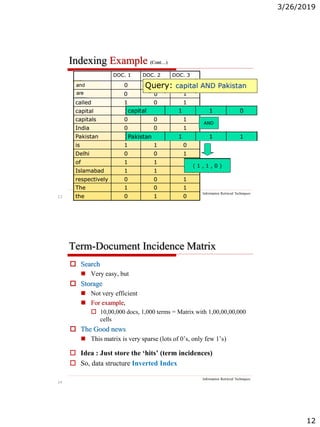
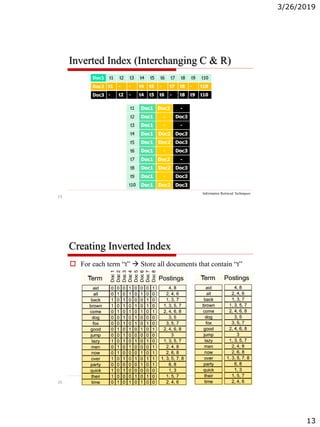
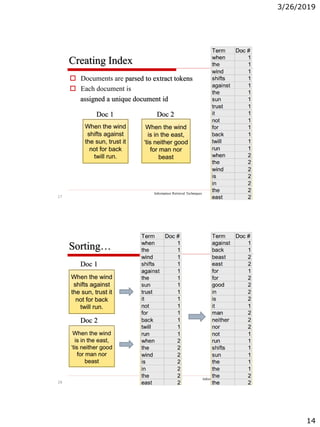
The document discusses the architecture of information retrieval systems (IRS). It describes how IRS typically indexes documents, accepts queries, matches query terms to the index, and presents results. It notes the requirements of scalability, efficient indexing and querying, and relevant results. It outlines the types of content an IRS may contain like text, images, audio and video. It discusses document structure and representation for retrieval, including indexing terms and creating an inverted index for efficient searching.