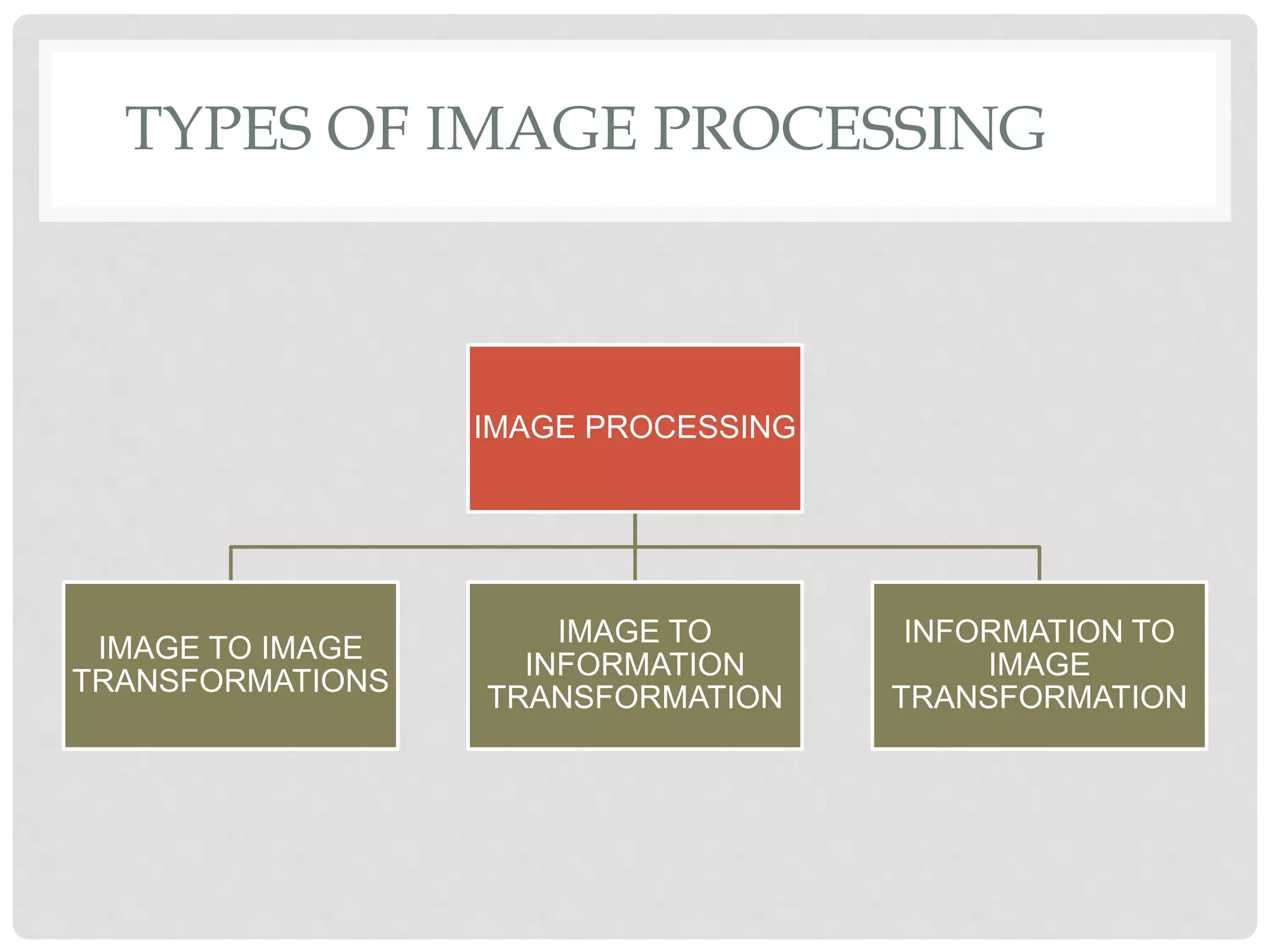
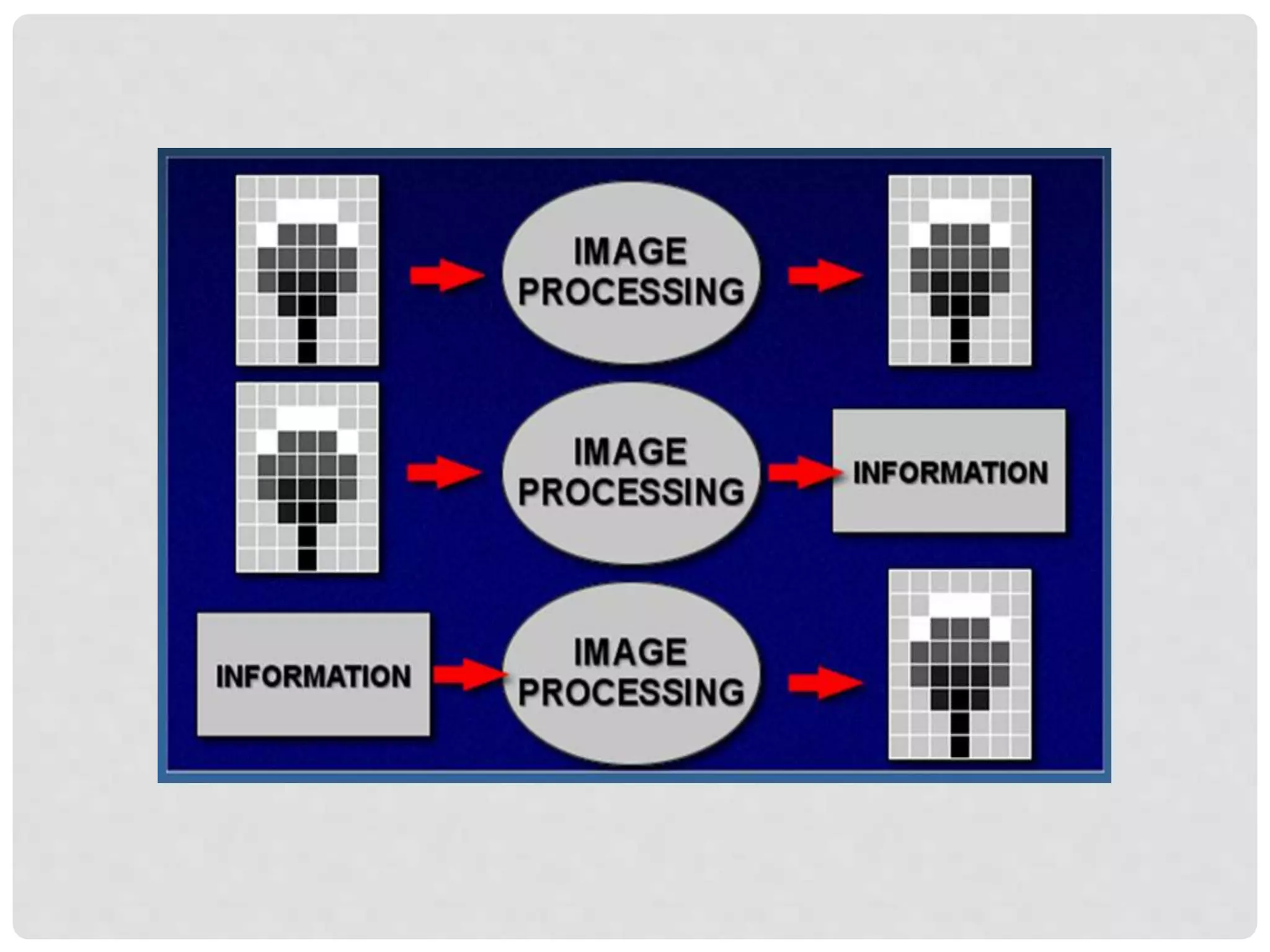
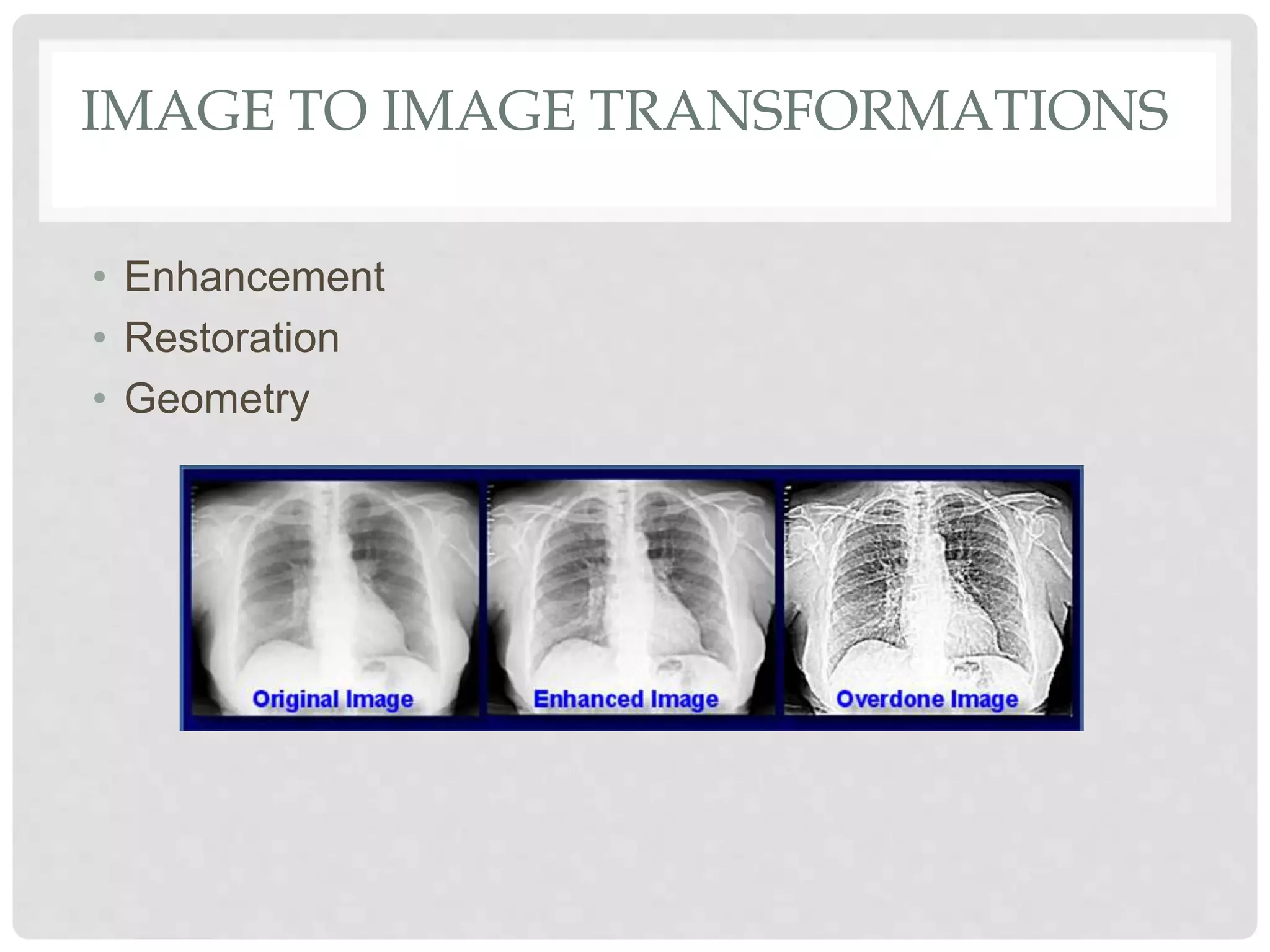
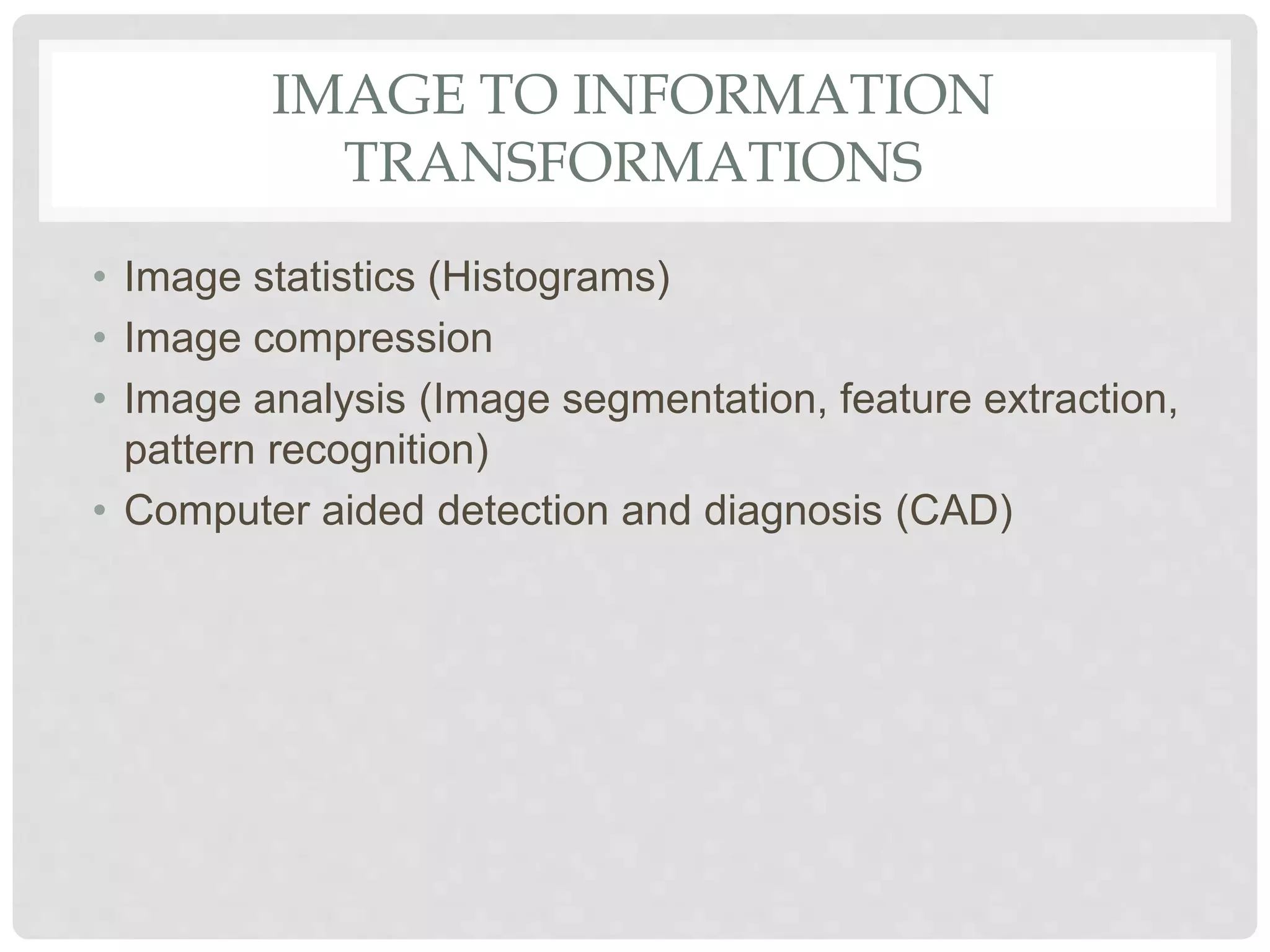
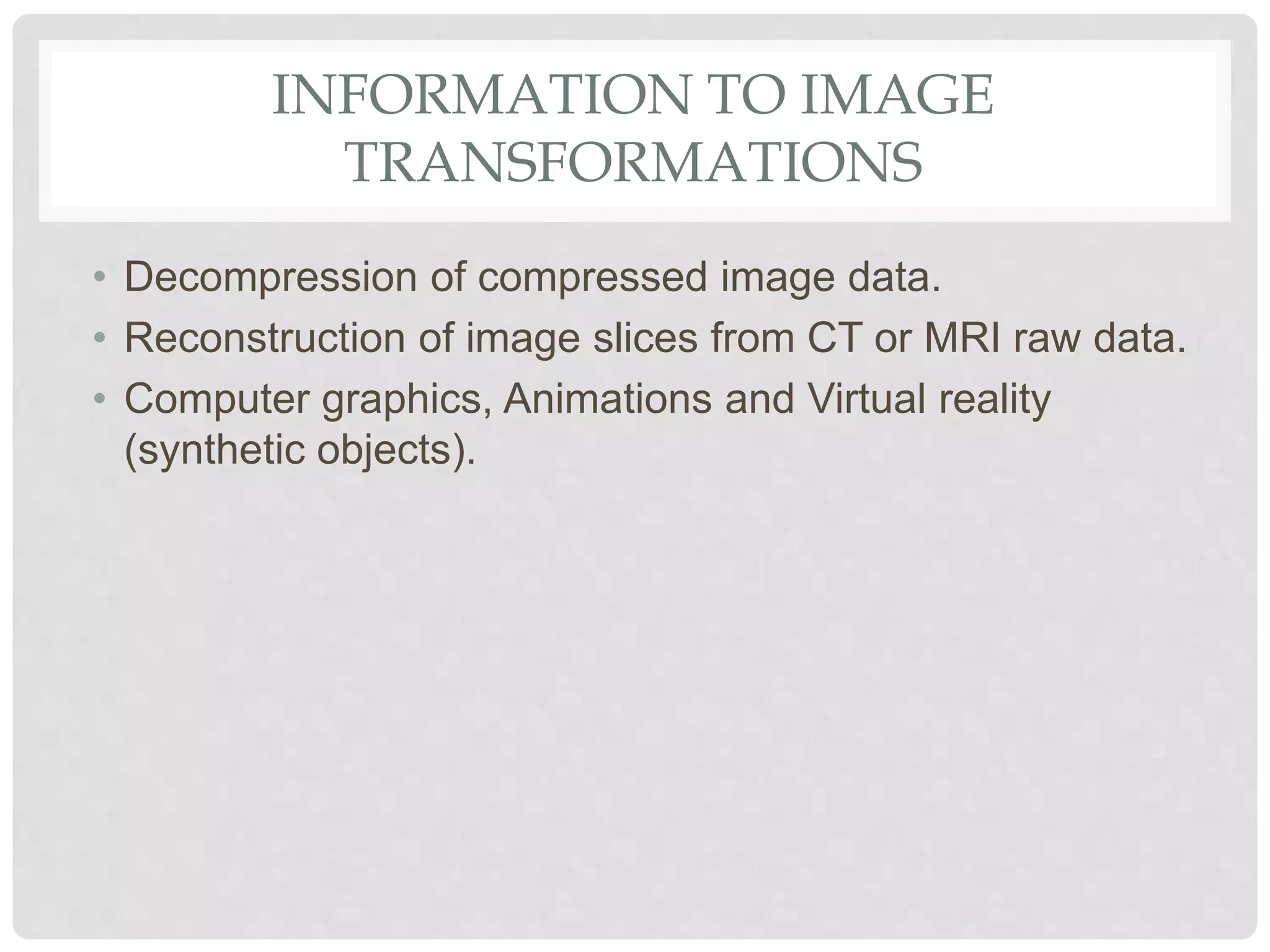
This document provides an introduction to image processing. It discusses that image processing involves applying mathematical operations to images using signal processing techniques. The input is an image or video and the output is either an improved image or extracted image features. Image processing is used to enhance images for human viewing and to analyze image structures and features. It allows analyzing medical images to help detect abnormalities. Key hardware requirements for image processing include high resolution, display, memory, storage, and computing power. Common software used includes Adobe Photoshop, Corel Draw, and Serif PhotoPlus.