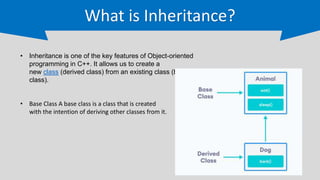
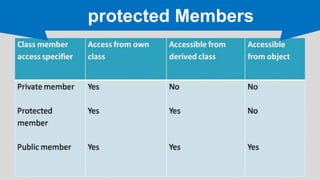
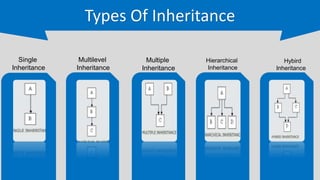
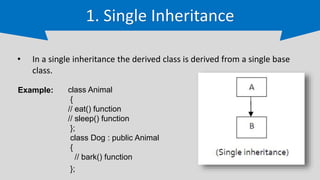
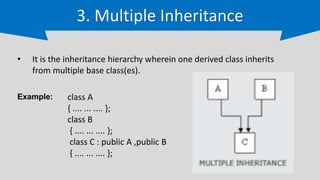
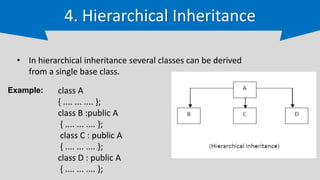
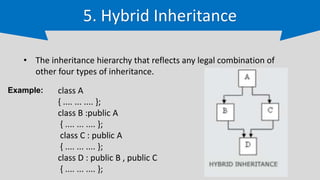
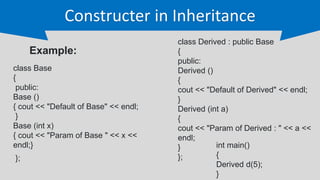
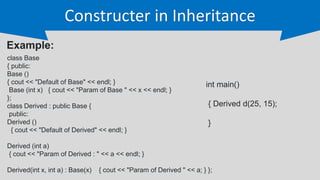
The document provides an overview of inheritance in C++, a key feature of object-oriented programming, detailing its definition, types (single, multilevel, multiple, hierarchical, and hybrid), and the functionality of protected members. It includes syntax and code examples to illustrate different inheritance types and constructors in derived classes. The material serves as a foundational guide for understanding how classes can inherit properties and methods from other classes in C++.