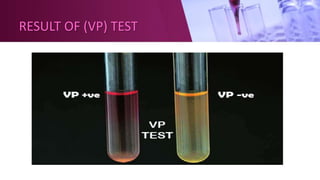
This document summarizes several microbiology tests including the Indole test, Methyl Red test, Voges-Proskauer test, and Citrate utilization test. For each test, it describes the aim, culture medium used, principle, and provides examples of bacteria that test positive or negative. The Indole test detects the ability of bacteria to produce indole from tryptophan, while the Methyl Red and Voges-Proskauer tests determine if bacteria produce acid or alkaline end products from glucose fermentation respectively. The Citrate utilization test identifies bacteria that can use citrate as a sole carbon source.