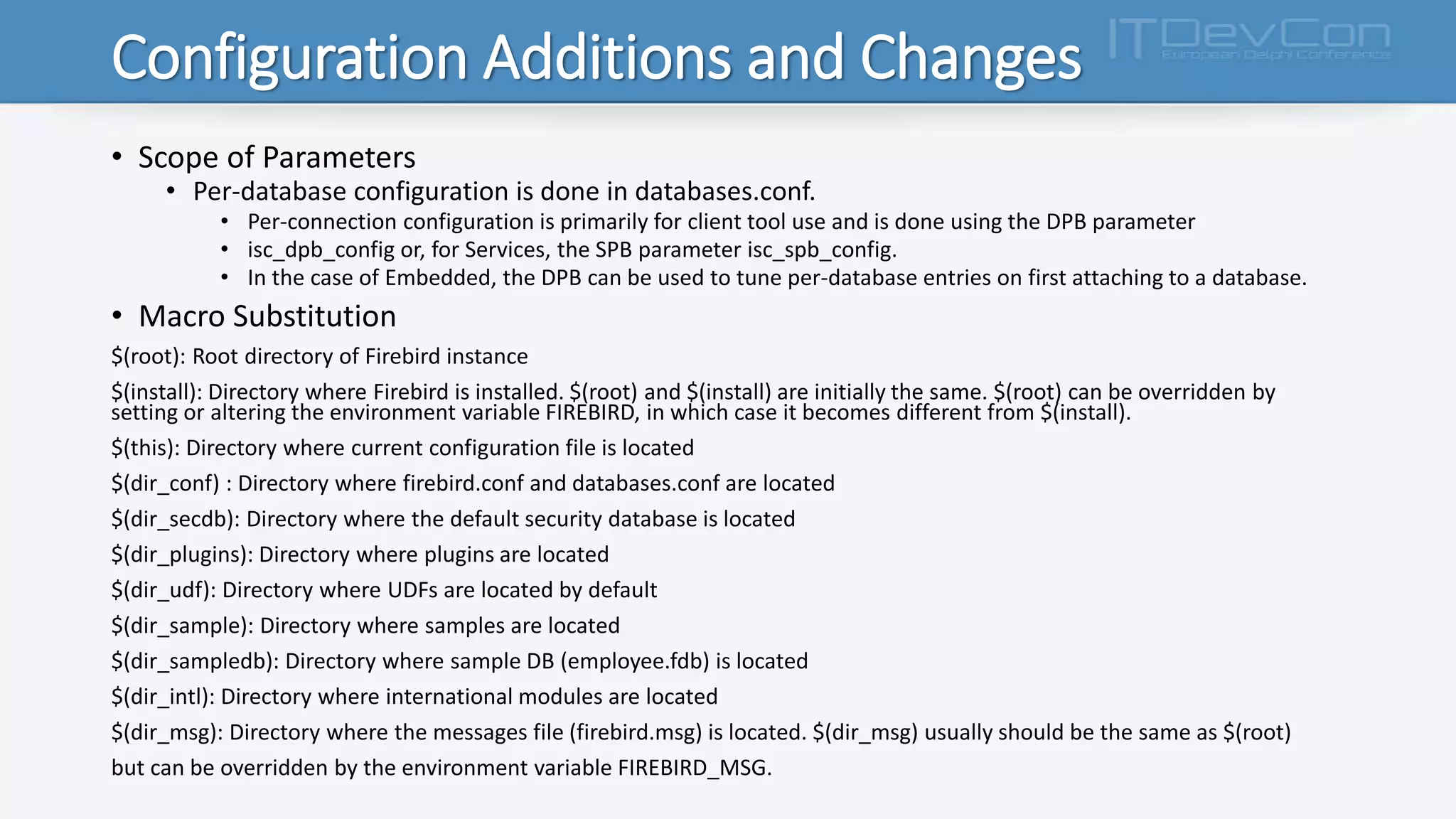
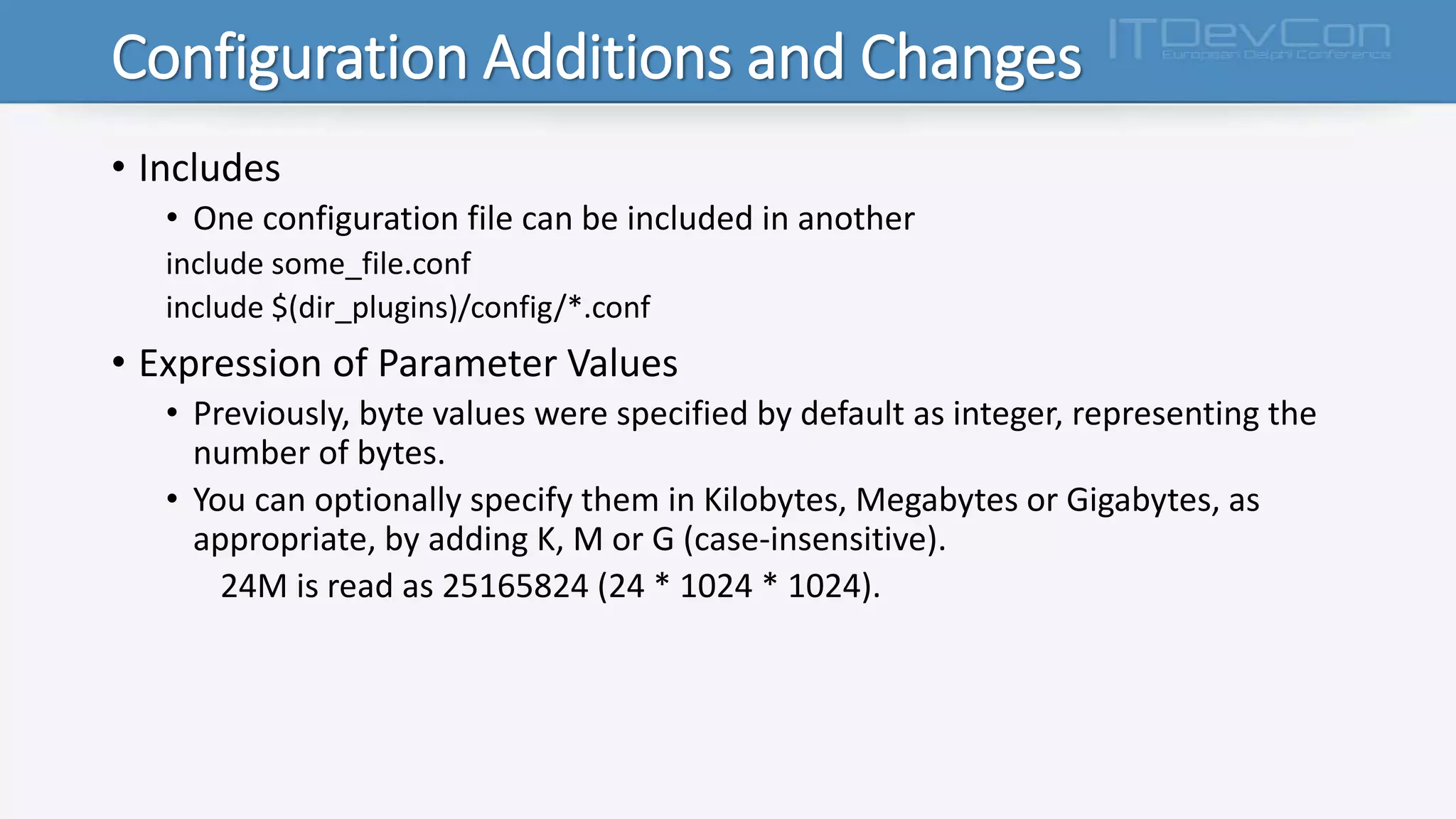
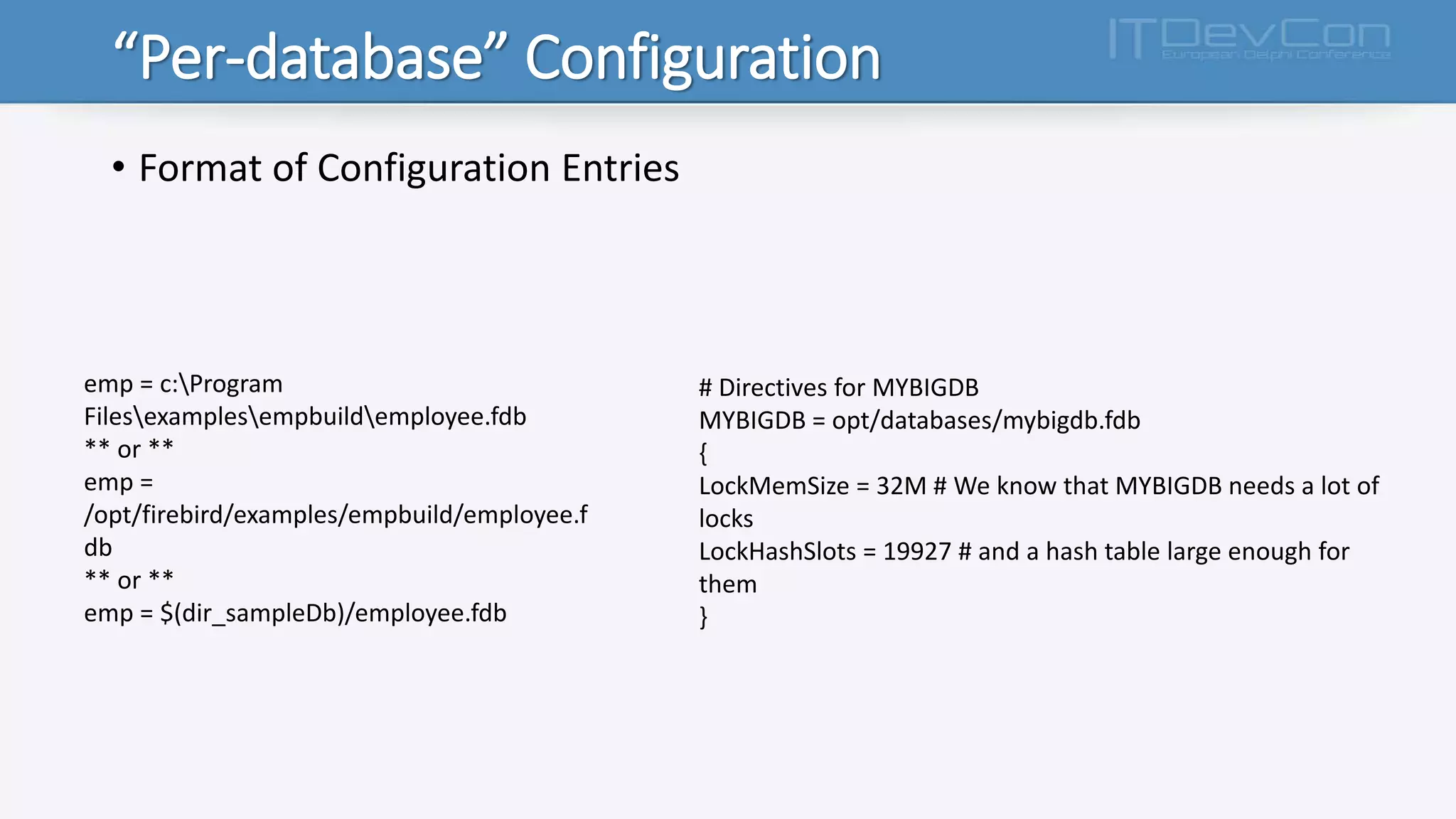
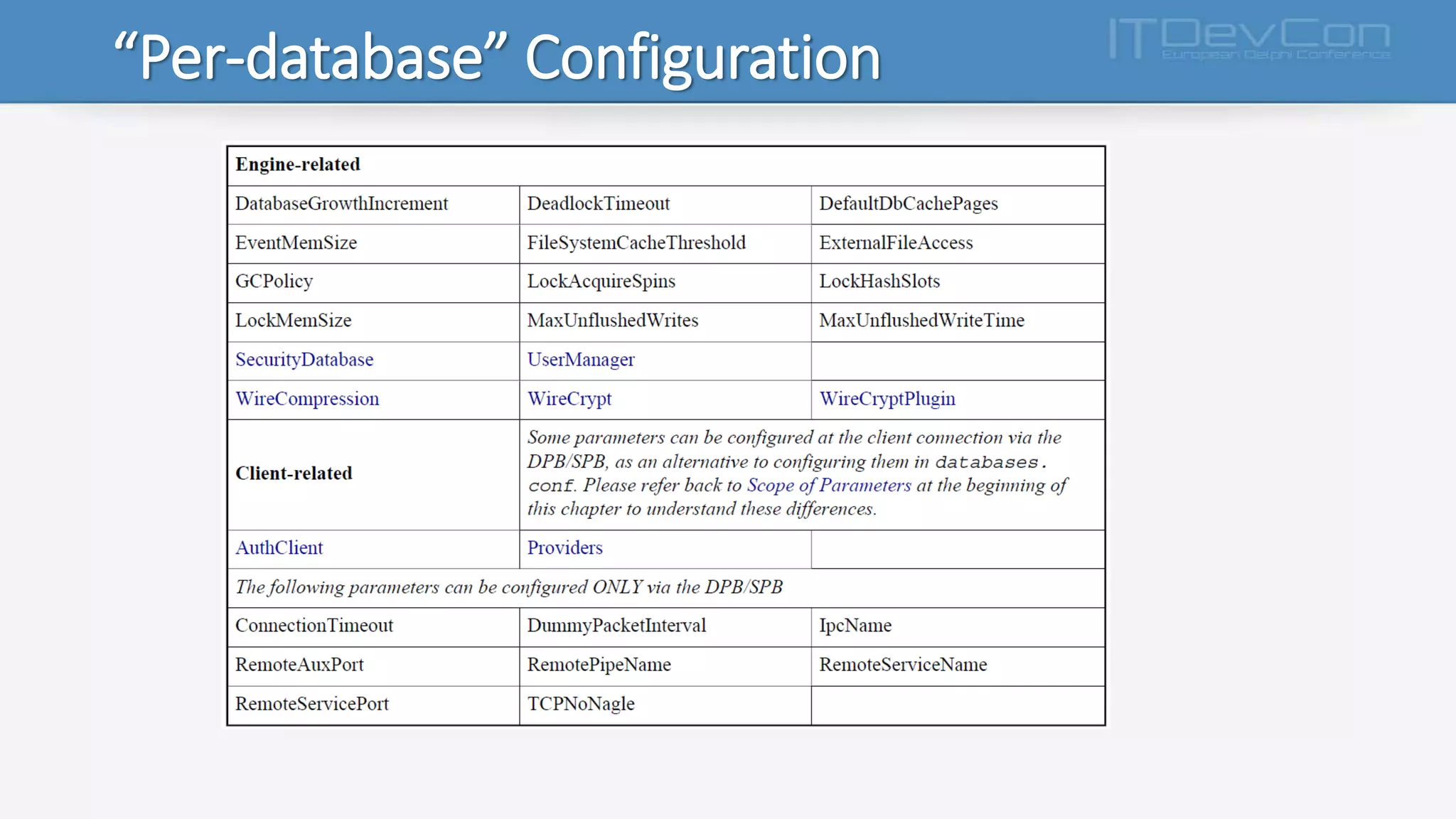
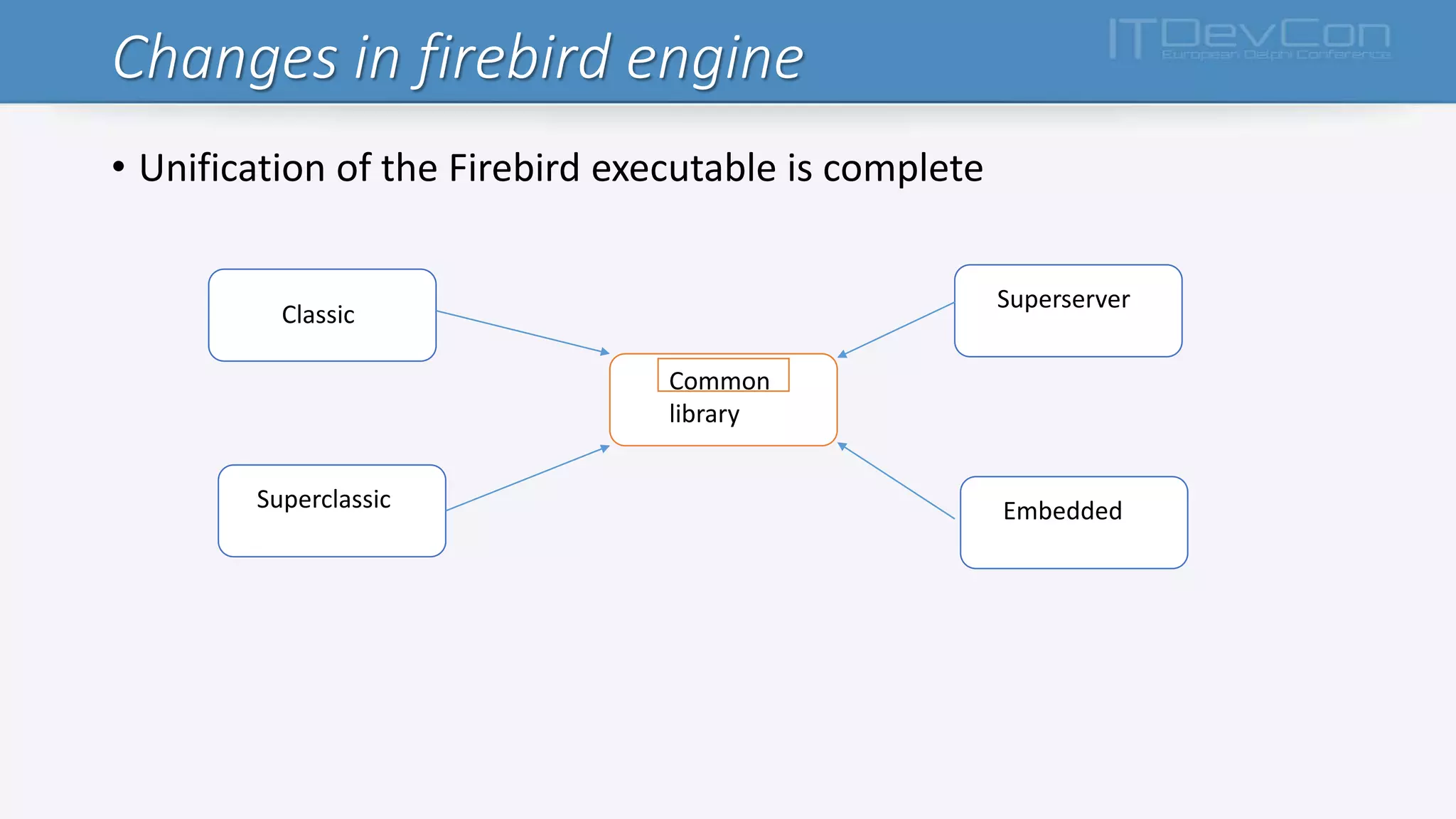
Firebird 3.x introduces several new features and changes from previous versions, including true SMP support, improved APIs, per-database configuration, increased limits, multiple security databases, and new SQL commands. The Firebird executable is now unified, and the cache, lock, and connection behaviors are determined by new configuration parameters. Additional changes include support for new data types, functions, triggers, international characters, and IPv6. The database engine and plug-in architecture were also updated.






![Providers
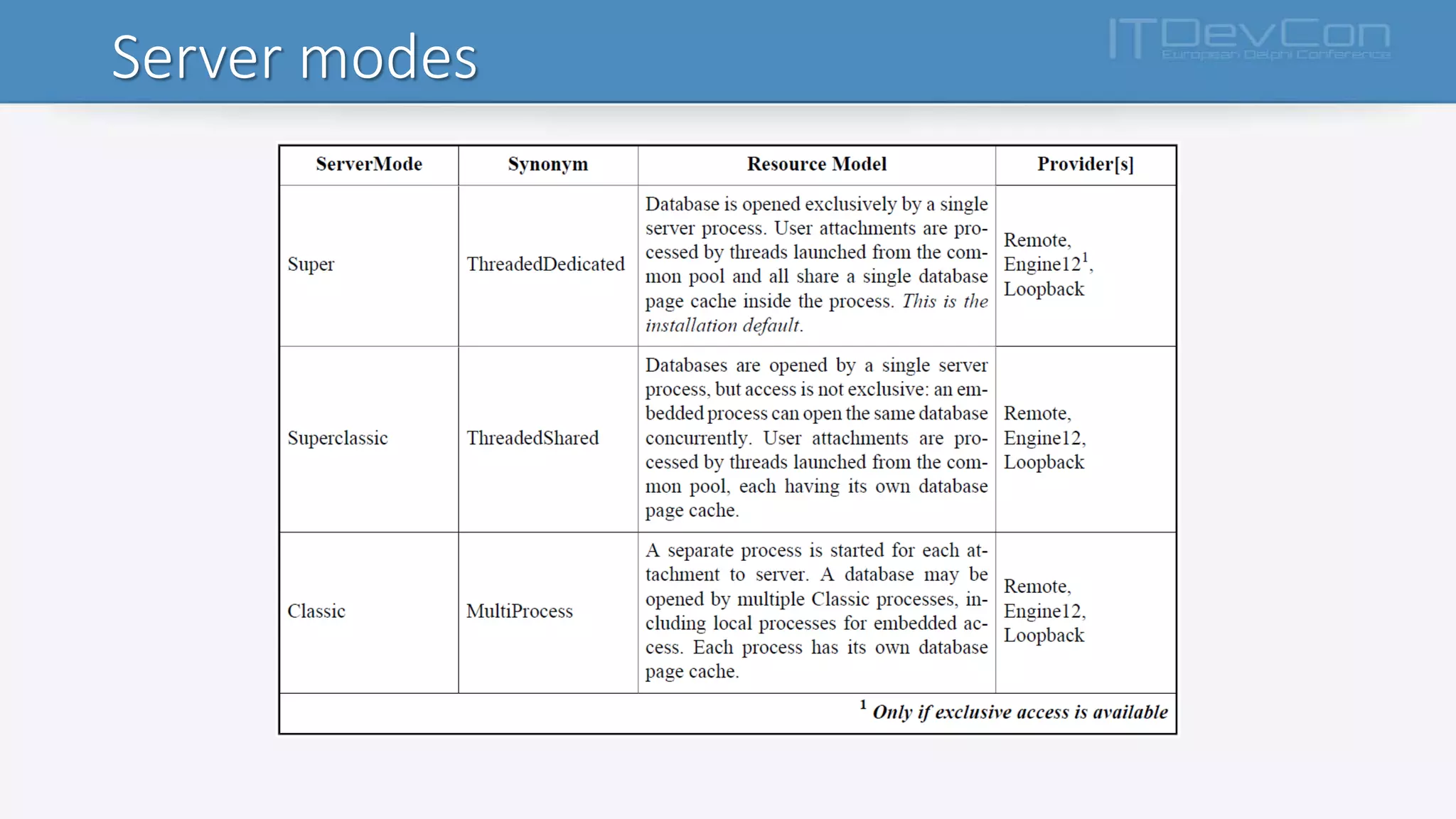
• PROVIDERS… IS LIKE WE ALREADY KNOWN
• methods used to connect a client to a server:
• across a network,
• host-locally,
• via the local loopback (“localhost”)
In firebird.conf, all are available by default, as follows:
#Providers = Remote,Engine12,Loopback
In databases.conf, one or more providers can be blocked by pasting the line
from firebird.conf,
uncommenting it, and deleting the unwanted provider[s].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introduzioneafirebird3-161110144421/75/Introduction-to-firebidSQL-3-x-9-2048.jpg)
![Connection strings
• For TCP/IP (aka INET) protocol
<host> [ / <port>] : <database file path or alias>
• For named pipes (aka NetBEUI, aka WNET) protocol:
<host> [ @ <port>] <database file path or alias>
• For local connections, simply:
<database file path or alias>
• URL-Style Connection Strings – Firebird 3.0
<protocol> : // [ <host> [ : <port> ] ] ] / <database file path or alias>
<protocol> ::= INET | WNET | XNET](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introduzioneafirebird3-161110144421/75/Introduction-to-firebidSQL-3-x-10-2048.jpg)