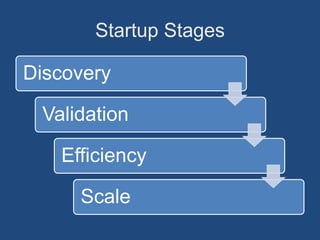
This document discusses business plans, business models, entrepreneurship, and starting a new business. It provides frameworks and examples for developing business ideas, business models, and business plans. It also examines the characteristics, skills, attitudes, and types of entrepreneurs. Common reasons for entrepreneurial success and failure are explored. Finally, typical stages of starting a new business are outlined.