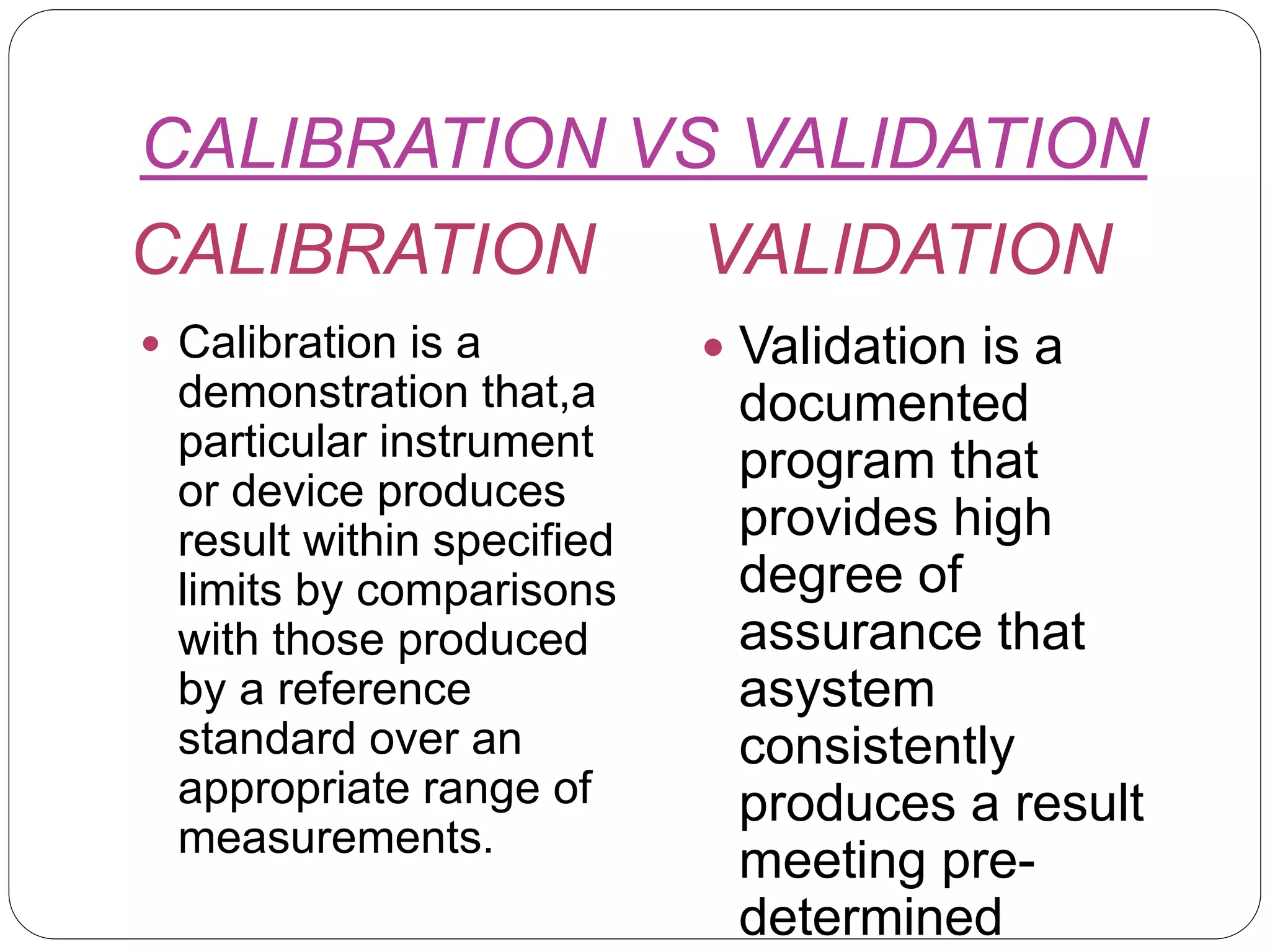
This document provides an introduction to validation, including calibration, qualification, and the difference between calibration and validation. It discusses the scope and purpose of calibration to ensure consistent and accurate measurements. Qualification refers to demonstrating equipment is suitable for its intended use and performs properly, including design, installation, operational, and performance qualification phases. Validation involves systematically determining if facilities, systems, and processes perform as intended. The key difference between calibration and validation is that calibration compares measurements to a reference standard, while validation does not use reference standards. The scope of validation requires appropriate organization, documentation, personnel, and finances.