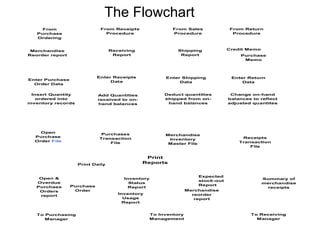
The flowchart describes the inventory management system for a retail company. It shows the process from receiving merchandise reorder reports to printing various daily reports. Key data is entered into the system from purchase orders, receipts, sales, and returns. This data is then stored in files and used to update inventory records and print reports for managers. The reports provide information on open orders, inventory status and needs, and receipts. Threats like systems failures or errors are mitigated by backups, access controls, and staff training.