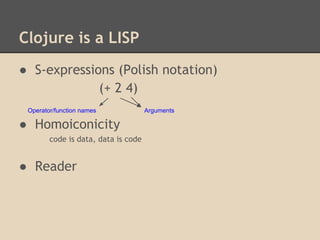
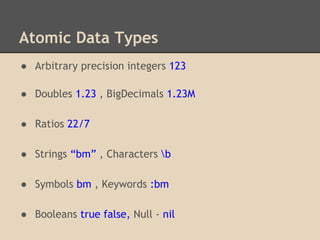
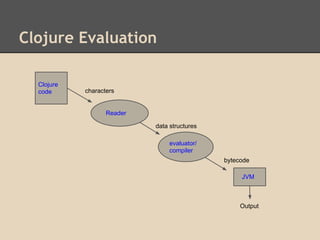
Clojure is a Lisp dialect created by Rich Hickey in 2008 that runs on the Java Virtual Machine. It is a dynamic, functional programming language with immutable persistent data structures and supports proper equality semantics. Clojure code is made up of data structures and uses homoiconicity, where code is represented as standard data structures. It has many standard data types like integers, doubles, ratios, strings, symbols and keywords, as well as collection data structures like lists, vectors, and maps.


![Data Structures
● Lists (1 2 3)
● Vectors [1 2 3]
● Maps {:a 1 :b 2}
maps are functions of their keys
● Sets #{1 2}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontoclojure-130912060114-phpapp02/85/Introduction-to-clojure-6-320.jpg)




![Functions
● First class values
○ (def five 5)
○ (def add-1 (fn[x] (+ x 1)))
○ (add-1 five) = 6
● Higher order functions (HOF)
● fn special op is used to create functions](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontoclojure-130912060114-phpapp02/85/Introduction-to-clojure-12-320.jpg)

