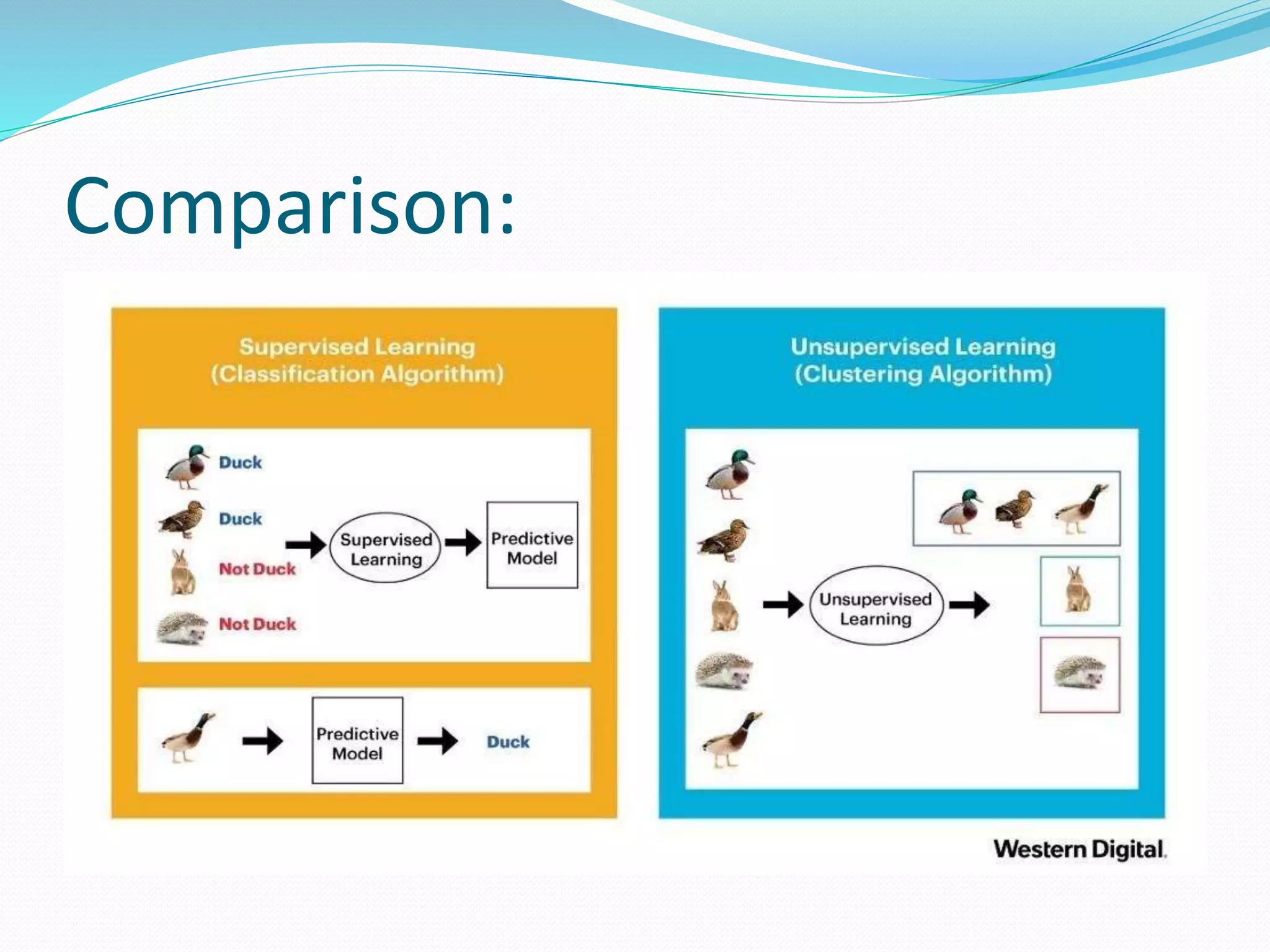
Generative adversarial networks (GANs) are a type of deep learning model used for generative modeling. GANs involve training two neural networks - a generator and a discriminator. The generator produces synthetic data while the discriminator evaluates it as real or fake. This adversarial process trains the generator to produce increasingly realistic samples. GANs frame generative modeling as an adversarial game to learn the training data distribution in an unsupervised manner.