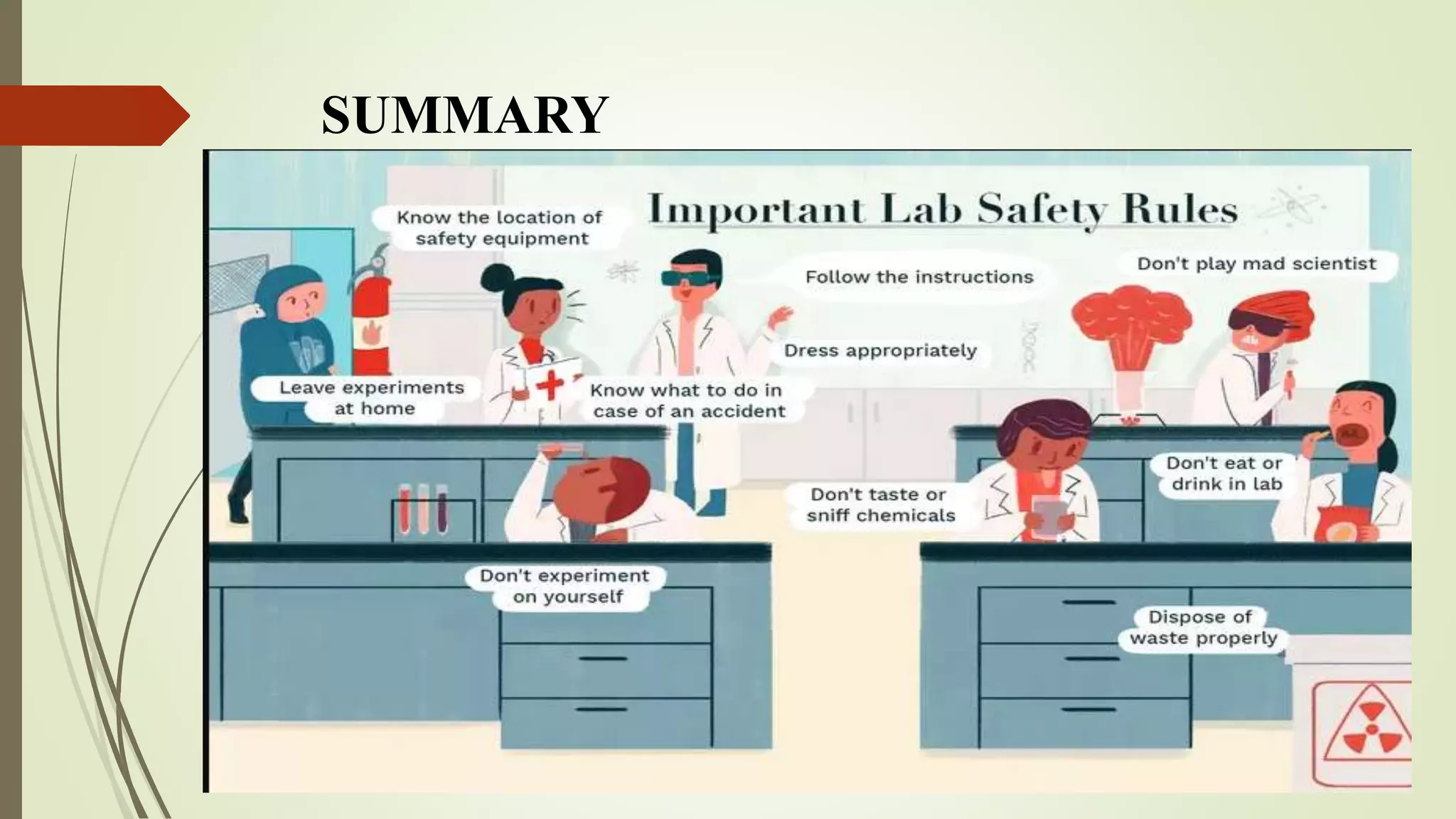
The document provides an introduction to lab safety protocols. It emphasizes the importance of following safety rules to protect oneself, colleagues, and laboratory equipment from harm. Consequences of not complying with safety protocols include endangering people, ruining experiments, and risking accidents. Key safety tips include wearing proper protective equipment, practicing good hygiene, avoiding unsafe behaviors like tasting chemicals, and properly disposing of waste.