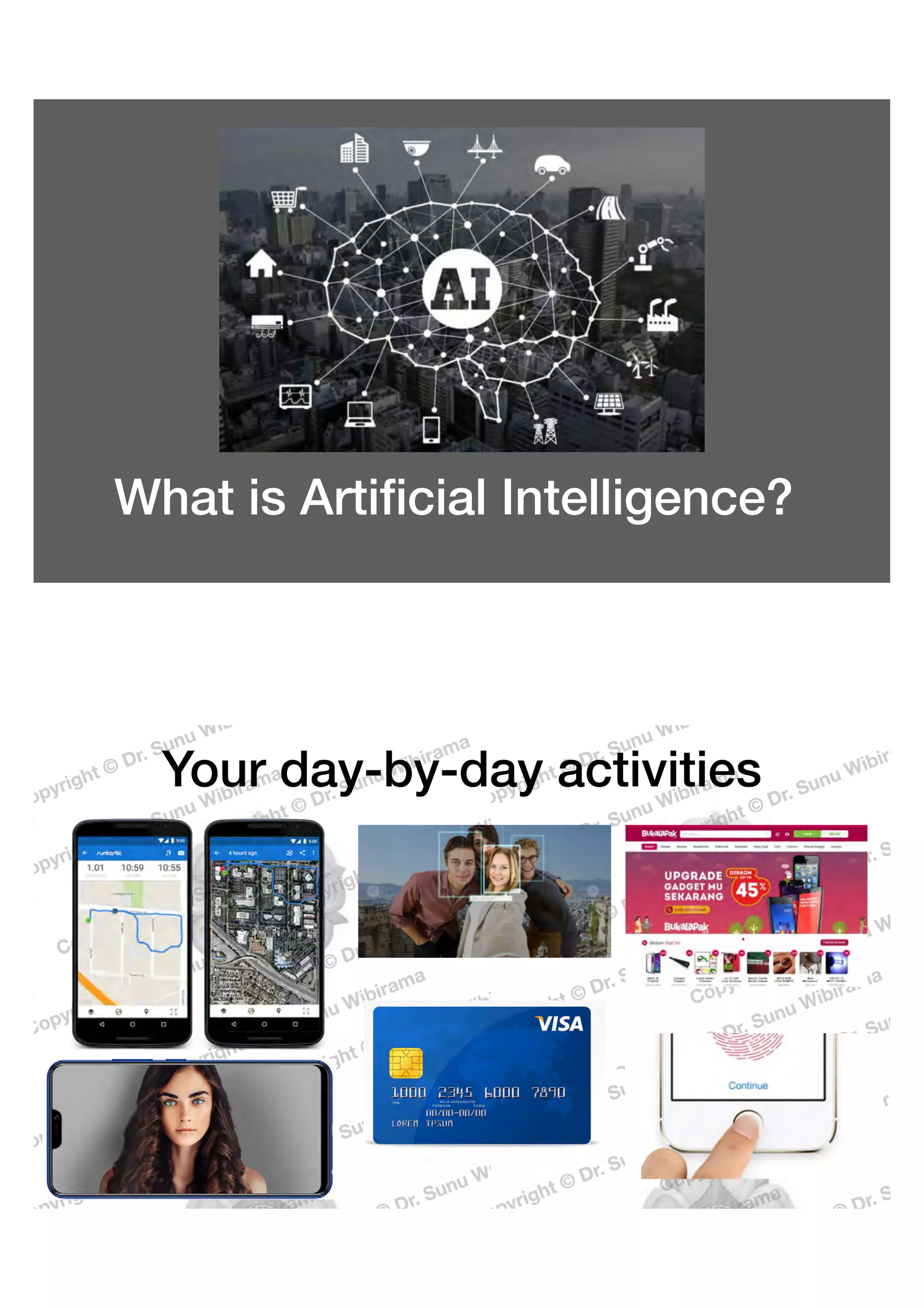
The document provides an introduction to artificial intelligence (AI), its differentiation from machine learning and deep learning, and its applications in daily life. It also covers historical milestones in AI, including the Turing test and advancements in machine learning algorithms, particularly deep neural networks. The content highlights the significance of AI in the fourth industrial revolution and its growing impact across various industries.