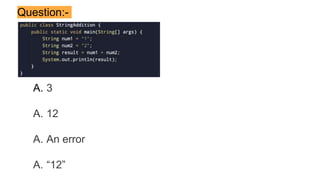
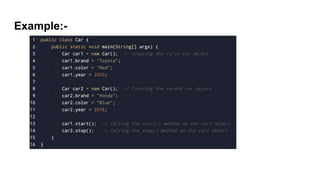
Object-oriented programming (OOP) is a programming paradigm based on objects and classes. The primary purpose of OOP is to increase flexibility and maintainability by structuring a program around reusable pieces of code (classes) that are used to create individual instances (objects). A class defines the variables and methods that characterize objects of a certain kind. For example, a Car class could define characteristics like wheels, a steering wheel, etc. that all car objects would share. Objects are instantiated from classes using the new keyword in Java.