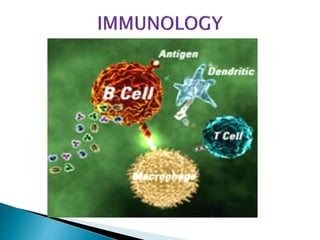
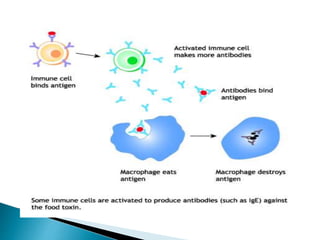
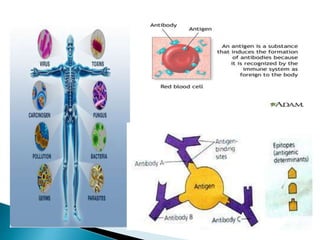
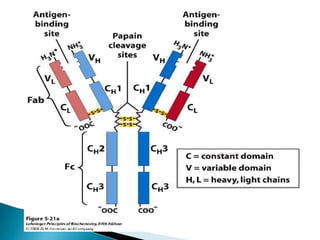
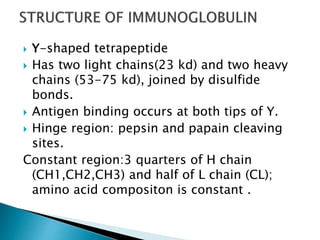
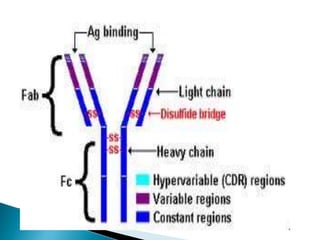
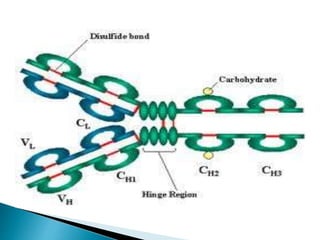
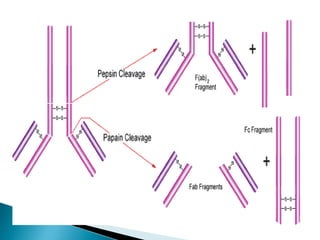
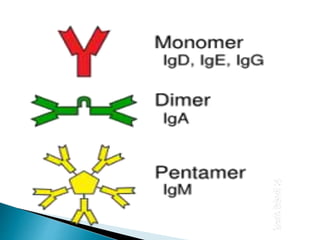
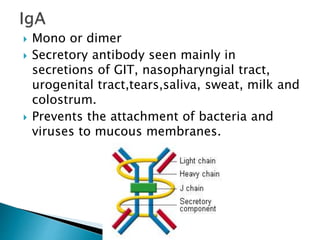
The document summarizes key aspects of the immune system and immunoglobulins. It describes the immune system's mechanisms for recognizing self from non-self. There are five main classes of immunoglobulins - IgG, IgA, IgM, IgD, and IgE - which differ in structure, function, and location. IgG is the most abundant immunoglobulin and provides secondary immune response and antibody-mediated immunity. IgM is the first antibody produced during primary response and fixes complement. IgA provides mucosal immunity through secretions. IgD and IgE have uncertain functions but IgE mediates allergic reactions.