This document discusses the history and basics of the C programming language. It covers:
- The origins and evolution of C from languages like ALGOL and BCPL in the 1960s-1970s. Key developments include Dennis Ritchie creating C at Bell Labs in 1972 and the standardization of ANSI C in 1989.
- Characteristics of C like being robust, portable, supporting structured programming, and having a rich set of operators and data types.
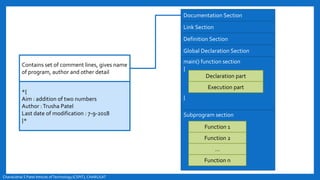
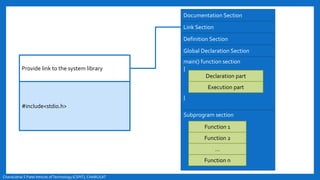
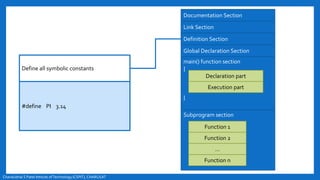
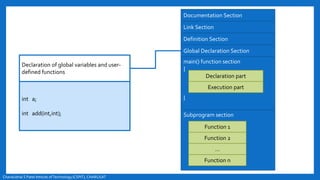
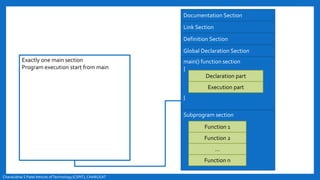
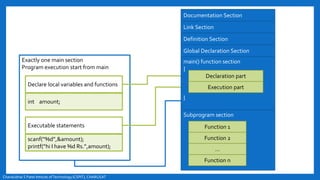
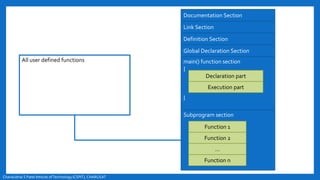
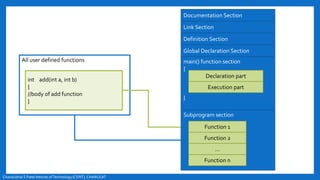
- The basic structure of a C program including documentation, library links, global declarations, the main function, and other functions.
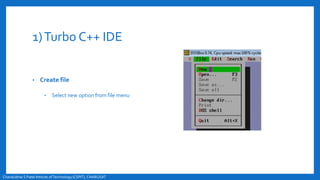
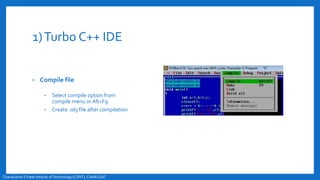
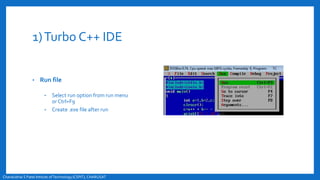
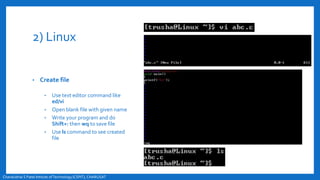
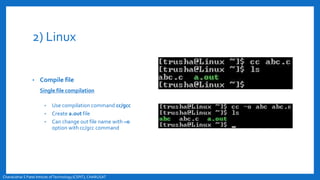
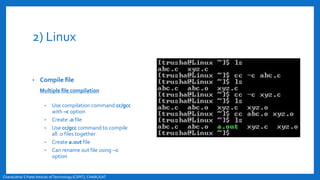
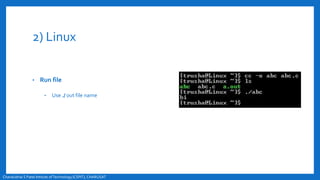
- An overview of the compilation process in environments like Turbo C++ and Linux, involving creating, compiling,