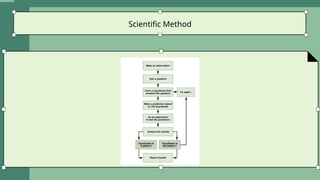
The document provides an overview of environmental science, detailing its multidisciplinary nature and covering various resource categories, including non-renewable, renewable, water, mineral, food, and energy resources. It discusses the importance and usage of these resources, highlighting factors like energy consumption patterns, ecological significance of forests, and the essential role of water. Furthermore, it emphasizes the interconnectedness of these resources and their impact on human life and the environment.