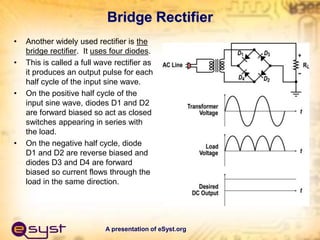
- The document describes the key components and functioning of a typical power supply system, including how it converts alternating current (AC) from a power outlet into direct current (DC) to power electronic circuits and components.
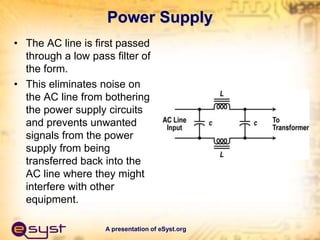
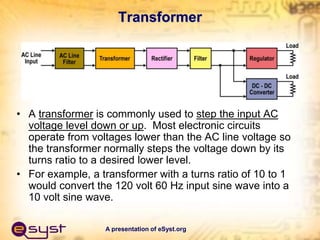
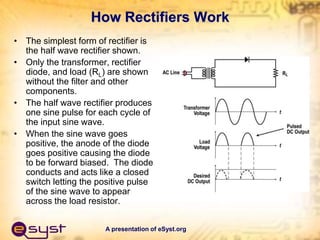
- The main components are a transformer, rectifier, filter, and regulator. The transformer steps down the AC voltage, the rectifier converts it to pulsating DC, the filter smooths it to constant DC, and the regulator maintains a fixed output voltage.
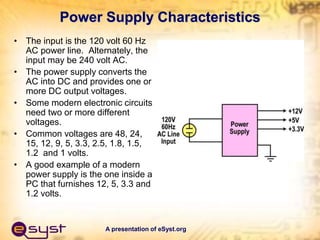
- Power supplies are essential to power all electronic equipment and provide properly regulated voltage levels required by semiconductor devices and integrated circuits.