This document discusses income that falls under the category of "Income from Other Sources" according to India's Income Tax Act of 1961. It provides definitions and examples of various types of income taxable as "residuary income" including interest income, dividend income, family pension, casual income, and income from property acquired without adequate consideration. It also outlines deductions that can be claimed and expenses that are not deductible for this category of income.


![DEDUCTIONS [SEC. 57]:
The following expenditures are allowed as deductions from income chargeable to tax under the head ‘Income from Other Sources’:
S.No. Section Nature of Income Deductions allowed
1 57(i) Dividend or Interest on securities
Any reasonable sum paid by way of commission or remuneration
to banker or any other person for purpose of realizing dividend or
interest on securities
2 57(ia)
Employee’s contribution towards Provident Fund,
Superannuation Fund, ESI Fund or any other fund
setup for the welfare of such employees
If employees’ contribution is credited to their account in
relevant fund on or before the due date
3 57(ii)
Rental income letting of plant, machinery, furniture
or building
Rent, rates, taxes, repairs, insurance and depreciation etc.
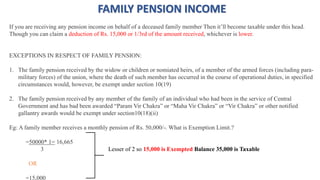
4 57(iia) Family Pension 1/3rd of family pension subject to maximum of Rs. 15,000.
5 57(iii) Any other income
Any other expenditure (not being capital expenditure) expended
wholly and exclusively for earning such income
6 57 (iv) Interest on compensation or enhanced compensation 50% of such interest (subject to certain conditions)
7 58(4) Proviso
Income from activity of owning and maintaining race
horses.
All expenditure relating to such activity.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/incomefromothersourcesbase-230707115428-07459e31/85/INCOME-FROM-OTHER-SOURCES-Base-pptx-3-320.jpg)
![Expenses not deductible [Section 58]:
S.N. Section Nature of Income
1 58(1)(a)(i) Personal expenses
2 58(1)(a)(ii)
Interest chargeable to tax which is payable outside
India on which tax has not been paid or deducted at
source
3 58(1)(a)(iii)
‘Salaries’ payable outside India on which no tax is paid
or deducted at source
4 58(1A) Wealth-tax
5 58(2) Expenditure of the nature specified in section 40A
6 58(4)
Expenditure in connection with winnings from
lotteries, crossword puzzles, races, games, gambling
or betting](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/incomefromothersourcesbase-230707115428-07459e31/85/INCOME-FROM-OTHER-SOURCES-Base-pptx-4-320.jpg)



![EMPLOYEES’ CONTRIBUTIONS TO PROVIDENT FUND ETC,
[Sec. 56(2)(IC)]
It has to be remembered that any sum received by the assessee from his employees as contributions to any provident fund or
superannuation fund or any fund set up under the provisions of the Employees 'State Insurance Act, 1948 or any other fund for
the welfare of such employees is income in the hands of the assessee and is chargeable as Income from Other Sources if not
chargeable as Profits and Gains on Business or Profession [Sec. 2(24)(x)]
However, the tax payer is entitled to deduction of the sum of such contributions received from his employees if such sum is
credited by the taxpayer to the employee’s account in the relevant fund on or before the due date. Here, the due date means the
date by which the assessee is required as an employer to credit an employees’ contribution to the employees’ account in the
relevant fund under an Act, rule, etc. issued in that behalf [Sec. 36(1)(va)].
Therefore, any sum received by the assessee from his employees as contributions to any fund as aforesaid and is not deposited
or deposited belatedly to the employee’s account, it becomes income of the assessee.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/incomefromothersourcesbase-230707115428-07459e31/85/INCOME-FROM-OTHER-SOURCES-Base-pptx-11-320.jpg)