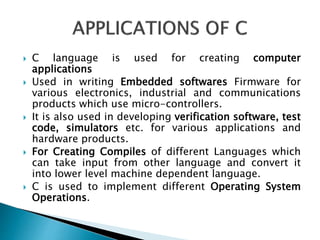
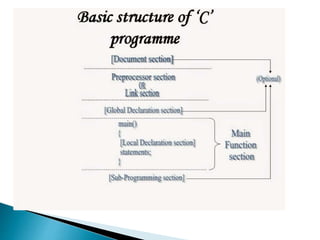
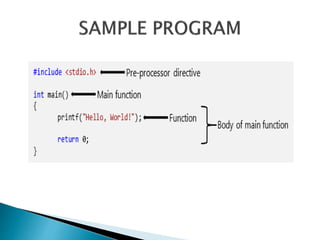
C programming is a general-purpose language developed in 1972 by Dennis Ritchie to develop UNIX. It is widely used and easy to learn. C is useful for systems programming and embedded systems. To create a C program, one writes code, compiles it, and runs it to get output. C covers fundamental programming concepts like data types, variables, operators, and functions.