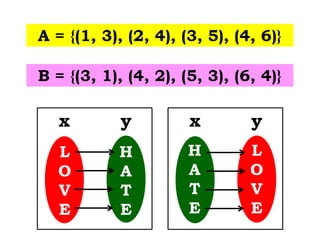
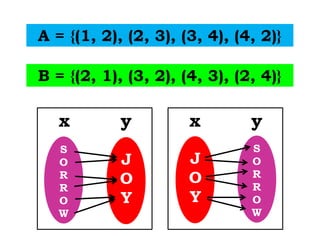
1) The document discusses properties of equality and inverse functions. It provides examples of finding the inverse of functions like f(x) = 3x + 6.
2) Students are asked to find the inverse of various functions through a series of examples and activities. This includes making tables, graphing functions and their inverses, and determining domains and ranges.
3) One example finds the inverse of the function y = 150 + 50x, which describes a math tutor's hourly earnings. The inverse represents the number of students that can be assisted in an hour given a particular earnings amount.