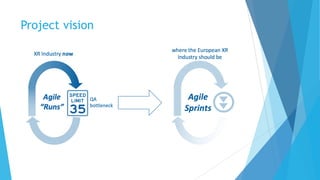
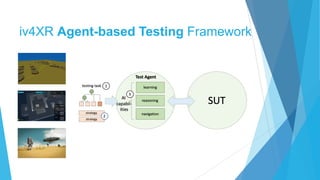
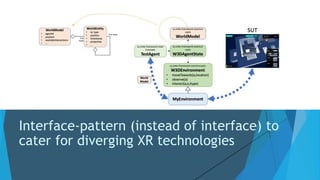
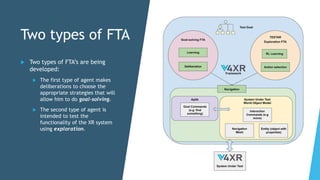
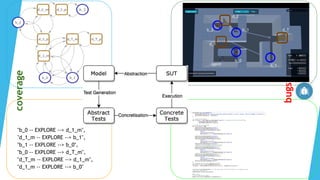
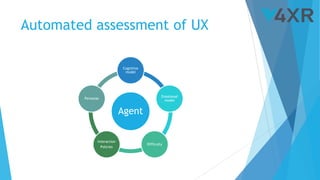
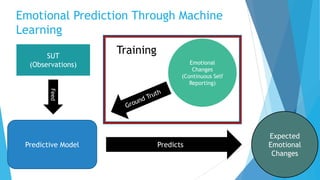
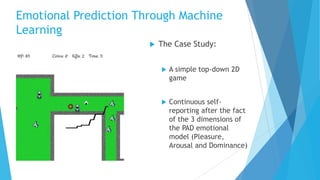
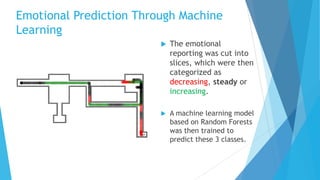
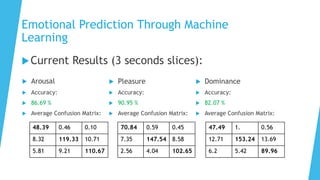
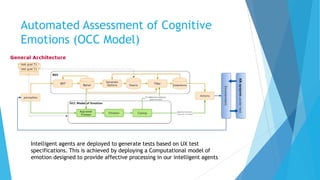
The document discusses the IV4XR project, which focuses on intelligent verification and validation of extended reality (XR) systems through automation and artificial intelligence. It details the development of autonomous testing agents aimed at improving user experience and system functionality while also providing insight into pilot studies conducted in gaming and simulation environments. The framework aims to address the complexities of testing XR technologies with models for emotional prediction and cognitive assessment.