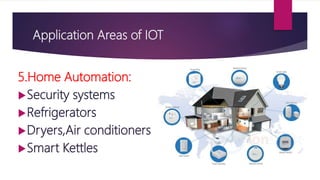
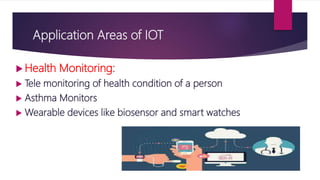
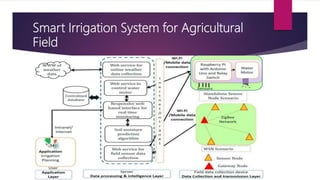
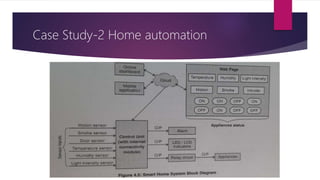
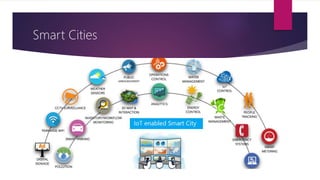
The document discusses applications of the Internet of Things (IoT). It describes major application areas of IoT such as manufacturing and logistics, smart transportation, environmental monitoring, energy and utilities, and home automation. Specific applications mentioned include automation, real-time stock monitoring, traffic data collection, weather forecasting, smart electricity grids, security systems, and health monitoring devices. The document also presents challenges of IoT like power consumption, security, and data storage and processing. It provides case studies on smart irrigation systems, home automation, and smart cities and their benefits.