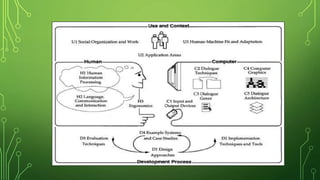
This document introduces human-computer interaction (HCI). HCI aims to improve the interaction between users and computers by making technology more usable and responsive. It covers topics such as what HCI is, why it is important given more people use computers, and its interdisciplinary nature, drawing from fields like psychology, computer science, and design. The document also discusses HCI's scope and goals, as well as the key components involved - the human, computer, and their interaction.