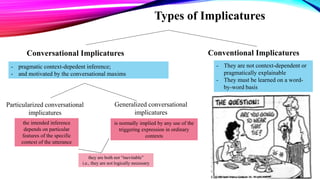
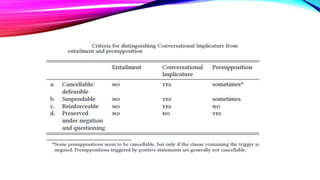
This document discusses Grice's theory of implicature, including types of implicatures, properties, and diagnostic tests. There are two main types of implicatures: conversational implicatures, which are context-dependent inferences, and conventional implicatures, which are meanings learned on a word-by-word basis. Conversational implicatures can be particularized or generalized. Generalized implicatures are normally implied by any use of a word, while particularized implicatures depend on specific context. The document provides examples and discusses how to distinguish implicatures from other inferences using tests of being defeasible, suspendable, calculable, indeterminate, nondetachable, and reinforceable.