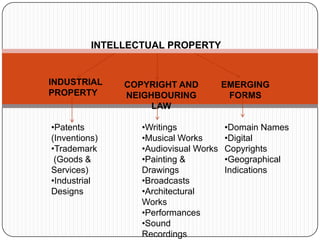
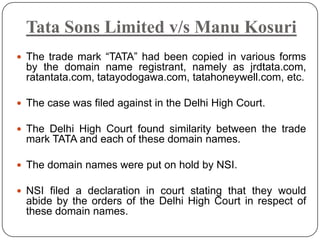
This document discusses intellectual property and different types of intellectual property rights. It defines intellectual property as the creation of the human mind and intellect. Common types of intellectual property rights mentioned include copyrights, trademarks, patents, industrial design rights, and trade secrets. Examples are also provided of court cases involving intellectual property rights violations related to trademarks, copyright, patents, and trade secrets.