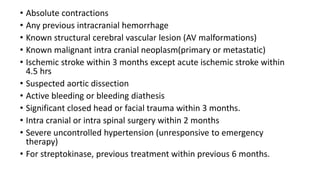
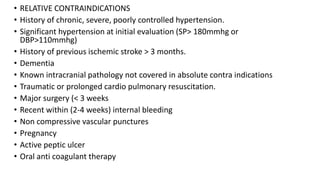
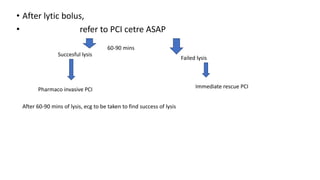
The document lists several indications for thrombolysis and percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI). Thrombolysis is indicated for conditions involving thrombosis including acute myocardial infarction, deep vein thrombosis, pulmonary embolism, and acute ischemic stroke. PCI is indicated for chronic stable angina and acute coronary syndromes. For STEMI, primary PCI is preferred over thrombolysis if it can be performed within 120 minutes of diagnosis, otherwise immediate thrombolysis should be administered.
![INDICATIONS FOR THROMBOLYSIS
• Acute myocardial infarction [AMI]
• Deep vein thrombosis [DVT]
• Pulmonary embolism [PE]
• Acute ischemic stroke [AIS]
• Acute peripheral arterial occlusion
• Occlusion of indwelling catheters
• Intracardiac thrombus formation
• Severe frostbite](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/indicationsforptca-230822121607-f2d14e27/75/INDICATIONS-FOR-PTCA-pptx-1-2048.jpg)