More Related Content
ODP
Light introduction to HTML PPTX
9781285852645_CH01 research and analysis of data.pptx PPTX
An Overview of HTML, CSS & Java Script PPTX
PPT ON SEMINAR REPORT.pptx. bhvhvhchchvhchch PPTX
Introduction to web design discussing which languages is used for website des... PPTX
Tech Winter Break - GDG on Campus - PIET PPTX
PDF
Web Concepts - an introduction - introduction Similar to introduction to_HTML_CSS_presentationpreso.ppt
PPTX
Web development using HTML and CSS PPT
PPTX
Introduction to HTML+CSS+Javascript.pptx PPTX
Introduction to HTML+CSS+Javascript.pptx PDF
HTML/CSS Crash Course (april 4 2017) PPT
PDF
Html & Html5 from scratch PDF
PDF
GDI Seattle Intro to HTML and CSS - Class 1 PPTX
Introduction to HTML+CSS+Javascript.pptx PPTX
Web Information Systems Html and css PPTX
PPTX
Introduction to HTML+CSS+Javascript.pptx PPTX
web pro web pro web pro web pro v w.pptx PPTX
Web Designing Lecture 2 in Software.pptx PPTX
Randompptpresentationonsportsforvtu.pptx KEY
PPTX
PPTX
PDF
Recently uploaded
PDF
What is Voice User Interface (VUI) Definition & Examples.pdf PDF
कम्प्यूटर.pdf for all computer examination PDF
Unit 1.2 Components of a Computer System.pdf PDF
Huawei Datacom – How To Pass H12-892 On Your First Try PPT
Carole BirdCarole BirdCarole BirdCarole Bird.ppt PPTX
AN Introduction to UNIX File System—An Approach PPTX
Digital transformation success powered by EPM and NexInfo.pptx PDF
Top Benefits of Using KVM VPS Hosting for Growing Businesses PDF
The map to conquer linear algebra for IT engineer PDF
Small Business Automation: A Comprehensive Cost and ROI Guide PPTX
Cybersecurity Basics: Understanding Threats, Protection Methods, and Safe Dig... PPTX
Why 2026 Could Be a Turning Point for Decentralized Exchanges.pptx PDF
How Azure DevOps Consultants Dubai Reduce Release Delays.pdf PPTX
Spacecraft Guidance Quick Research Guide by Arthur Morgan PDF
Ai In Courts Ai in courts AI in court AI in court PDF
Artificial Intelligence and Barbarism - Conceptual Map PPTX
Pizza Chain Market Data Scraping for Better Insights Report.pptx PPT
HDTV and DTV Standards: The United States Opts for a Digital HDTV Standard PDF
MAD (1).pdf Mobile application develipment PDF
Xemelgo - RFID Industry Predictions for 2026 introduction to_HTML_CSS_presentationpreso.ppt
- 1.
© 2012 AdobeSystems Incorporated. All Rights Reserved.
LEARNING THE LANGUAGE OF THE WEB
INTRODUCTION TO HTML AND CSS
- 2.
© 2012 AdobeSystems Incorporated. All Rights Reserved.
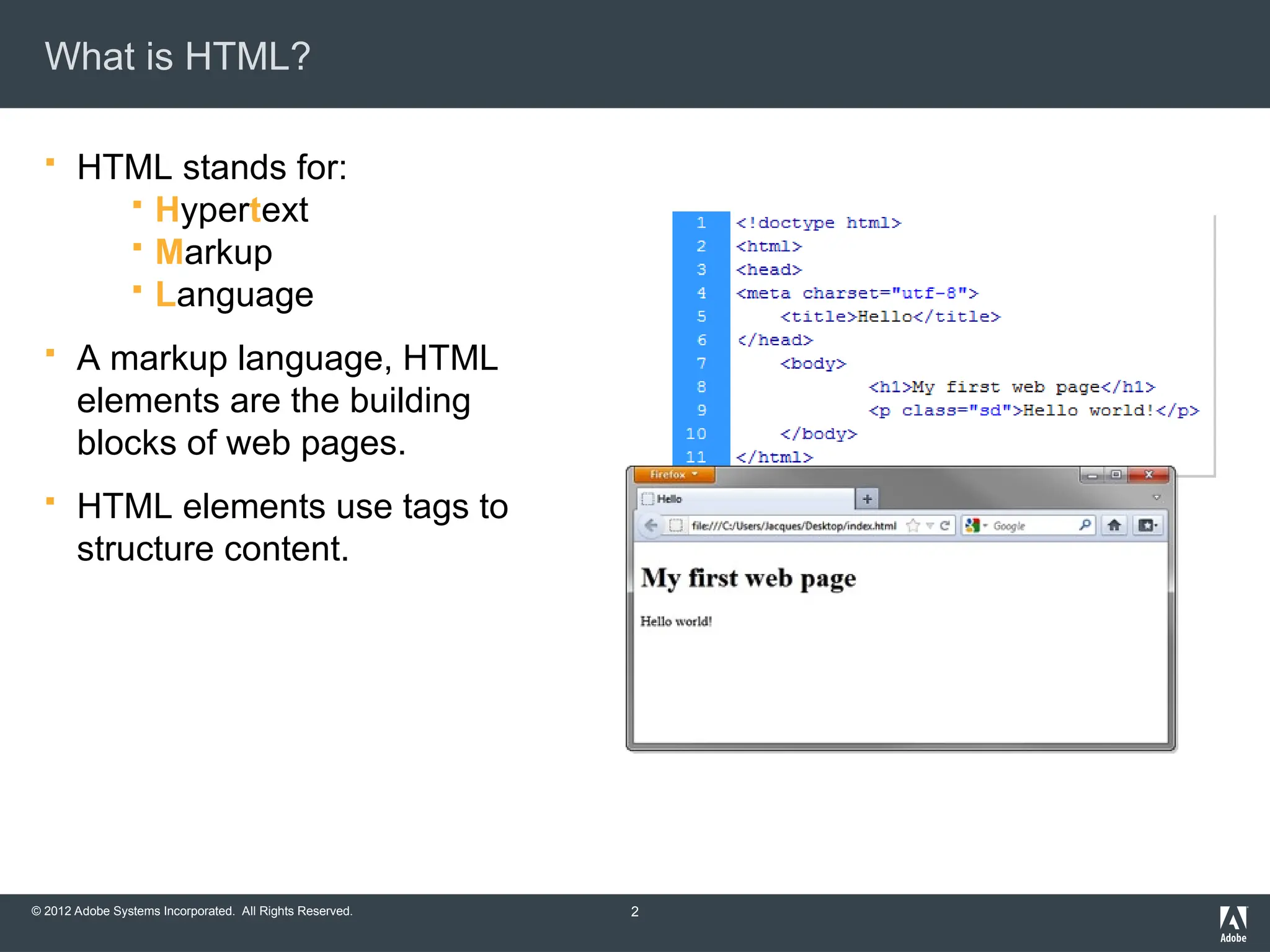
What is HTML?
HTML stands for:
Hypertext
Markup
Language
A markup language, HTML
elements are the building
blocks of web pages.
HTML elements use tags to
structure content.
2
- 3.
© 2012 AdobeSystems Incorporated. All Rights Reserved.
Tags
HTML elements consist of
tags.
Tags are enclosed by angle
brackets, like this: <html>
Tags usually come in pairs, like
this: <title> and </title>
Tags have a start (or opening)
and end (or closing).
Tags are not displayed in a
web browser.
Tags interpret how to display
content between the tags.
3
<html>
<head>
<title></title>
</head>
<body>
<h1></h1>
<p></p>
</body>
</html>
- 4.
© 2012 AdobeSystems Incorporated. All Rights Reserved.
Tags
<html></html> describes the web page.
<head></head> describes the header.
<body></body> describes visible page content.
Common formatting tags:
<h1></h1> displays a heading, ranging from size 1 (biggest) to 6 (smallest).
<p></p> formats text as a paragraph.
<strong></strong> bolds text.
<em></em> emphasizes text, displays as italics.
<br> creates a line break.
Links:
<a href="http://www.example.com"></a> creates a link to a web page.
4
- 5.
© 2012 AdobeSystems Incorporated. All Rights Reserved.
CSS
CSS stands for:
Cascading
Style
Sheets
Describes the “look and feel” of
HTML elements on a web page.
Helps separate document
content (HTML) from document
presentation (CSS).
Structures presentation
elements such as layout, colors,
and fonts.
5
- 6.
© 2012 AdobeSystems Incorporated. All Rights Reserved.
CSS
A style sheet contains a list of rules about how elements appear on a
page.
Consists of a selector and a declaration block:
Selectors tell which markup elements the style applies to.
A declaration block is a list of property and value pairs that define the style.
Can be embedded inside the HTML or linked as a separate document.
6
h1 {
font-family: Verdana, Geneva, sans-serif;
font-size: 24px;
font-weight: bold;
text-transform: uppercase;
color: #C00;
}
- 7.
© 2012 AdobeSystems Incorporated. All Rights Reserved.
Evolution of HTML and CSS
HTML and CSS are a collection of web
standards.
HTML and CSS are a set of best practices
for building websites.
HTML and CSS are constantly evolving:
HTML5 is the fifth iteration of HTML and adds
tags to support multimedia elements and
dynamic graphics in modern web browsers.
CSS3 defines a new set of modular rules for
how HTML content will be presented within
the web browser.
7
- 8.
© 2012 AdobeSystems Incorporated. All Rights Reserved.
HTML5 best practices
Use HTML5 <!doctype html> to tell a browser how to translate.
Use <meta charset="utf-8"> to tell a browser the character-set.
Use semantic markup tags <article>, <section>, <header>,
<nav>, and others to bring a higher level of structural meaning to
documents.
Design and test content across a range of browsers and devices that
support HTML5 capabilities.
8