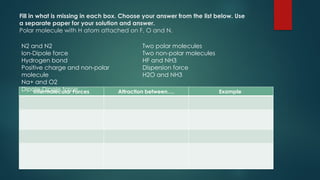
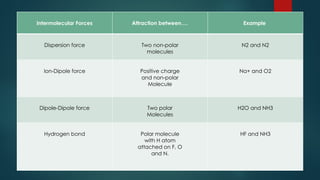
Intermolecular forces are attractive forces that hold molecules together and include four main types: hydrogen bonds, dipole-dipole, ion-dipole, and dispersion forces, with ion-dipole being the strongest and dispersion the weakest. Hydrogen bonds occur in polar molecules containing hydrogen and a highly electronegative atom, while dipole-dipole forces arise from interactions between polar molecules, and ion-dipole forces occur between ionic and polar molecules. Dispersion forces are the result of interactions between non-polar molecules and are the weakest type of intermolecular force.