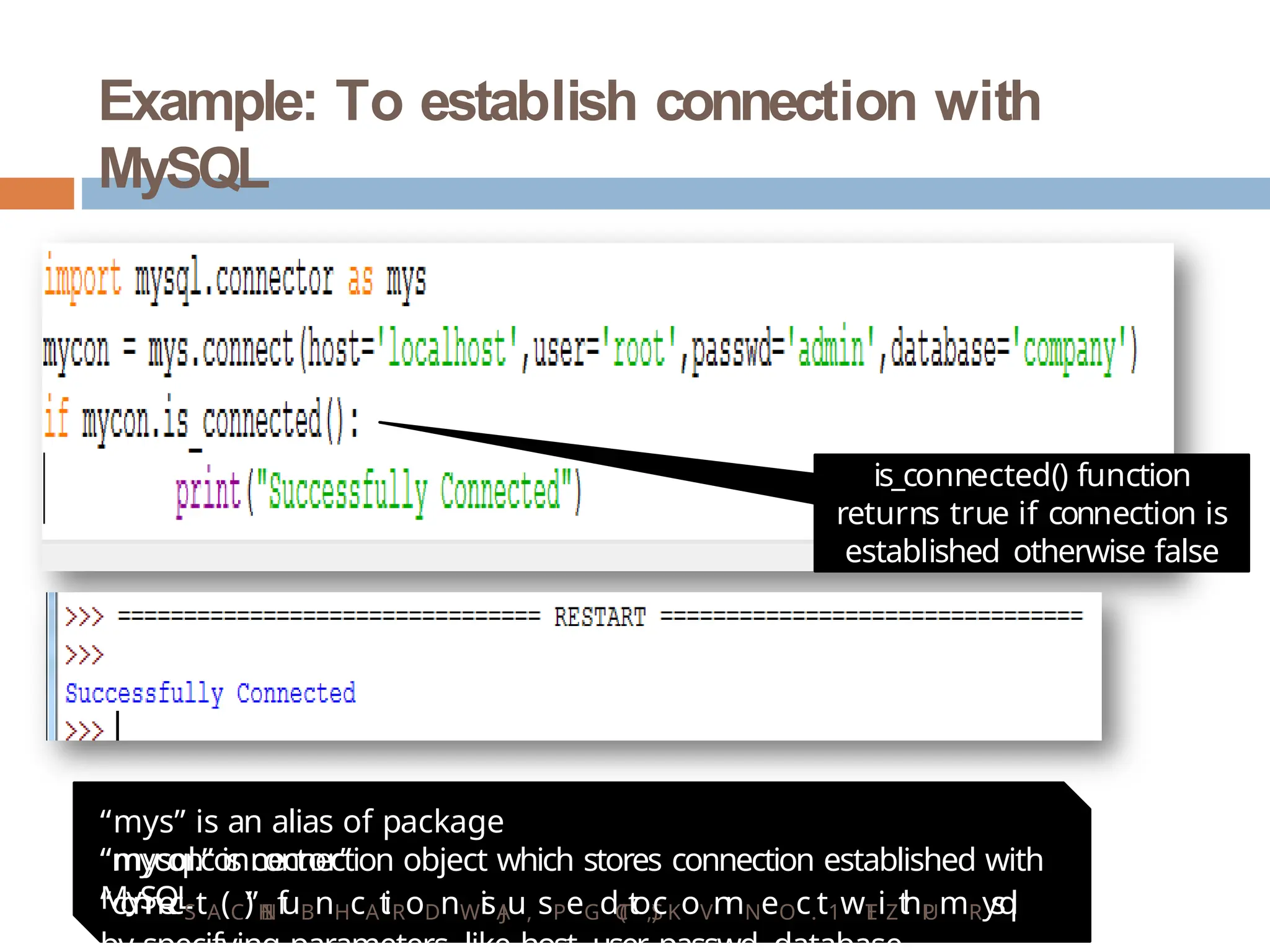
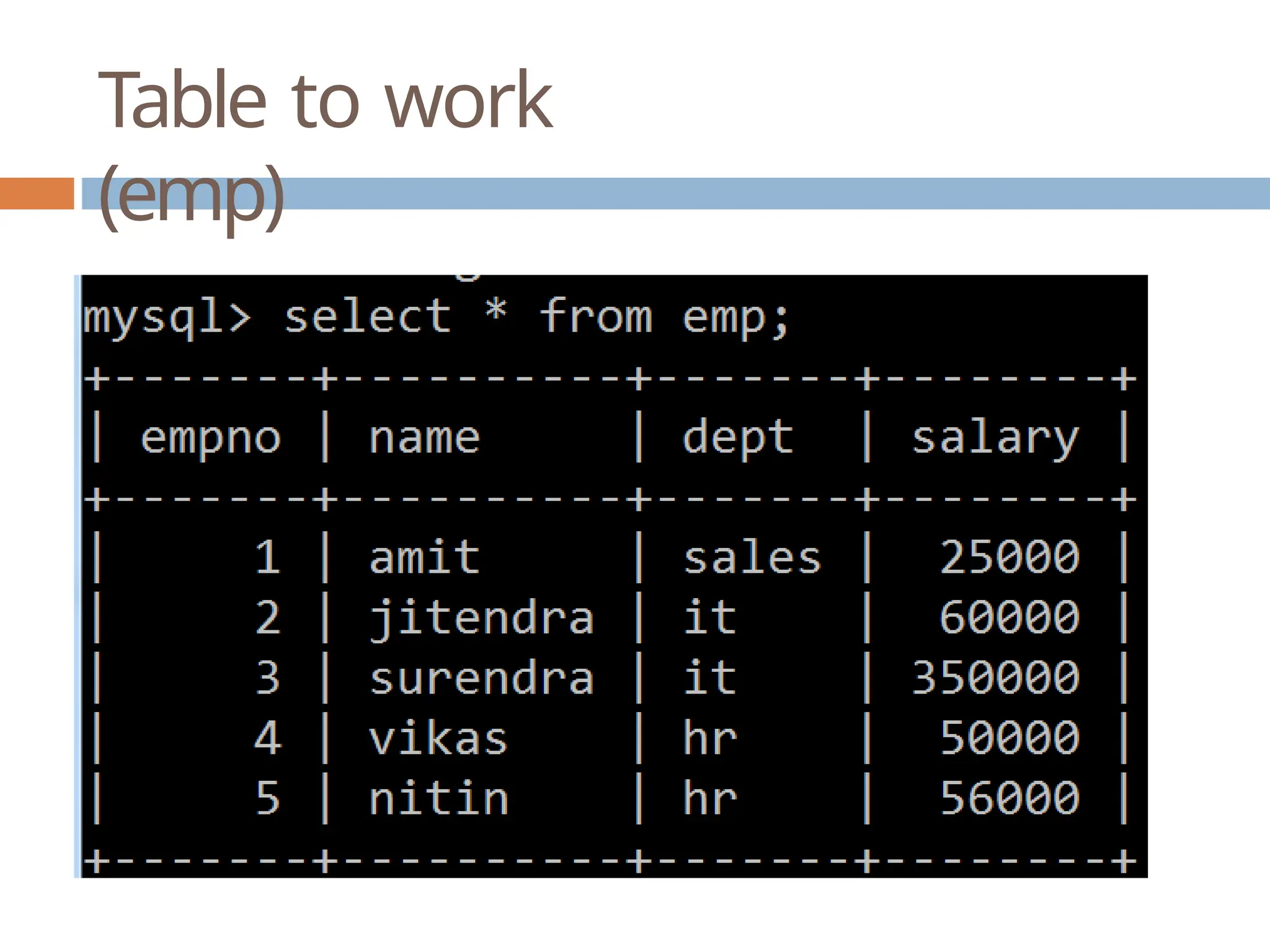
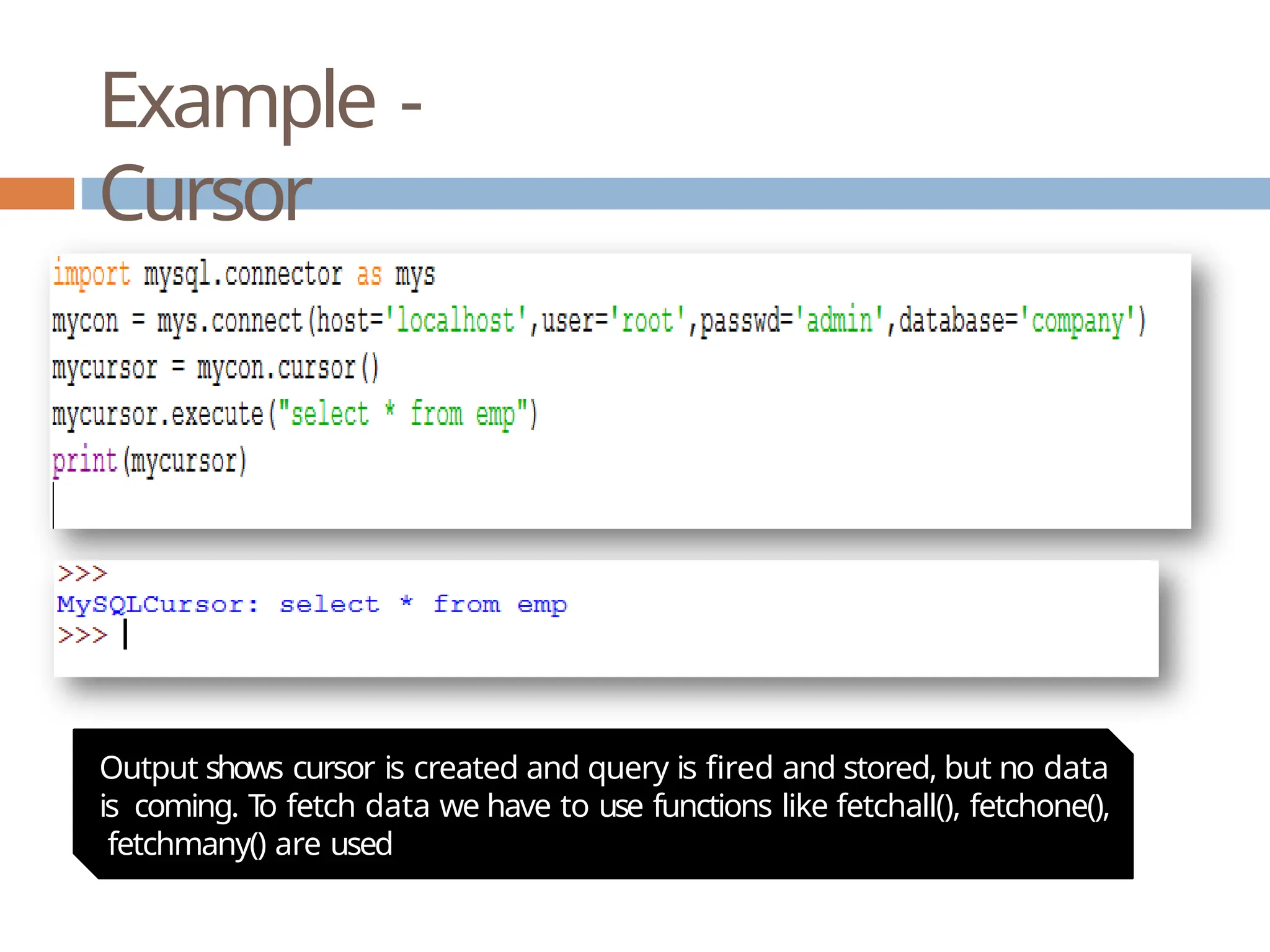
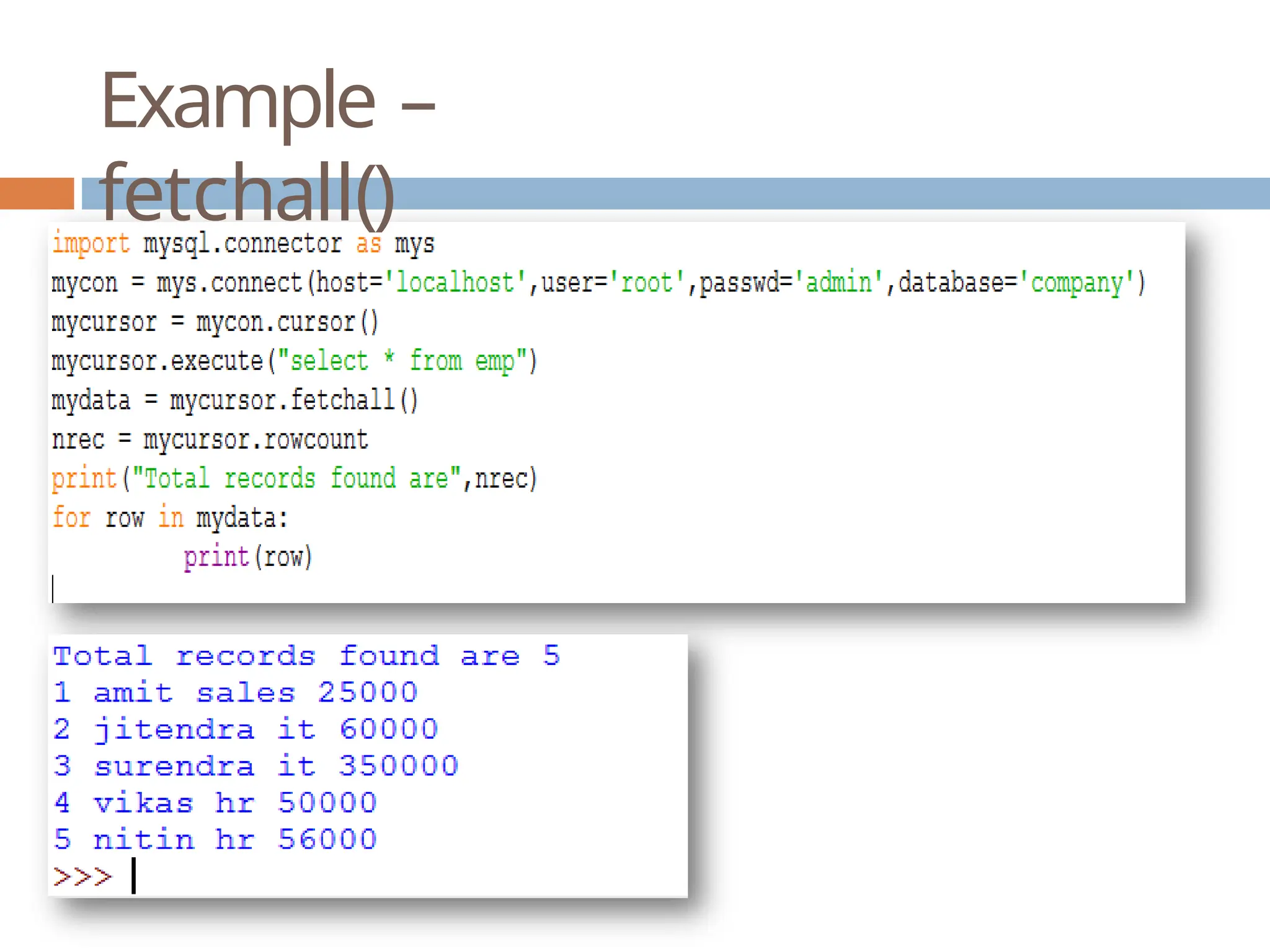
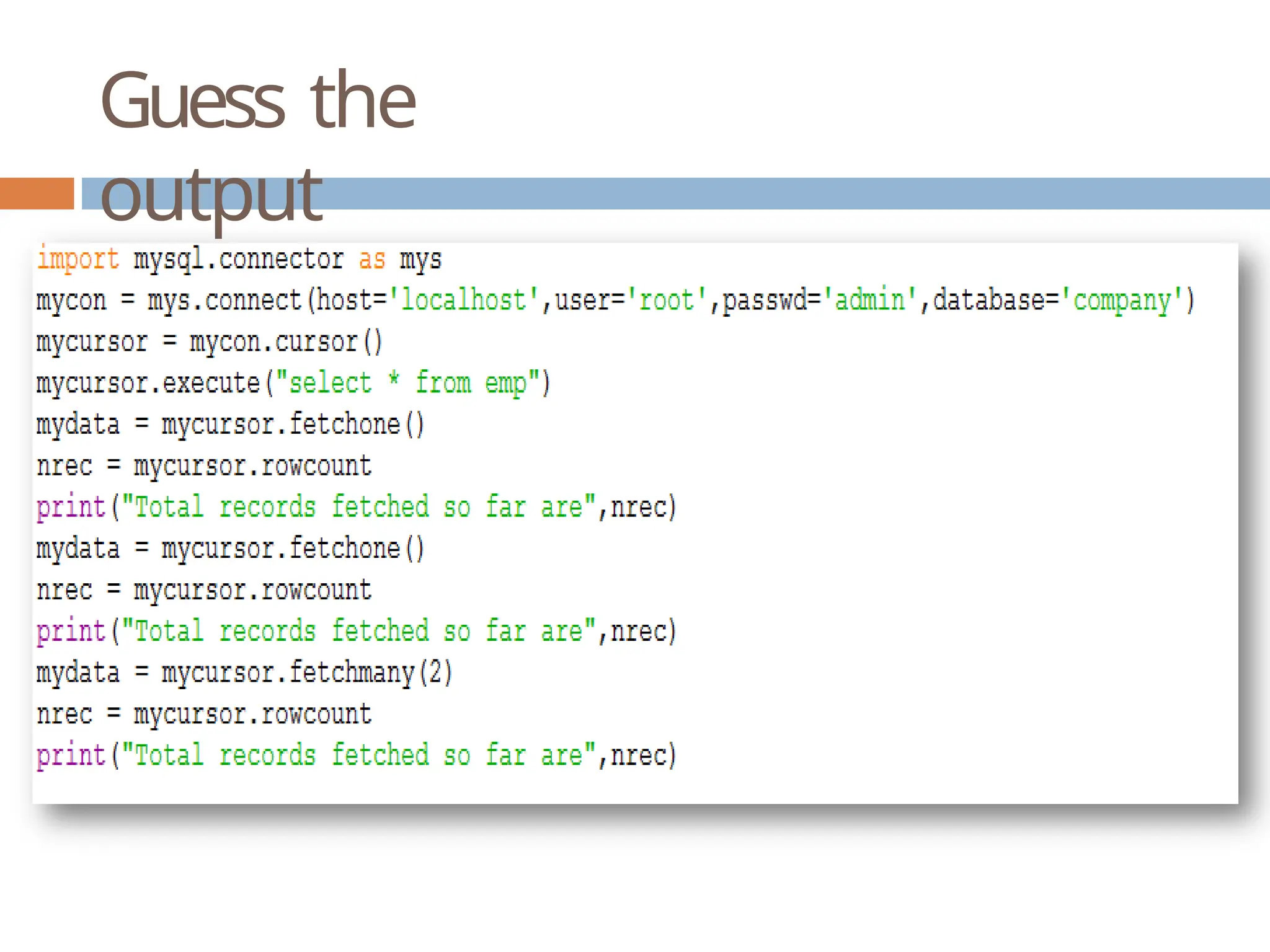
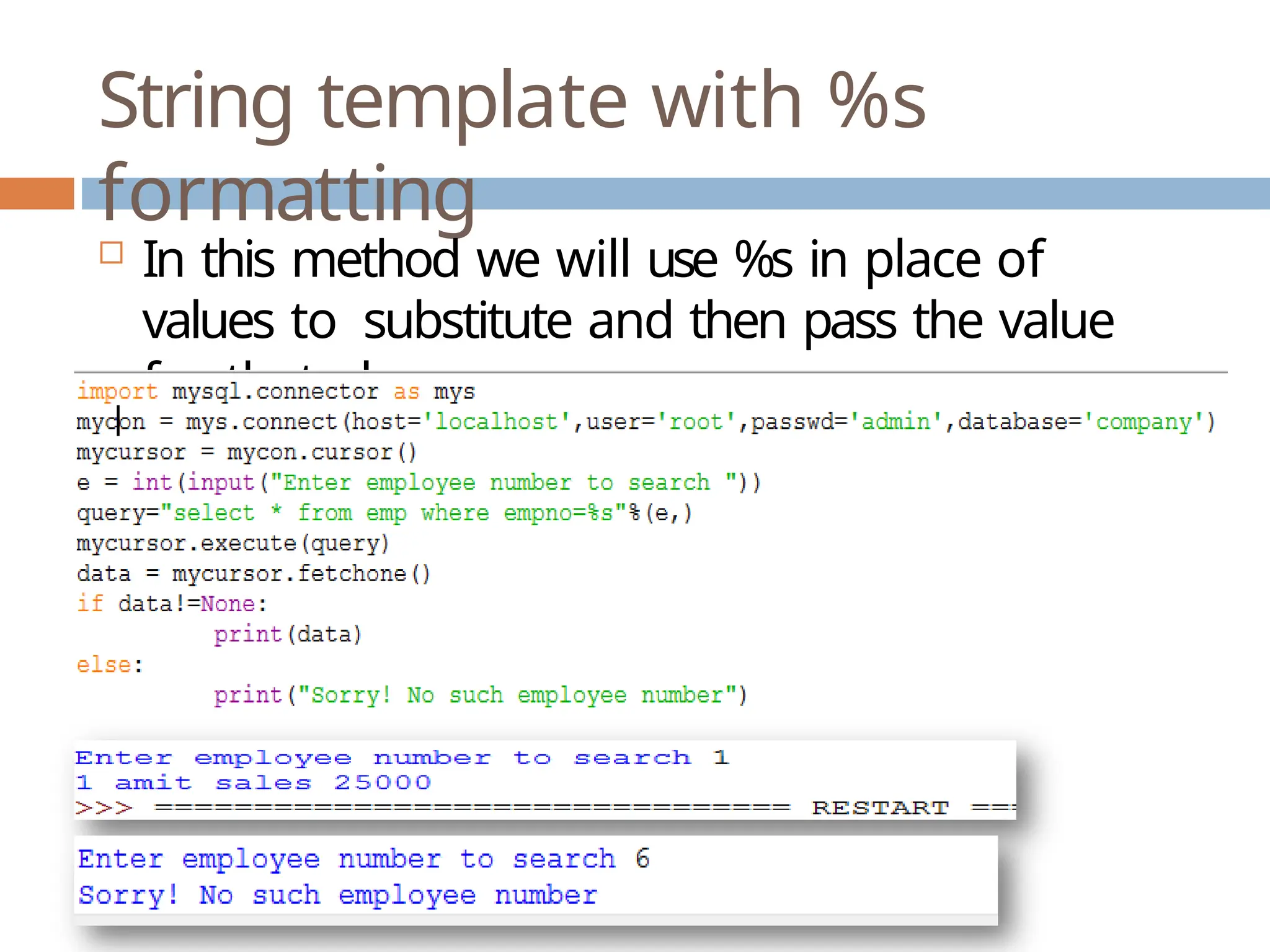
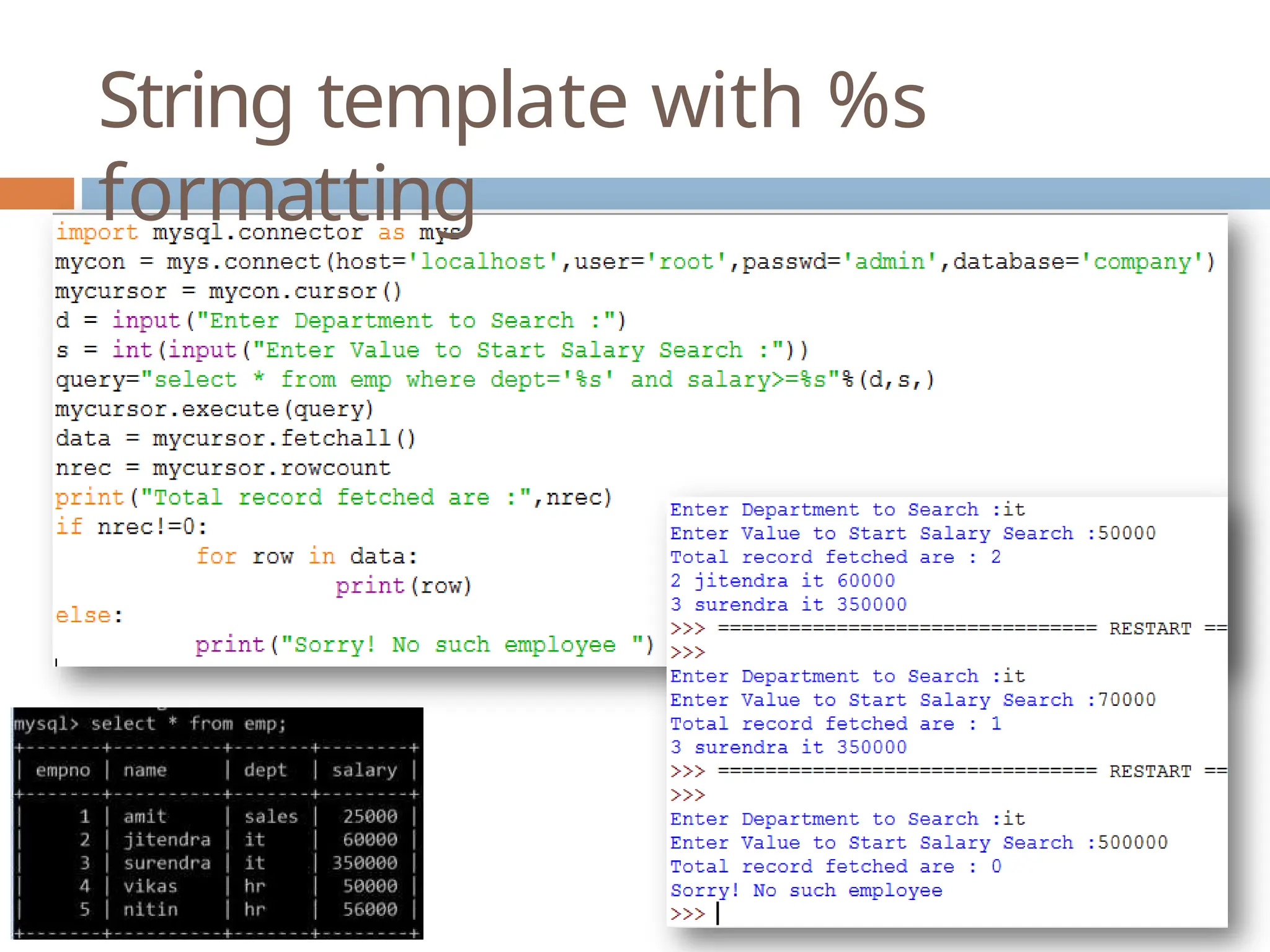
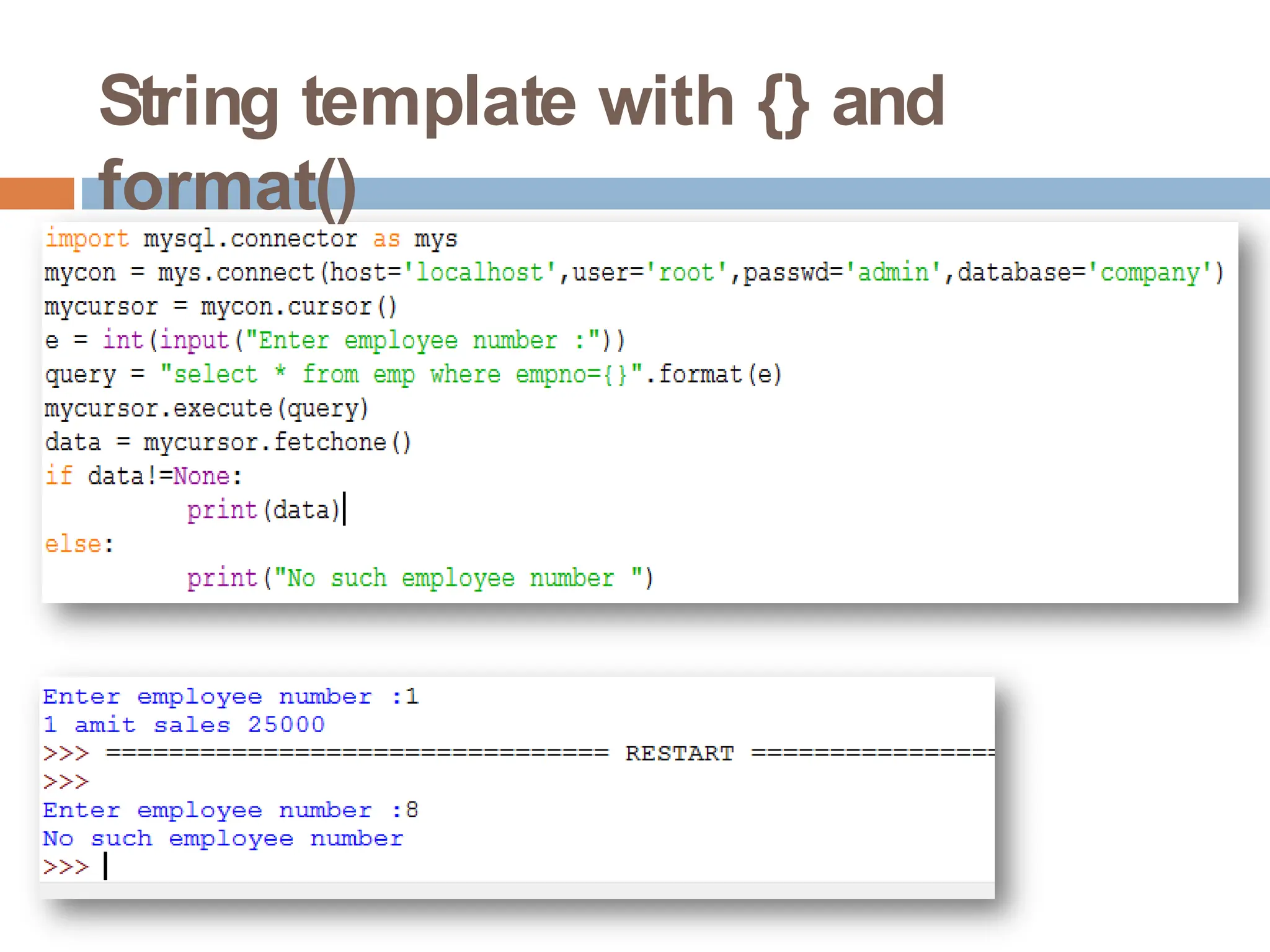
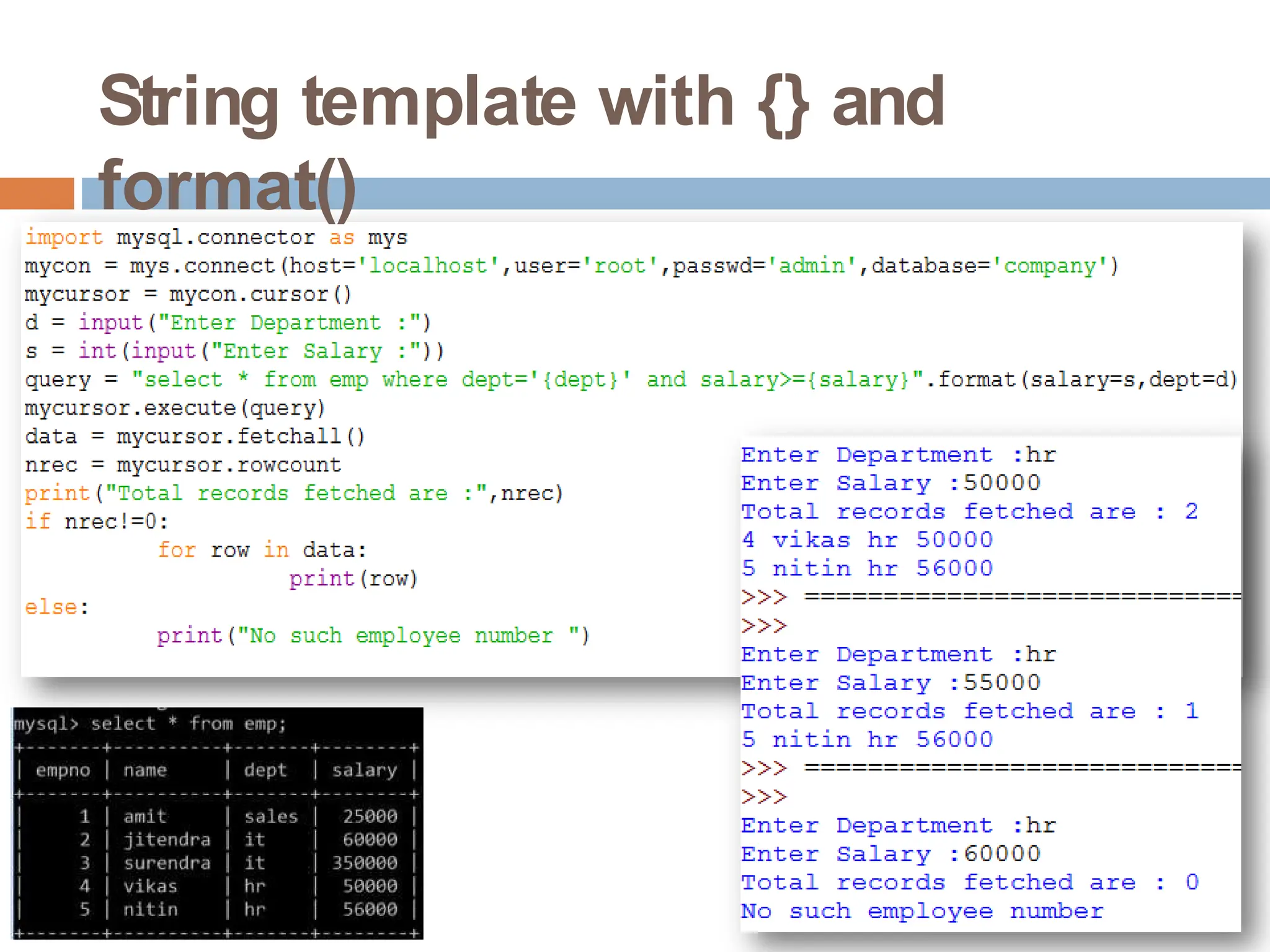
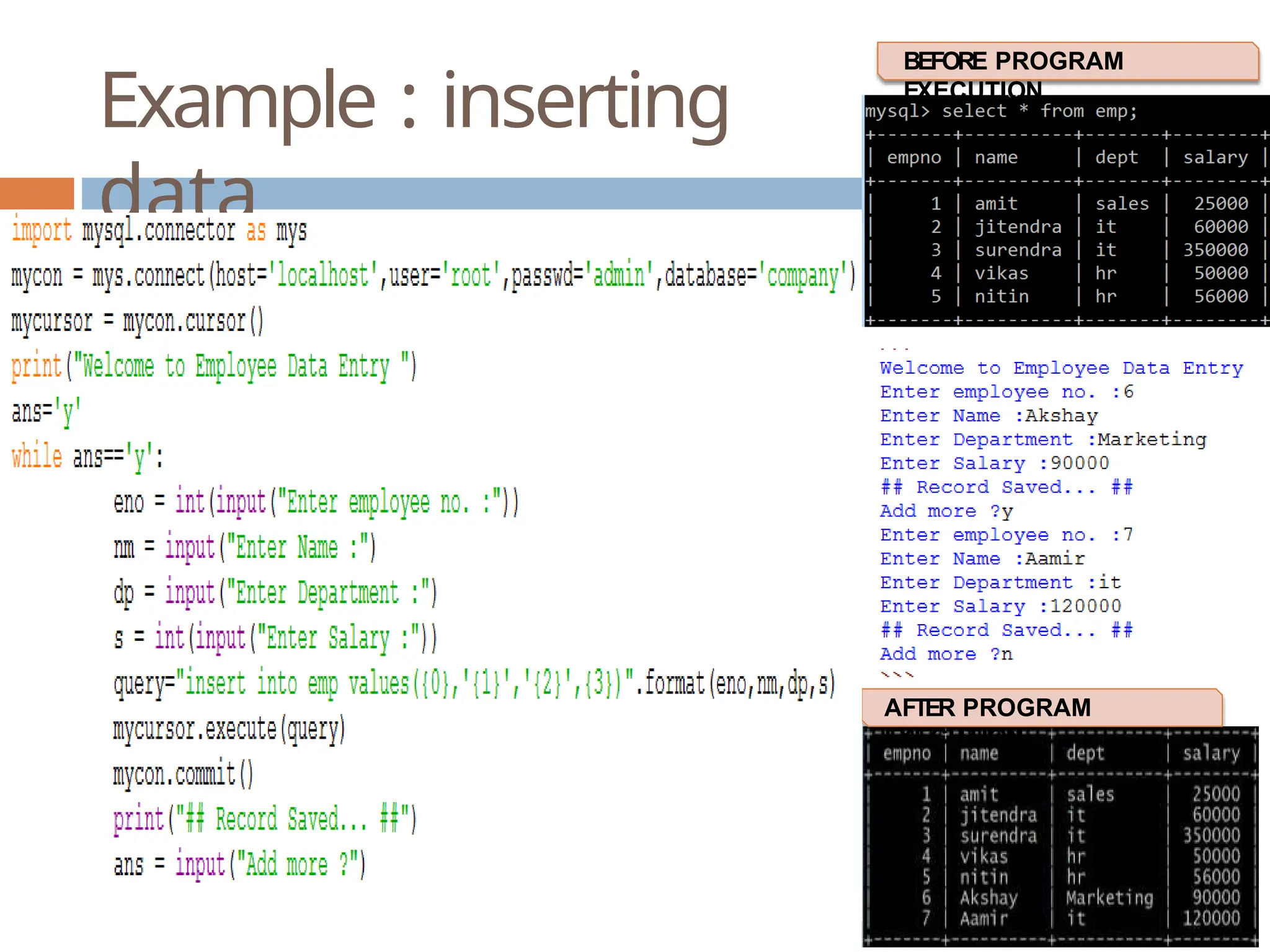
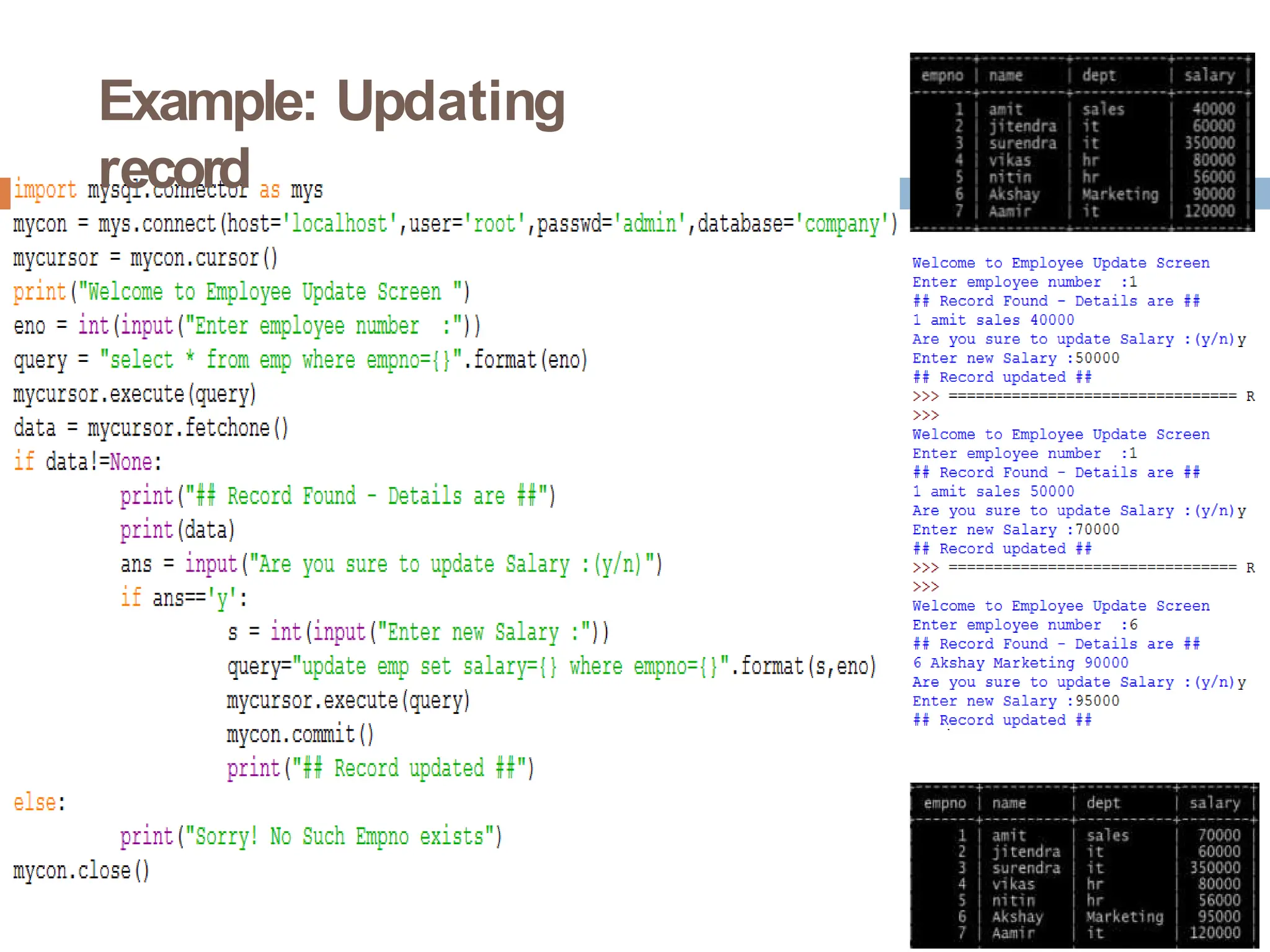
The document provides a comprehensive guide on connecting Python applications with MySQL databases using the 'mysql.connector' package. It outlines the steps for installing the connector, establishing a connection, creating a cursor for executing queries, and fetching data from the result set. Additionally, it explains how to perform parameterized queries and insert or update data in MySQL tables from Python.





![Open a connection to MySQL
Database
T
o create connection, connect() function is used
Its syntax is:
🞑 connect(host=<server_name>,user=<user_name>,
passwd=<password>[,database=<database>])
Here server_name means database servername,
generally it is given as “localhost”
User_name means user by which we connect with
mysql generally it is given as “root”
Password is the password of user “root”
Database is the name of database whose
data(table) we want to use](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/015-241018124237-34e0f9da/75/Interface-Python-with-MySQLwedgvwewefwefwe-pptx-6-2048.jpg)