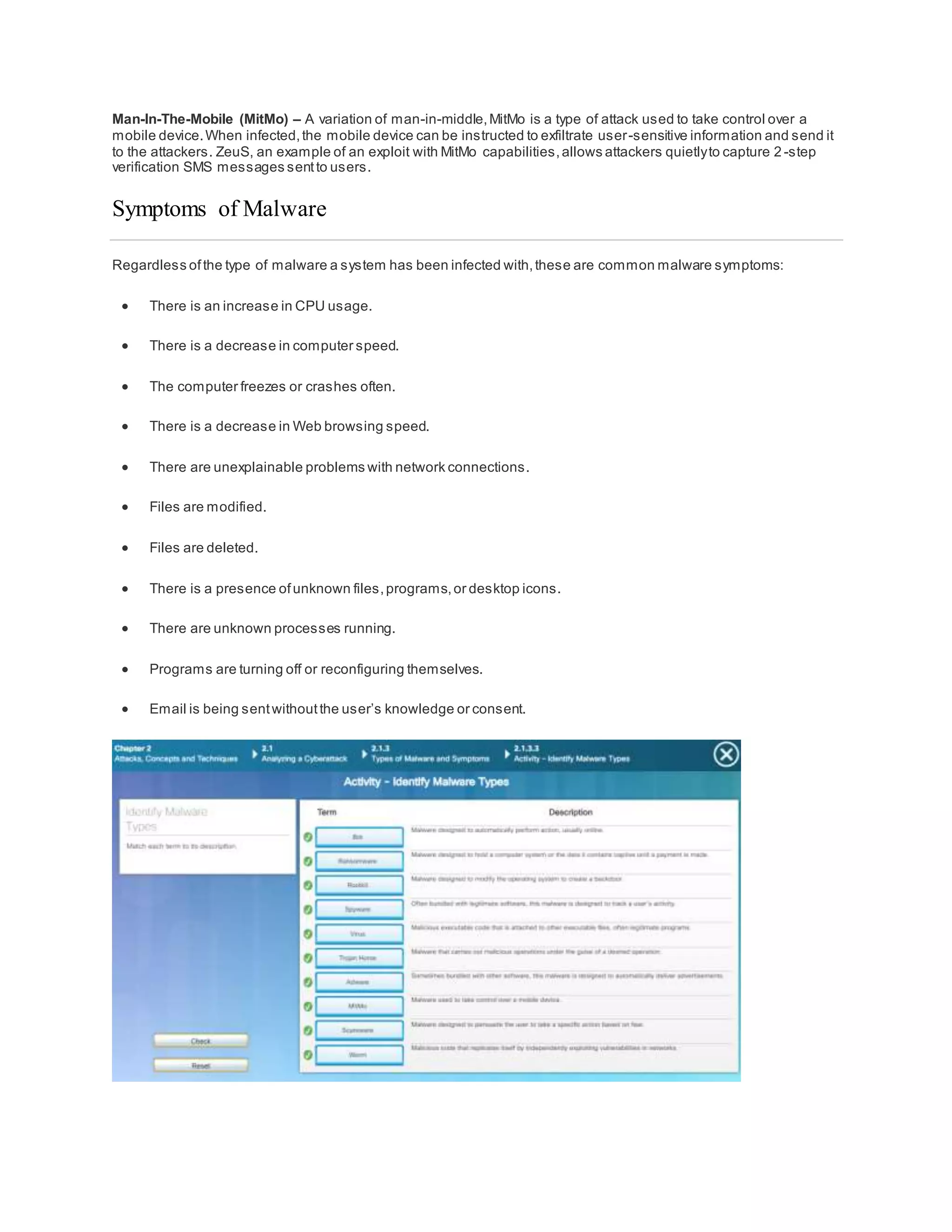
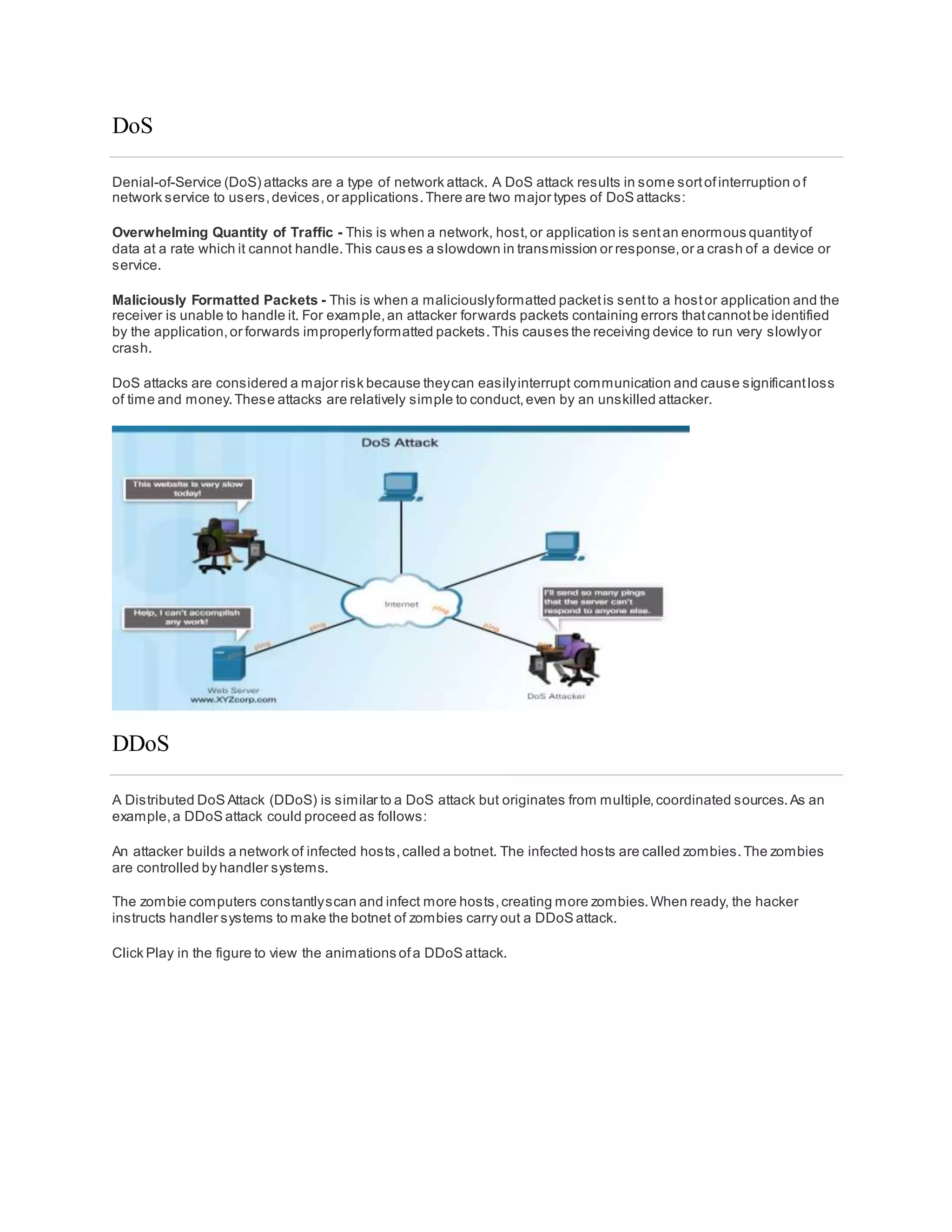
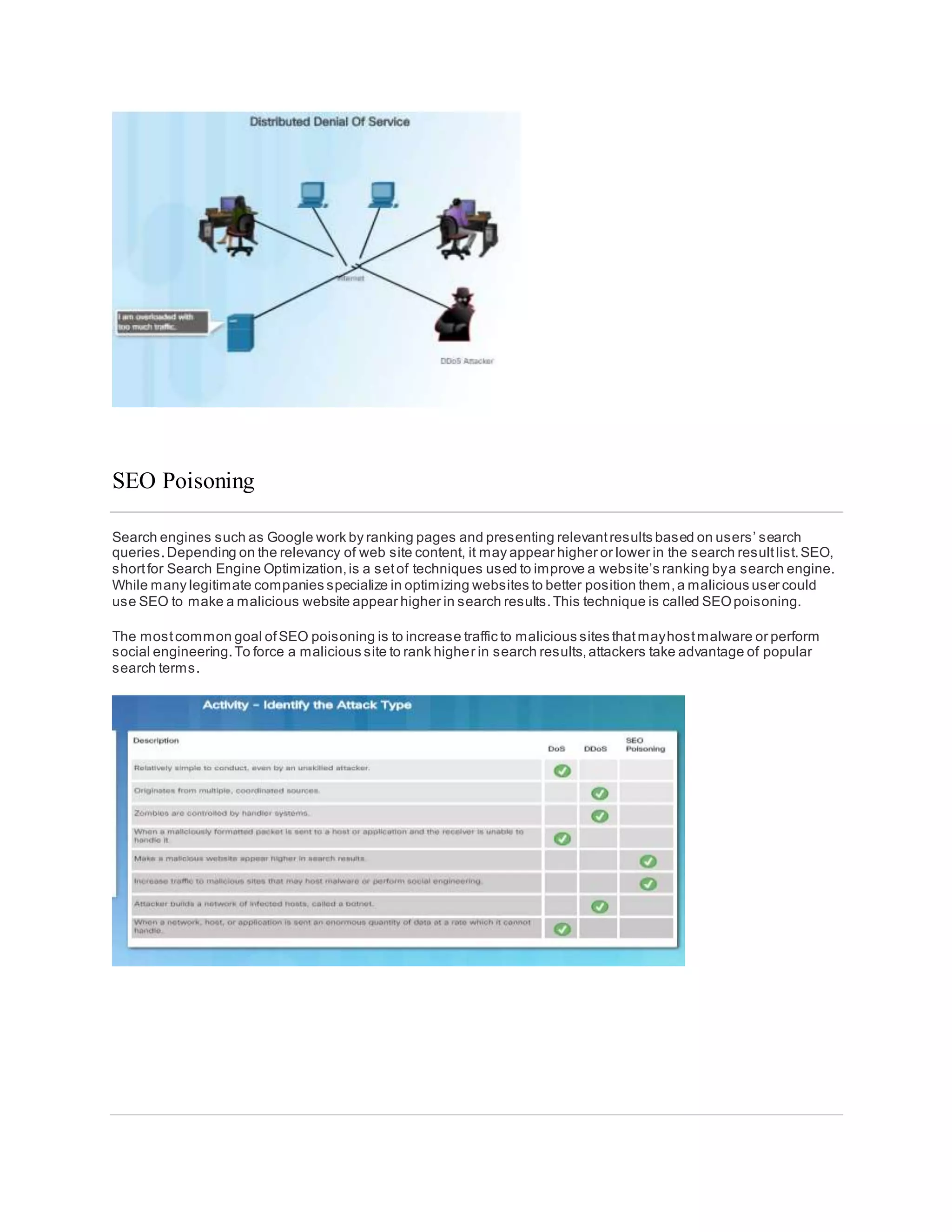
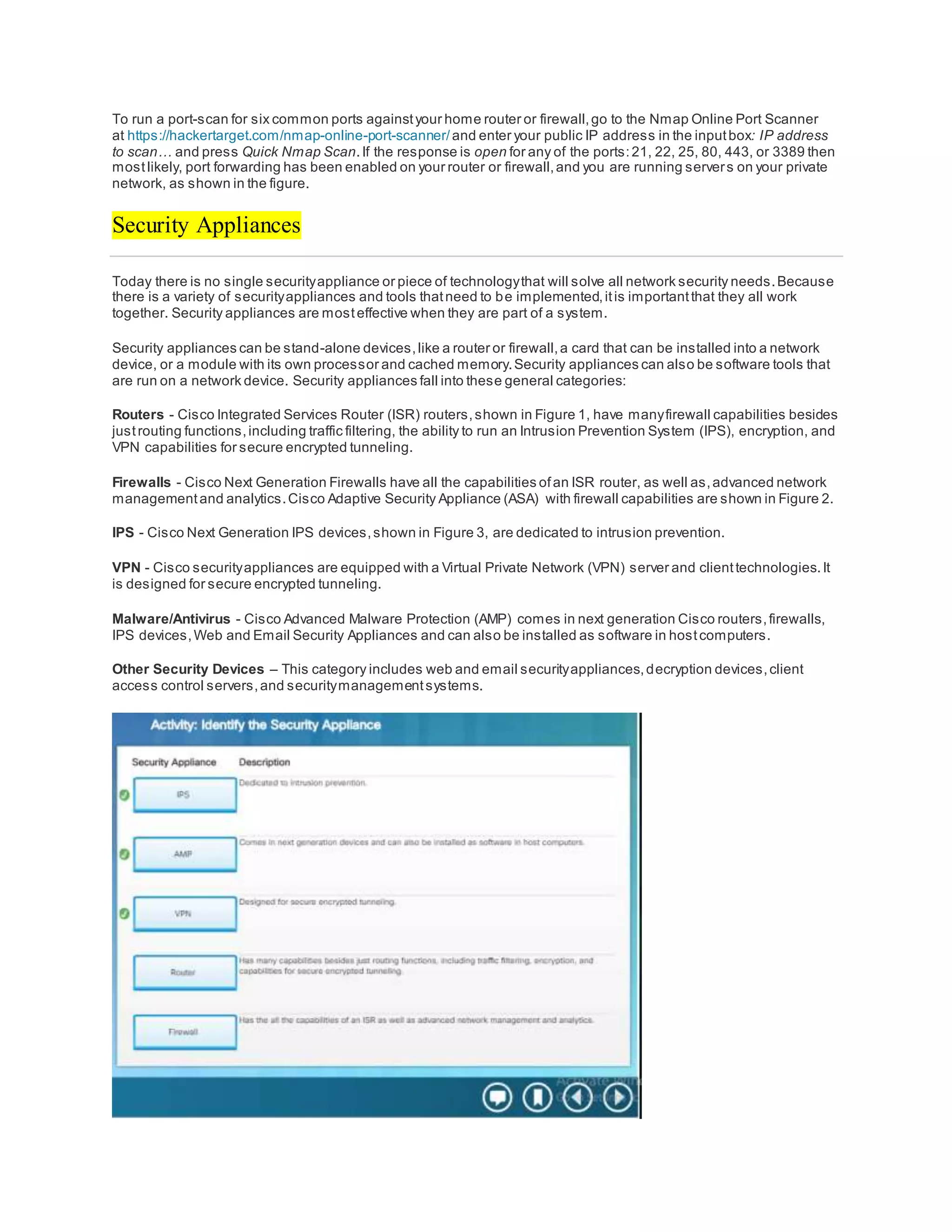
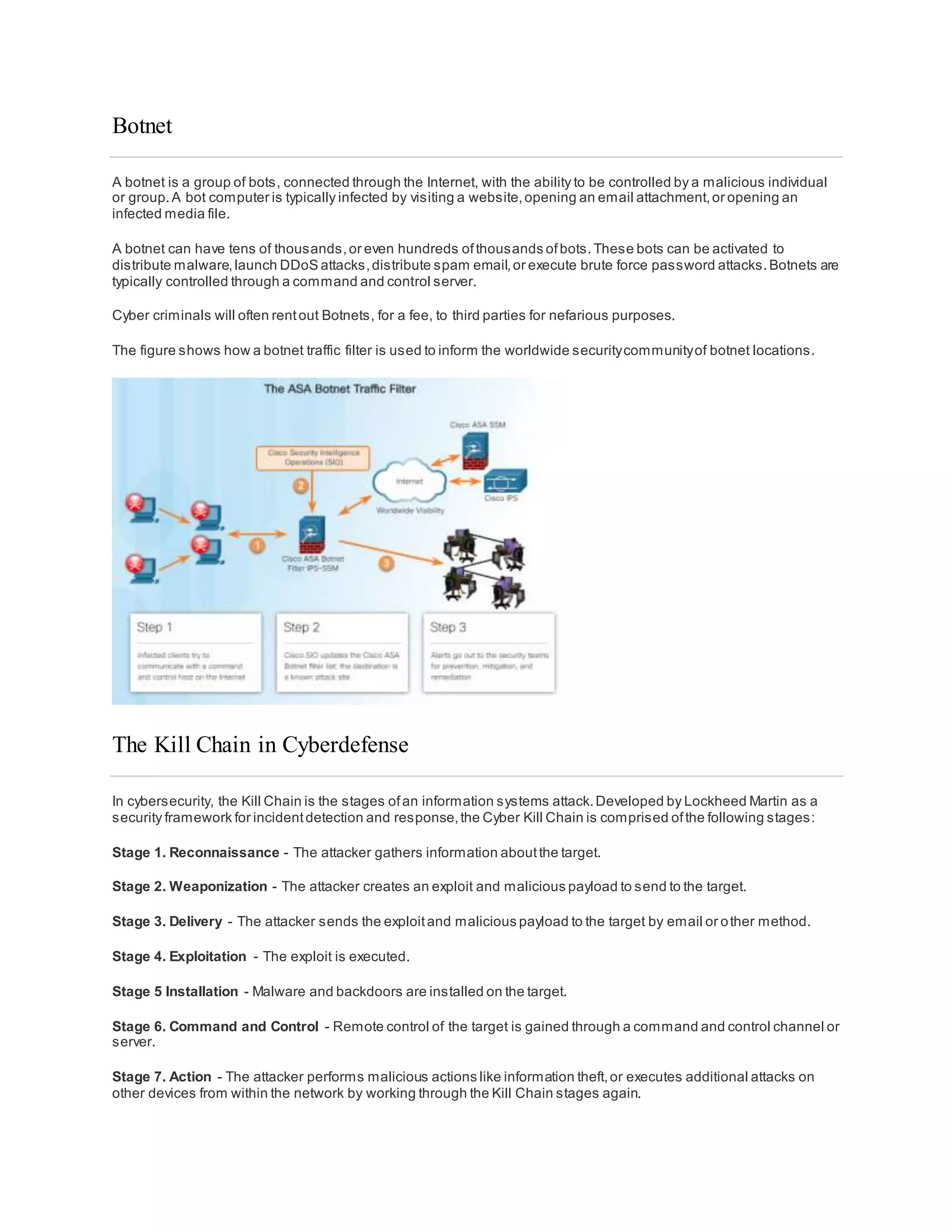
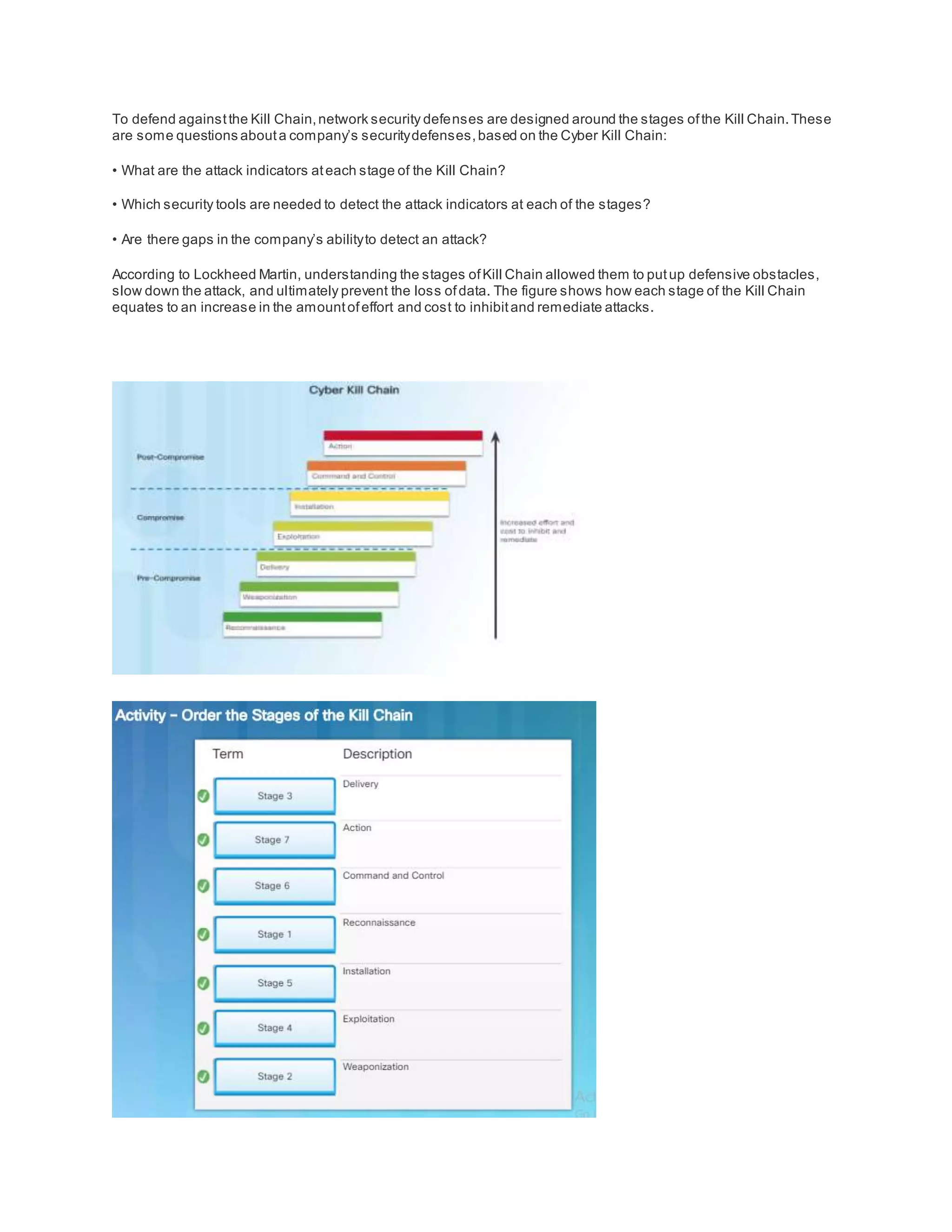
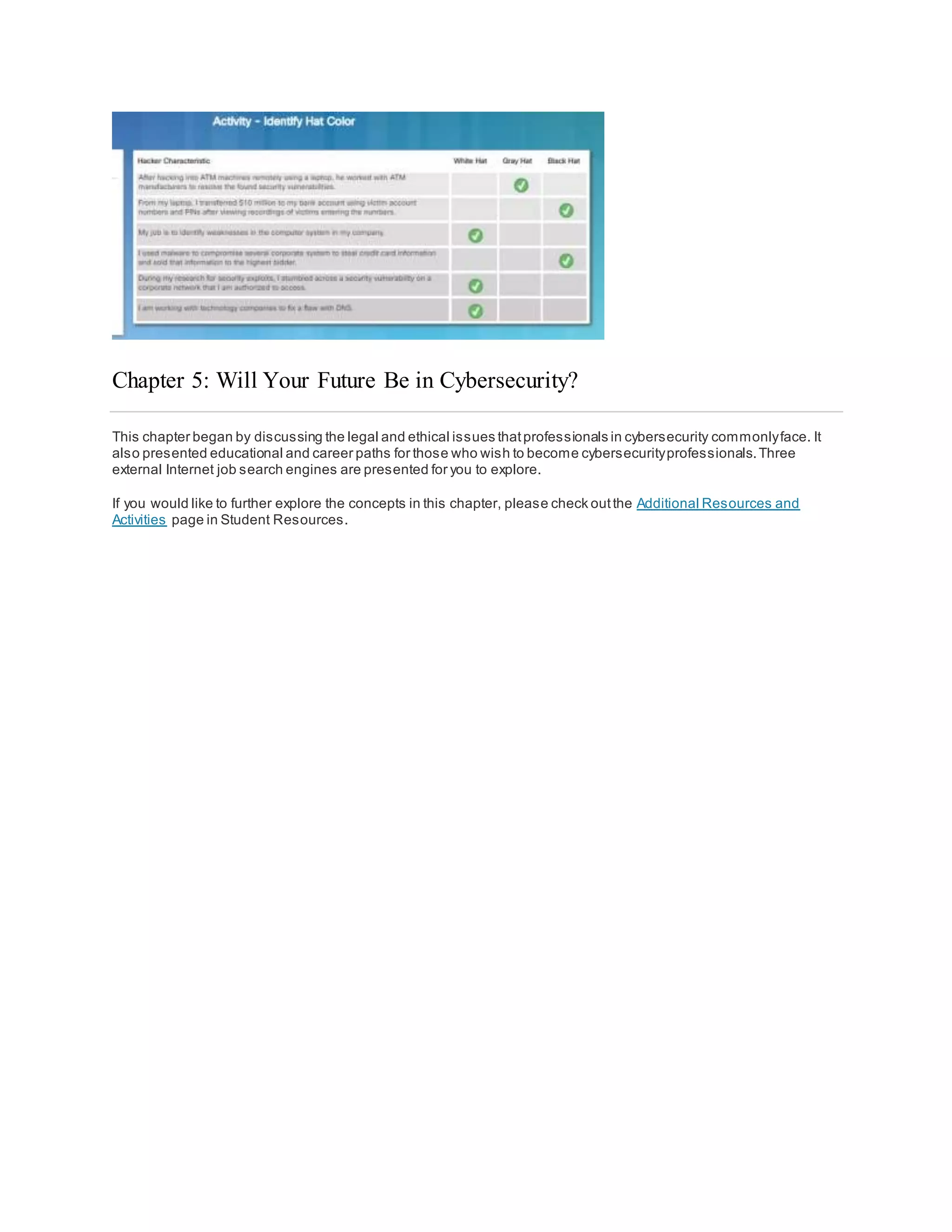
The document discusses cybersecurity and the importance of protecting personal, organizational, and government data from unauthorized access or harm. It defines cybersecurity as the ongoing effort to safeguard networked systems and data. It also provides examples of personal data like medical records, education records, employment and financial records that need to be secured. Additionally, it discusses the consequences of data breaches for individuals and organizations.