This document provides an introductory tutorial on Java, covering its history, basic definitions, and essential programming concepts such as variables, data types, boolean expressions, and control structures like if statements. It includes practical examples, code snippets, and explanations related to compiling and running Java applications. Additional topics discussed include exception handling, string manipulation, and arithmetic operations.






![TOPS Technologies – Java Introductory tutorial M1 7
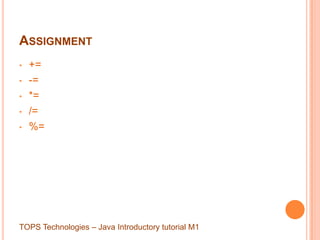
FIRST APPLICATION
/**
*Hello World, first application, only output.
*/
import java.io.*;
public class hello{
public static void main (String [] args) {
System.out.println(“Hello Worldn”);
} //end main
}//end class](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/10-09-2013-javatutorial-130910044737-phpapp02/85/Introduction-to-Java-programming-7-320.jpg)





![14
USING STRINGS
public class hello{
public static void main (String [] args) {
String s = “Hello Worldn”;
System.out.println(s); //output simple
string
} //end main
}//end class hello
TOPS Technologies – Java Introductory tutorial M1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/10-09-2013-javatutorial-130910044737-phpapp02/85/Introduction-to-Java-programming-14-320.jpg)