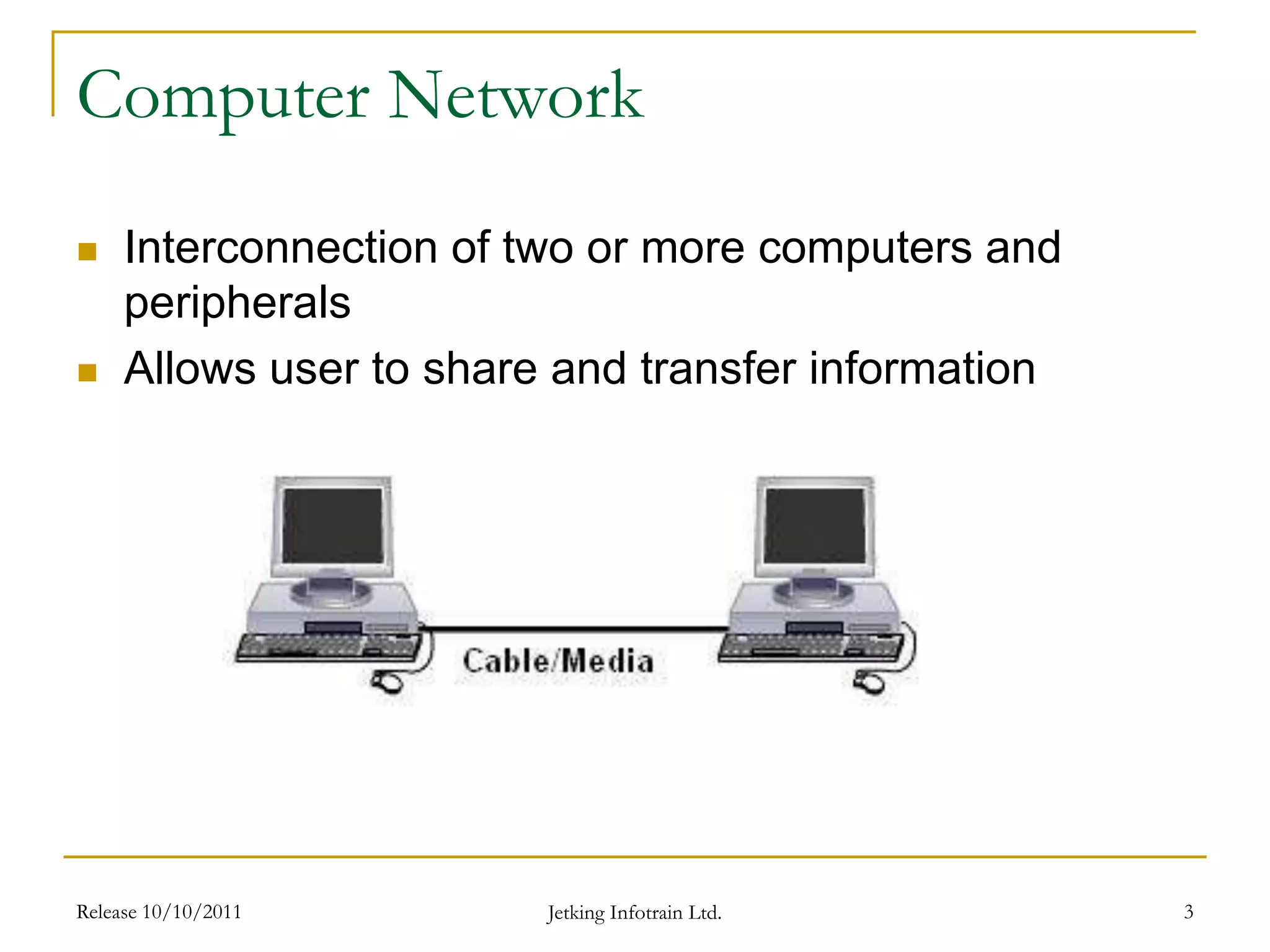
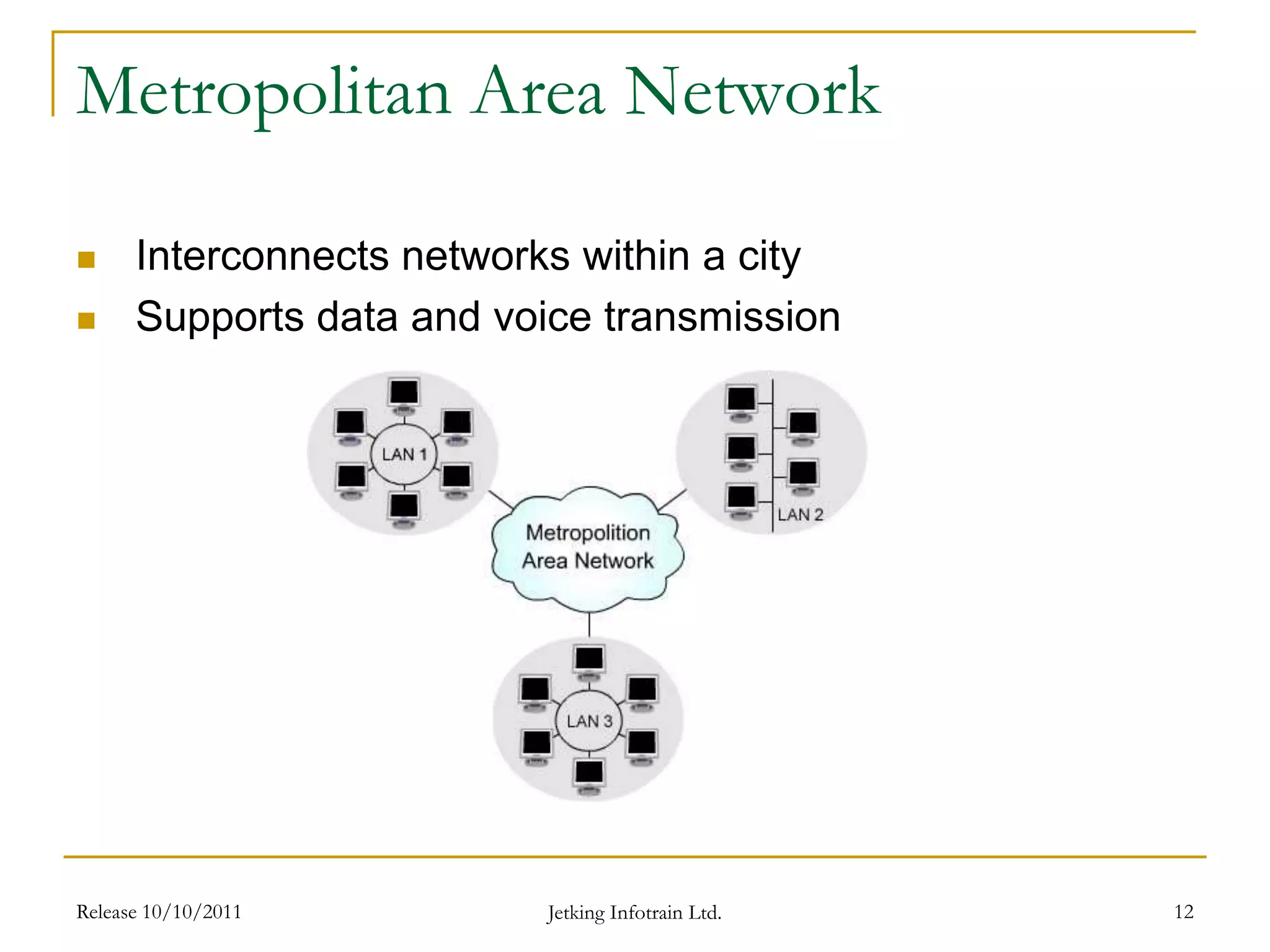
The document introduces computer networks and their applications. It defines a computer network as an interconnection of computers that allows users to share information and resources. The document outlines the objectives of the chapter which are to explain the concept, need, types and applications of computer networks as well as the workings of the Internet and email. It then proceeds to describe client-server and peer-to-peer network models, different types of networks based on geographical coverage, and applications of networks including the Internet, email and financial services.