The document discusses the implementation of an IPv4 network stack in Ada 2012 using the Ravenscar profile, designed for embedded ARM boards with a small footprint and standard protocols. It presents the architecture, implementation goals, and examples, particularly focusing on the Etherscope project, a network protocol analyzer. Additionally, it addresses challenges regarding random number generation, memory management, and concurrency, while highlighting the benefits of the Ada concurrency model in achieving reliability and robustness.




![https://github.com/stcarrez/ada-enet 7
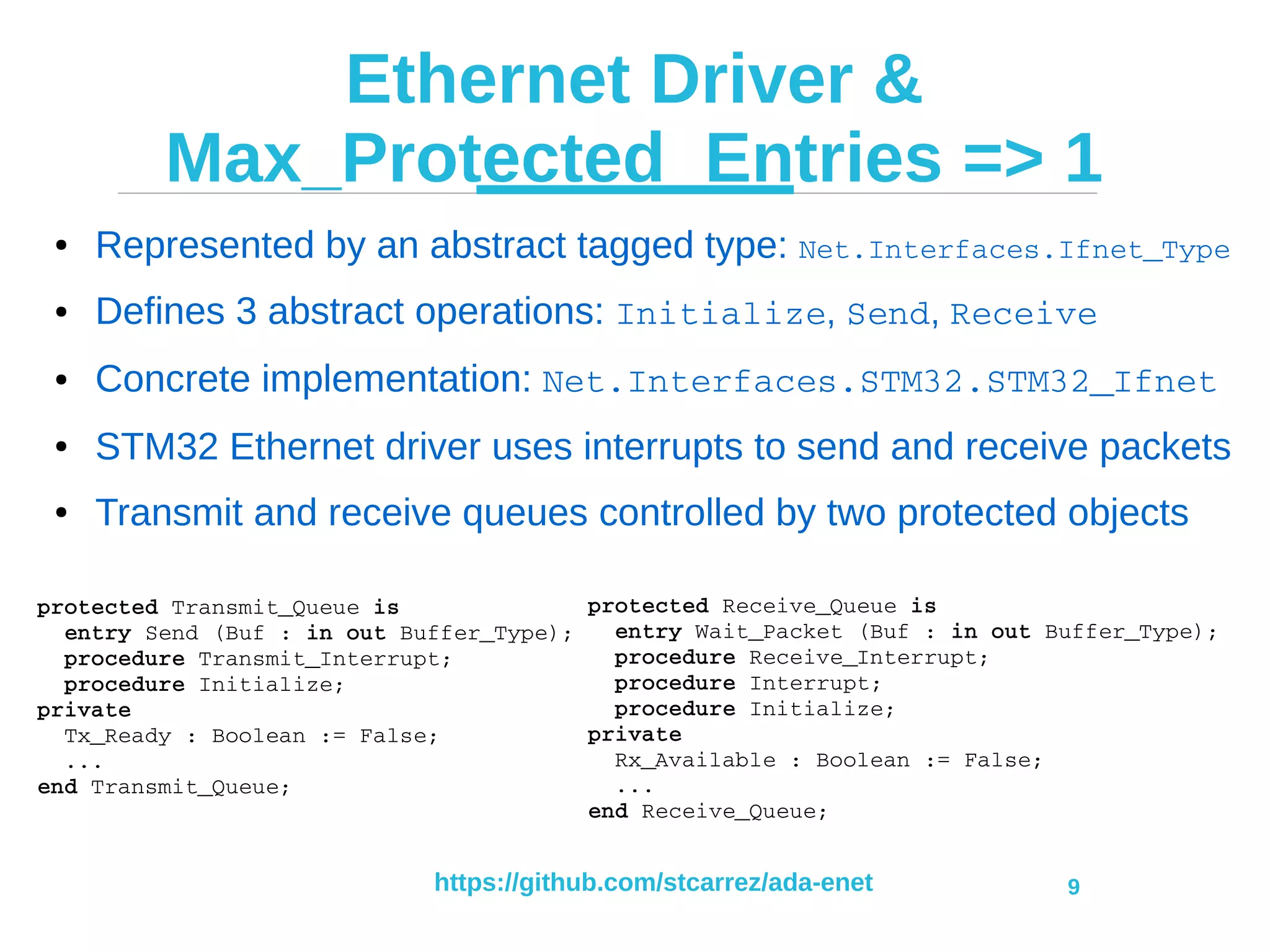
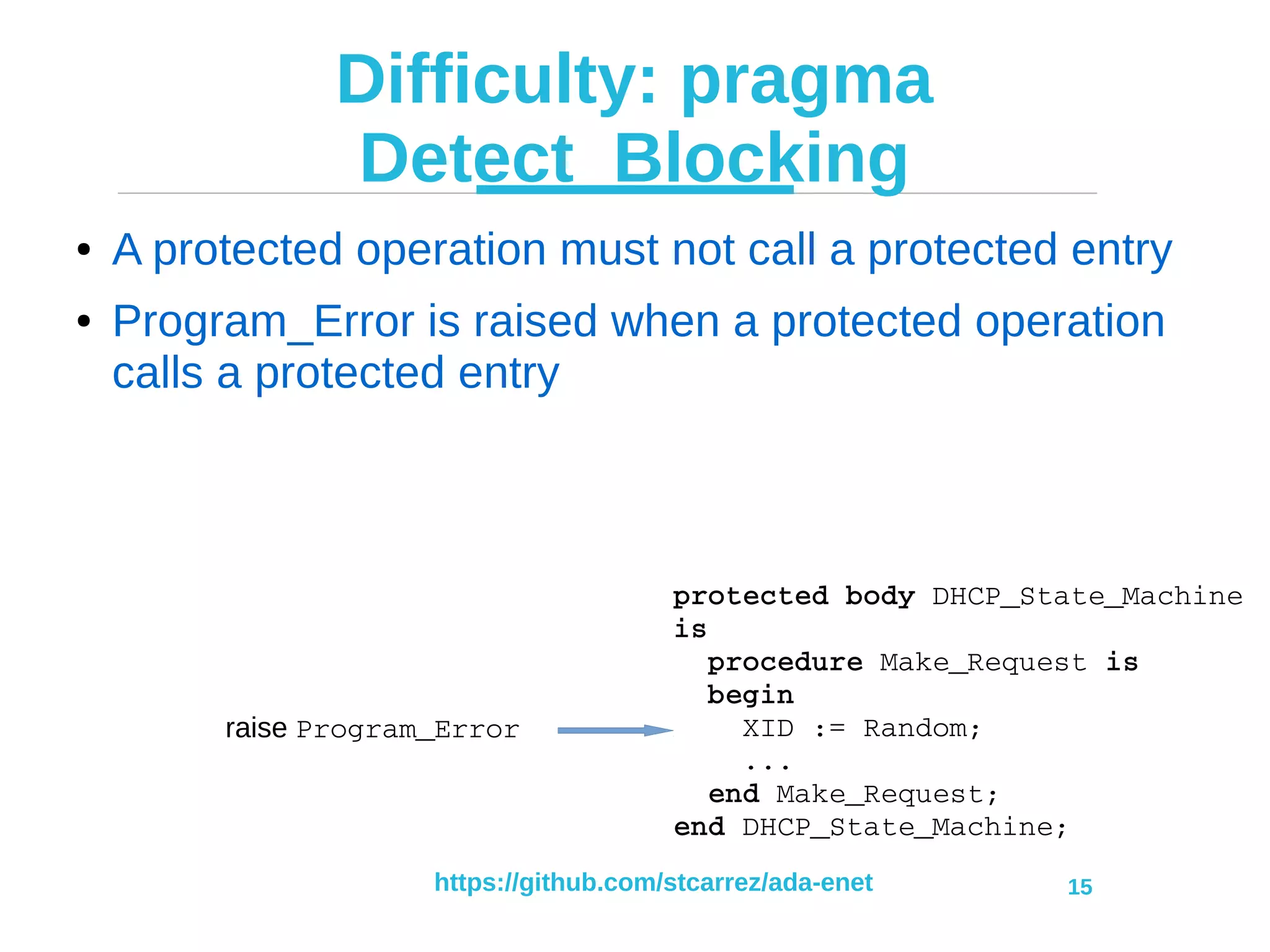
Sending a packet
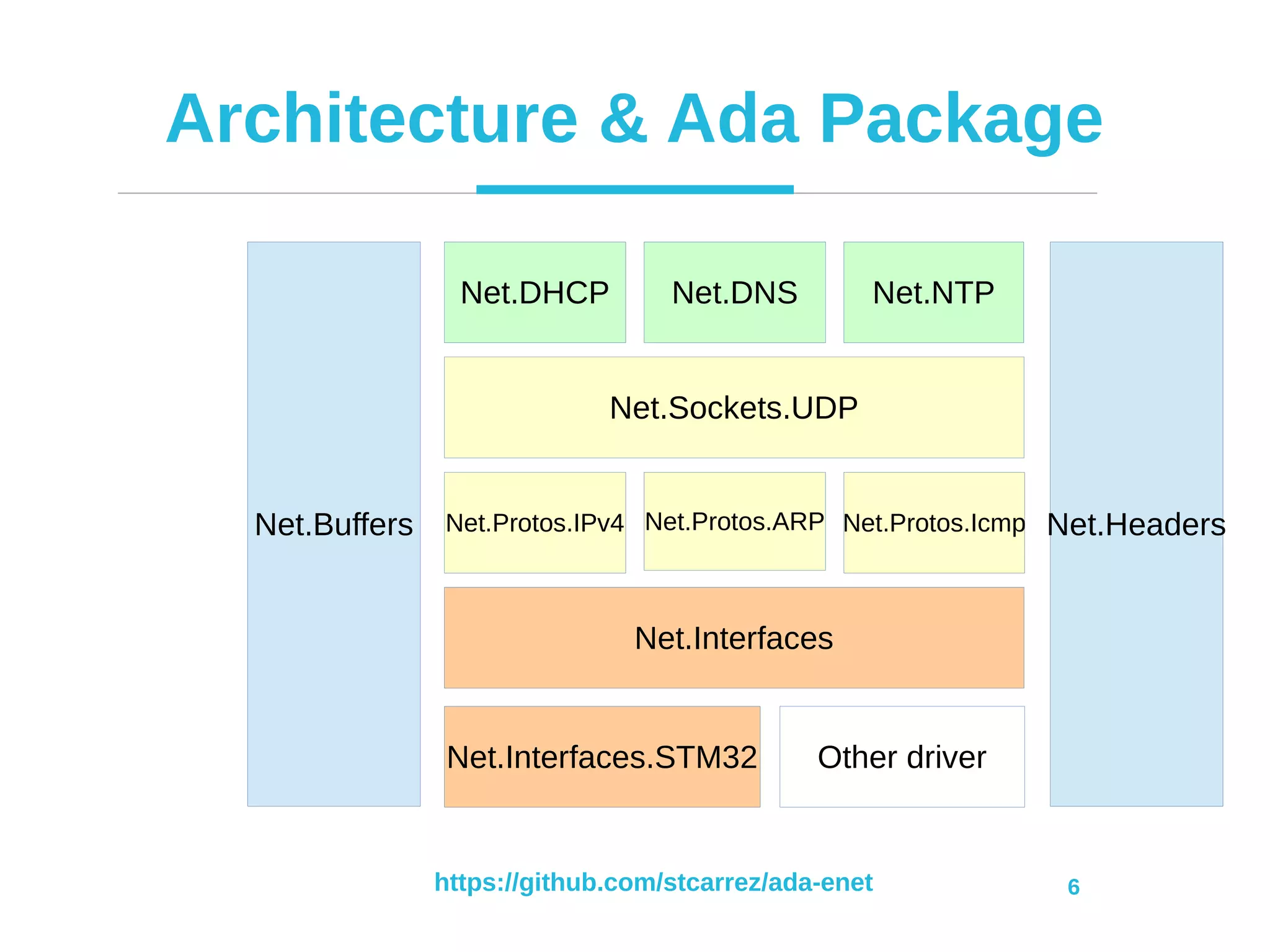
Net.DHCP Net.DNS
Net.Sockets.UDP
Net.Protos.IPv4 Net.Protos.ARP
Net.Interfaces
Net.Buffers Net.Protos.Icmp
Net.NTP
Net.Interfaces.STM32 Other driver
Net.Headers
[1] Allocate
[2] Send
[6] Release
[3] Send
[5] Send
[4] Resolve](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ada-enet-presentation-2017-06-13-170616104402/75/IP-Network-Stack-in-Ada-2012-and-the-Ravenscar-Profile-7-2048.jpg)
![https://github.com/stcarrez/ada-enet 8
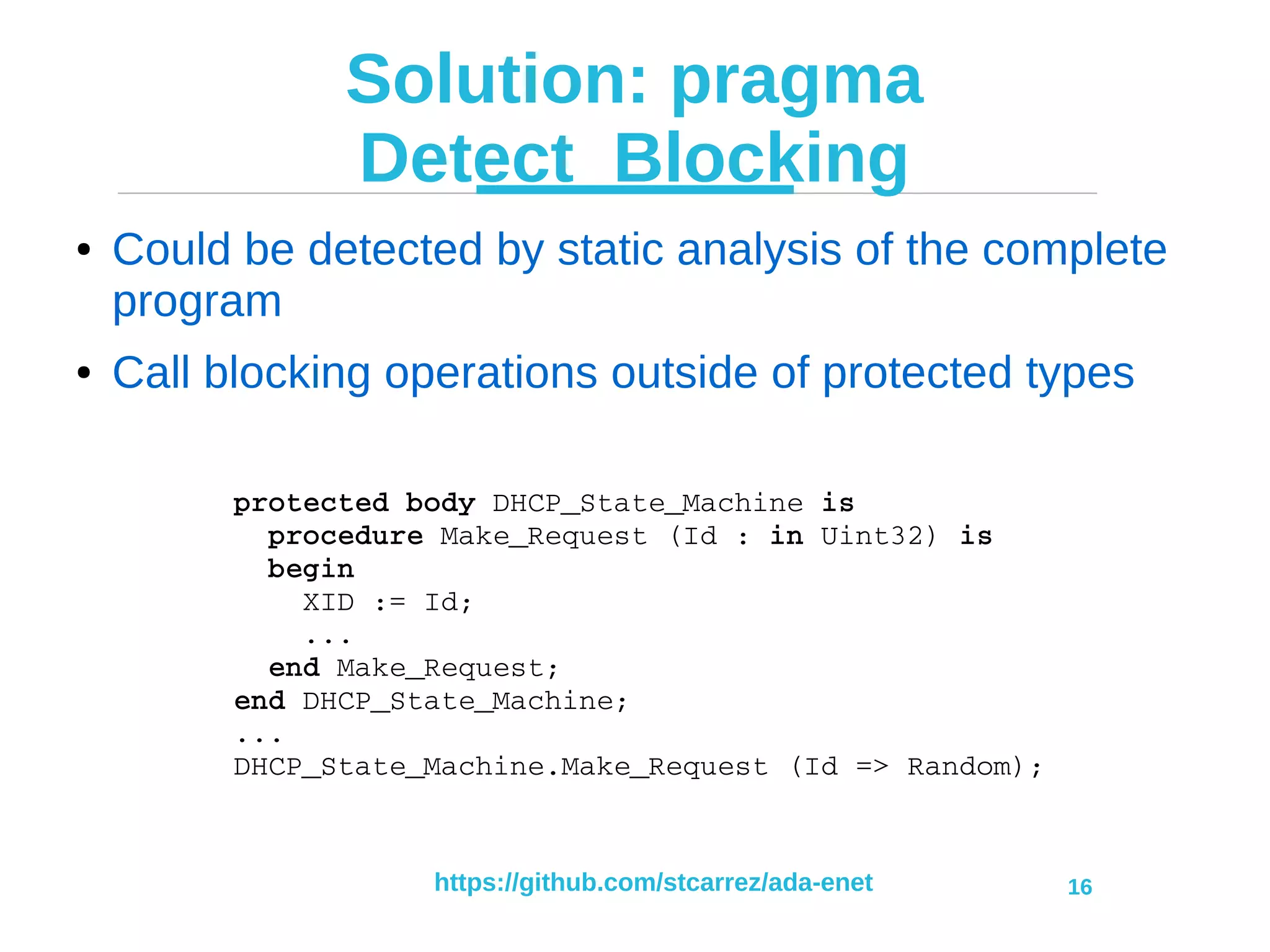
Receiving a packet
Net.DHCP Net.DNS
Net.Sockets.UDP
Net.Protos.IPv4 Net.Protos.ARP
Net.Interfaces
Net.Buffers Net.Protos.Icmp
Net.NTP
Net.Interfaces.STM32 Other driver
Net.Headers
[1] Allocate
[5] Receive
[3] Receive
[2] Receive
Application
Receive
Task
[4] Receive](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ada-enet-presentation-2017-06-13-170616104402/75/IP-Network-Stack-in-Ada-2012-and-the-Ravenscar-Profile-8-2048.jpg)