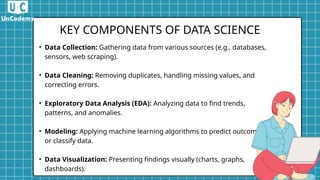
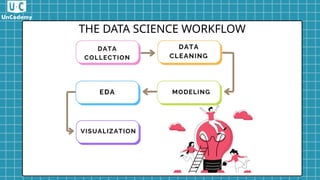
Data science combines scientific methods, algorithms, and expertise to extract knowledge from data, applied in various fields like healthcare and finance. The process involves data collection, cleaning, exploratory analysis, modeling, and visualization, incorporating machine learning techniques. Despite its challenges, data science offers valuable insights and growing career opportunities.