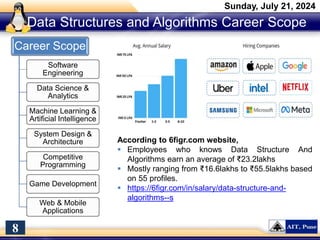
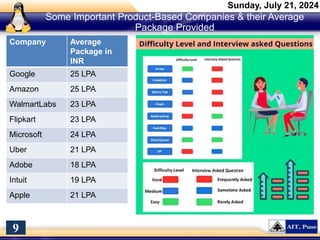
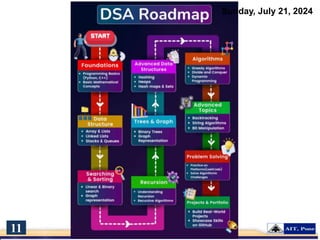
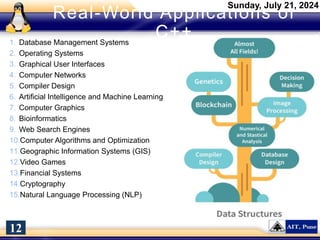
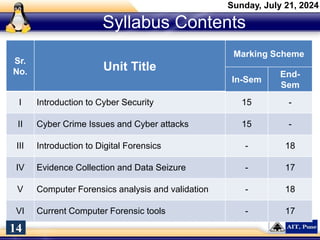
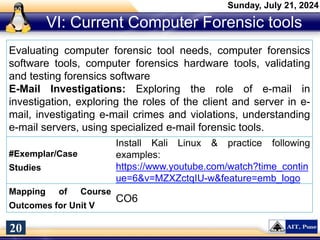
The document introduces a course on cyber security and digital forensics, outlining its objectives and course structure. It covers essential topics like cyber security definitions, types of cyber threats, and digital forensics techniques including evidence collection and analysis. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of digital forensics in crime solving and provides insight into related career opportunities and skills required in the field.











![Part II: Laboratory Practices[CSDF]
(410244(C))
Suggested List of Laboratory Experiments
Sr.
No.
Group 1
1.
Write a program for Tracking Emails & Investigating Email Crimes. i.e. Write a
program to
analyze e–mail header
2. Implement a program to generate & verify CAPTCHA image
3.
Write a computer forensic application program for Recovering permanent Deleted Files
and
Deleted Partitions
4. Write a program for Log Capturing and Event Correlation
5. Study and Implementation of Honeypot.
Sr.
No.
Group 2
1.
Mini–project: Perform the following steps:
a. Go to the National Child Exploitation Coordination Centre (NCECC) Web site at
http://www.ncecc.ca
b. Click on the Reporting child exploitation link.
c. Read “How to Report Internet Pornography or Internet Luring Related to Children.”
2.
Mini- Project: Perform the following steps:
a. Go to http://www.usdoj.gov/criminal/cybercrime/cyberstalking.htm.
Sunday, July 21, 2024
21](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontocourse1-240721063537-c7291907/85/Introduction-to-Course_1-for-Cyber-Security-21-320.jpg)