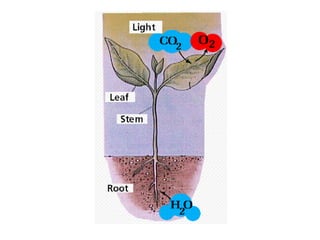
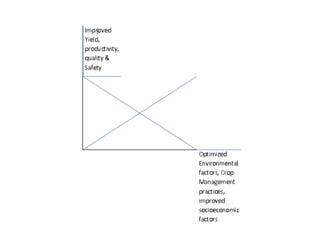
The document discusses the challenges of advanced fruit production due to population growth and land degradation, advocating for increased production and productivity through optimized management practices. It outlines various factors affecting fruit crop production, including environmental, soil, genetic, and socio-economic factors. Key management strategies involve careful crop handling, pest management, and addressing infrastructure deficiencies to improve quality and safety of fruit crops.