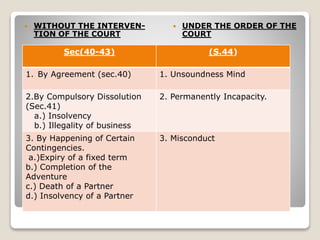
The Indian Partnership Act of 1932 outlines the dissolution of firms, defining dissolution as the end of the partnership between all partners. Various modes of dissolution are specified, including dissolution by agreement, compulsory dissolution due to insolvency or illegality, and dissolution upon certain contingencies such as the death of a partner. The act also details procedures for dissolution, including the role of courts and conditions under which a partner may give notice to dissolve a partnership at will.