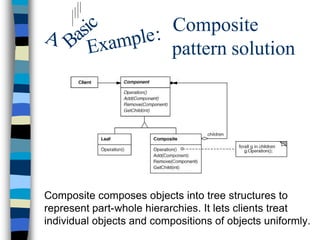
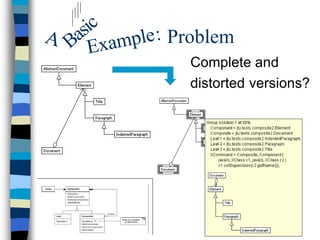
This document discusses using an explanation-based constraint programming (CP) approach to identify the use or misuse of design patterns in software code. It describes how design pattern solutions can be modeled as constraints over classes and relationships in code. The explanation-based CP system called PaLM is used to generate justifications for modifications to code that would transform a misuse into a proper use of a design pattern. Experiments applying this approach to various codebases, including JEdit and JHotDraw, showed promising results. Future work aims to improve the scalability and usability of the system.











![Conclusion and future
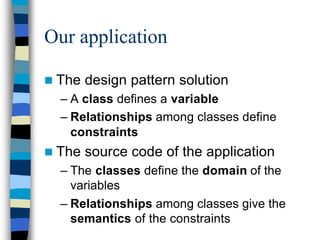
n An application of explanation-based CP
– Non-trivial problem
n Short term
– To add more design pattern solutions
– To develop the constraints system
• New algorithm CSP-NN [Morning session]
– Scalability and weights (noise)
n Long term
– automation and interaction (usability)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ijcai01mspc-ppt-130412083922-phpapp01/85/IJCAI01-MSPC-ppt-20-320.jpg)