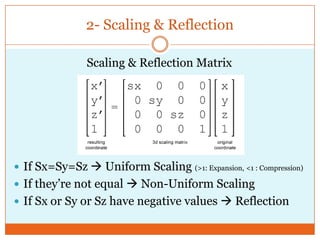
The document discusses the graphics processing pipeline and types of transformations in computer graphics. The graphics pipeline involves 7 steps: 1) game launch, 2) data loads to RAM, 3) CPU processes data, 4) graphics driver translates data, 5) graphics port transfers data, 6) VRAM stores data, and 7) GPU core processes data. There are 4 main types of transformations: 1) translation, 2) scaling and reflection, 3) shear, and 4) rotation. Each transformation uses a specific matrix operation to manipulate 3D coordinates. Examples are provided to illustrate each type of transformation.