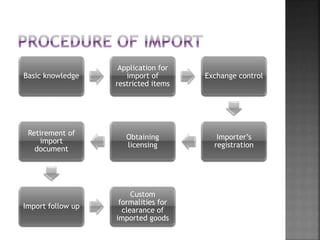
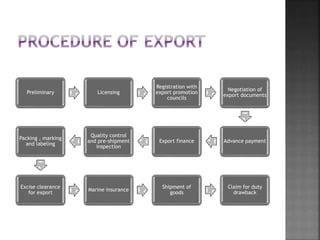
The document discusses international trade, defined as trade between countries involving the purchase and sale of goods and services. It highlights the complexities of foreign trade, including the need for various documents, currency differences, and higher transportation costs, compared to simpler home trade conducted within a country. Additionally, it outlines the procedures for importing and exporting goods, emphasizing the significance of licensing, documentation, and compliance with regulations.