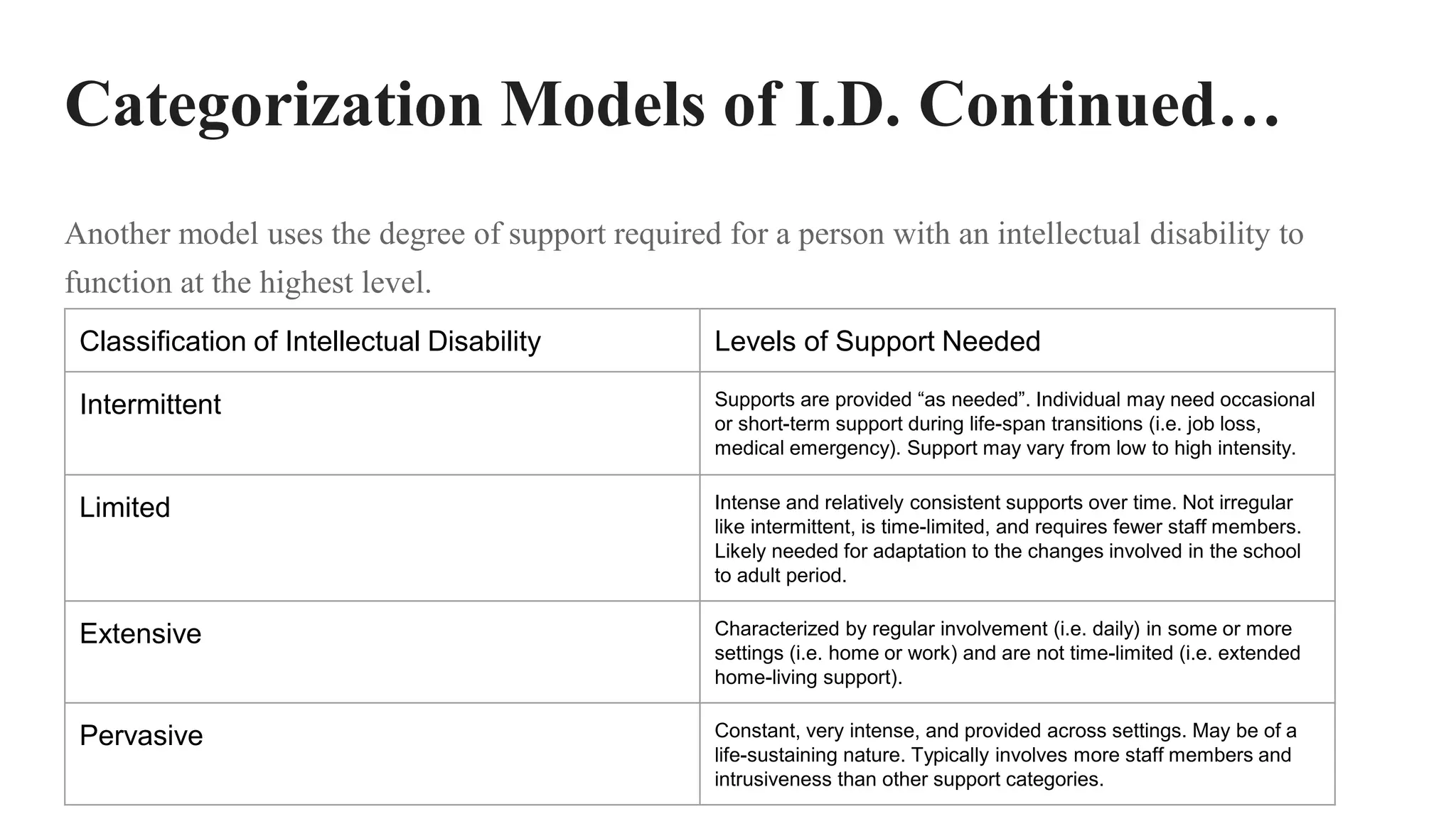
This document discusses intelligence, giftedness, and intellectual disability. It defines intelligence as the ability to solve problems and adapt based on experiences. It describes theories of multiple intelligences and IQ tests, noting limitations in measuring all types of intelligence. Giftedness is defined as having a high IQ (130+) or superior talent, with characteristics like precocity, independence, and passion. Resources are discussed for twice exceptional (gifted and autistic) children. Intellectual disability is defined as limited mental ability with low IQ (below 70) and difficulty adapting. Models categorize intellectual disability by IQ range and level of support needed. Organic causes include genetic disorders and brain damage.