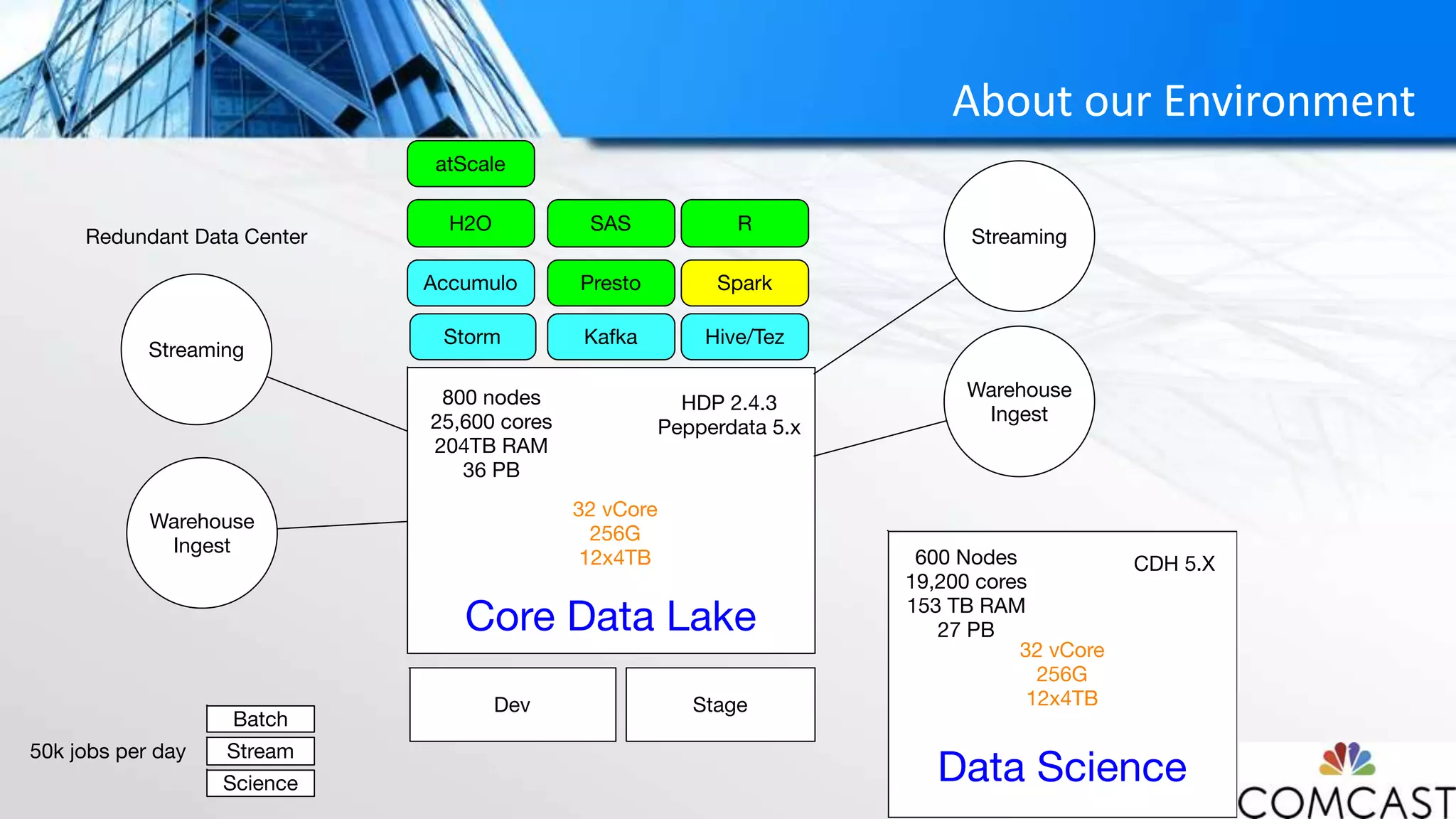
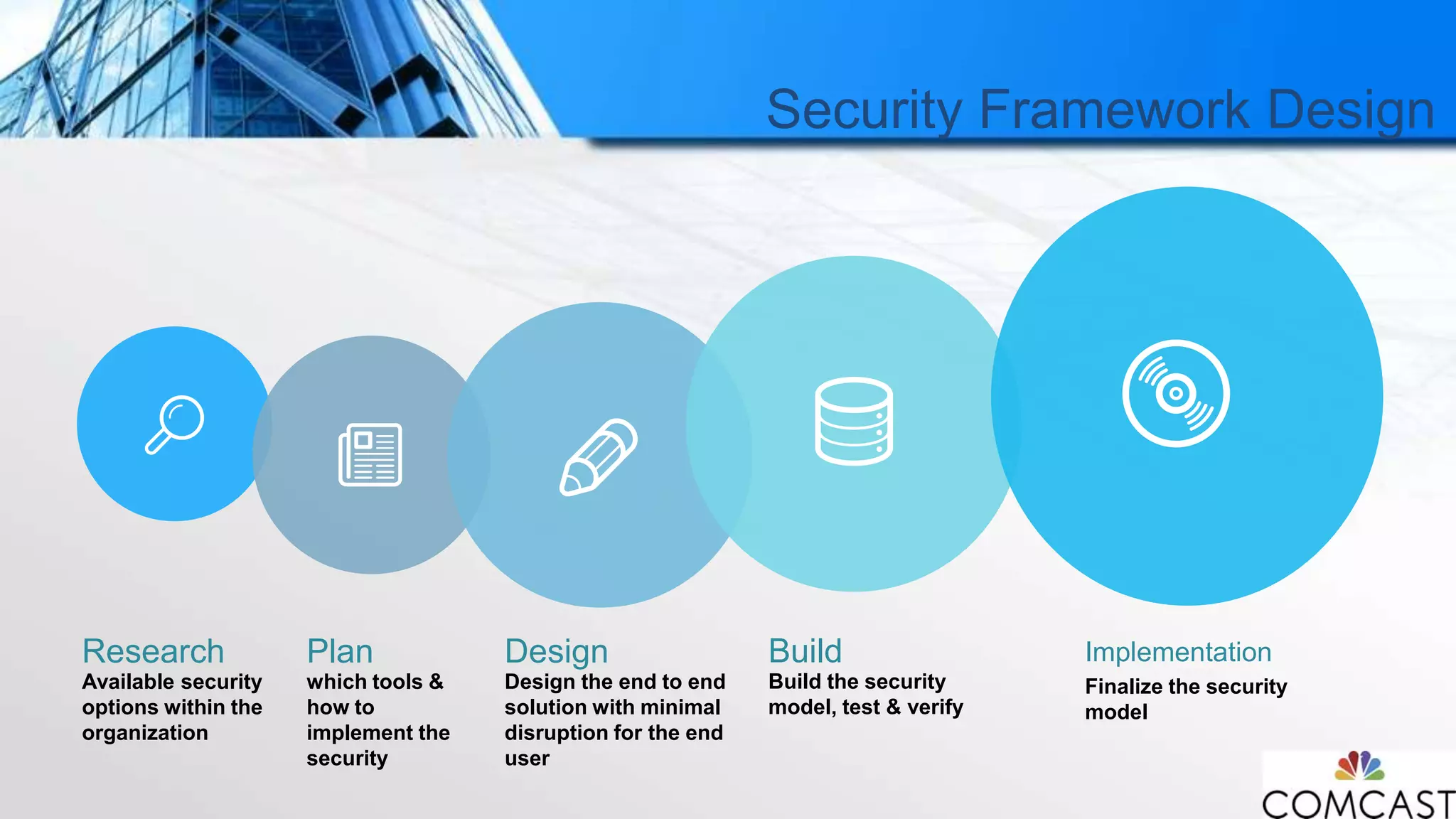
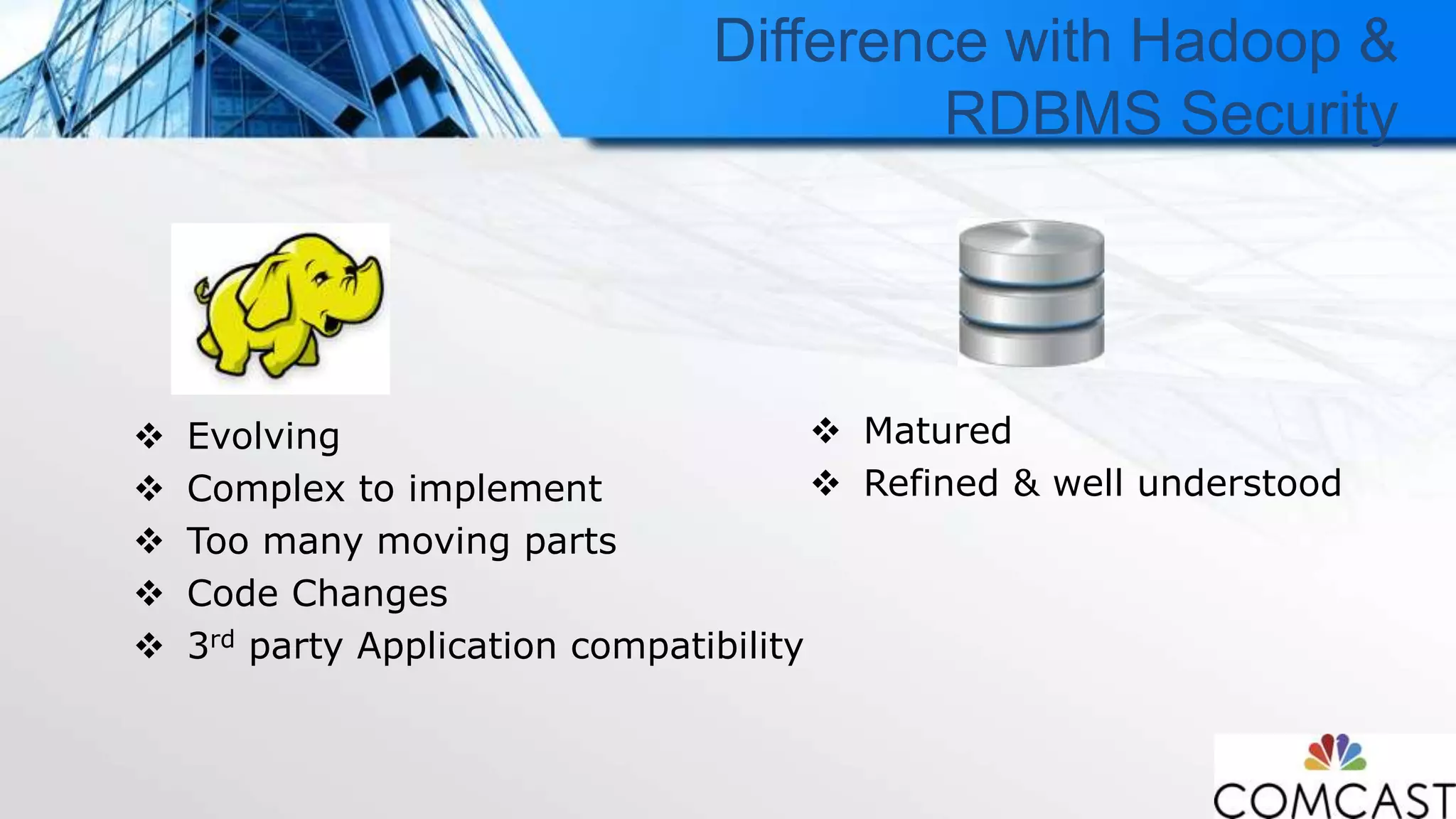
The document discusses Comcast's approach to Hadoop security, highlighting the challenges and evolution of security measures in handling big data across various customer-centric services. It details the security framework developed, which includes the use of Kerberos and Apache Ranger, and emphasizes the importance of collaboration among stakeholders for successful implementation. Additionally, it outlines the significant costs associated with data breaches and the complexities involved in maintaining a secure multi-tenant environment.