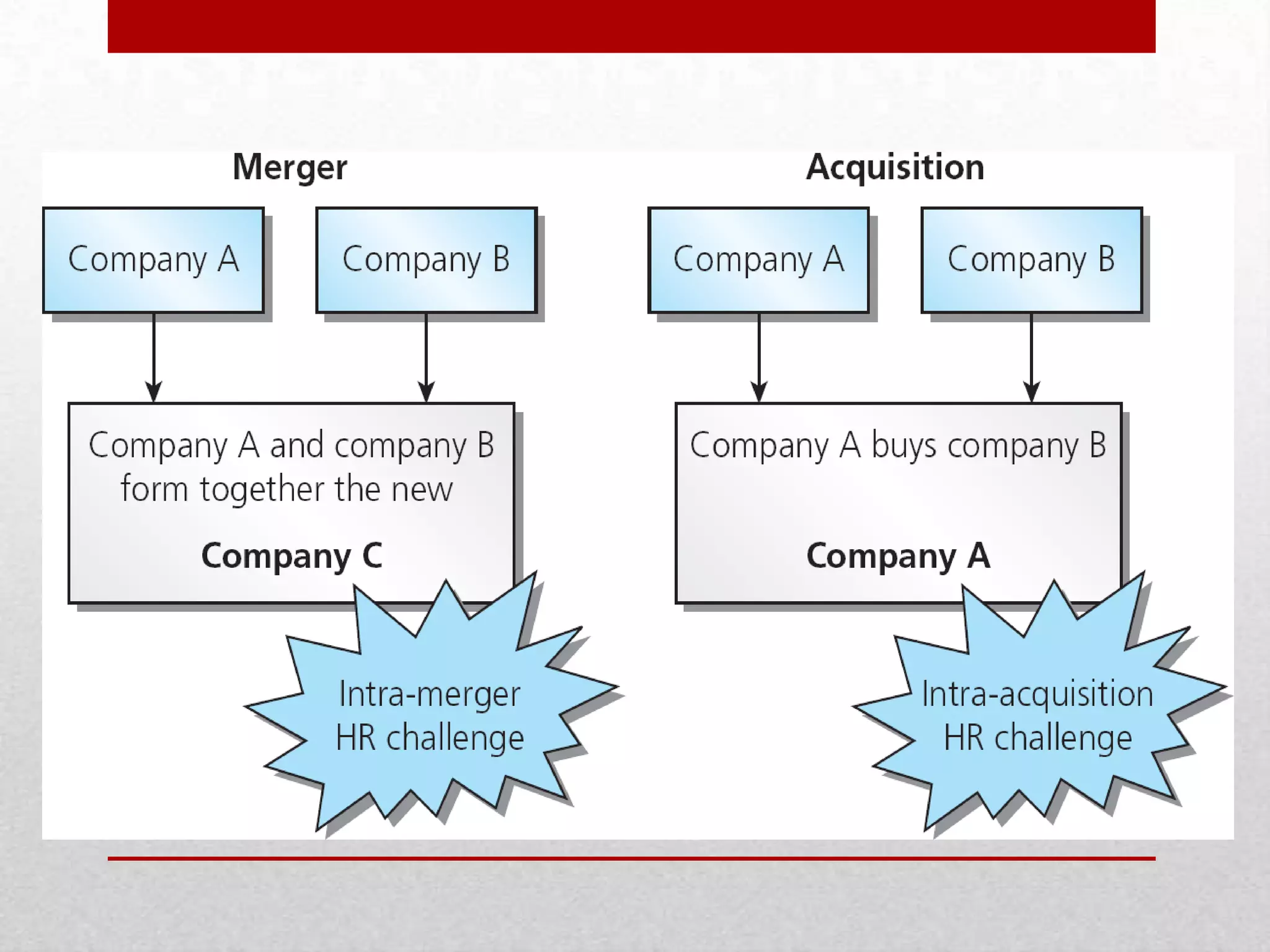
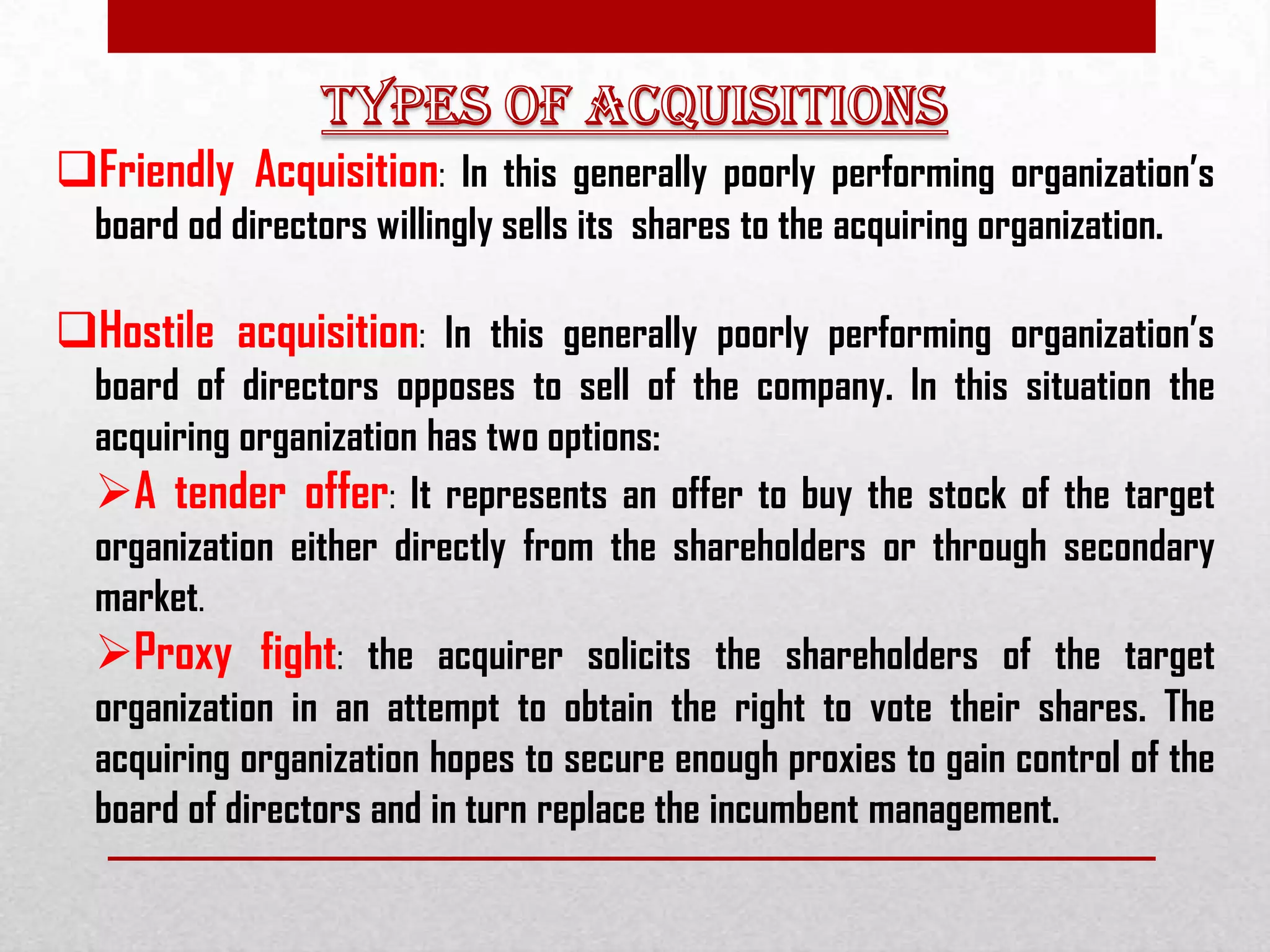
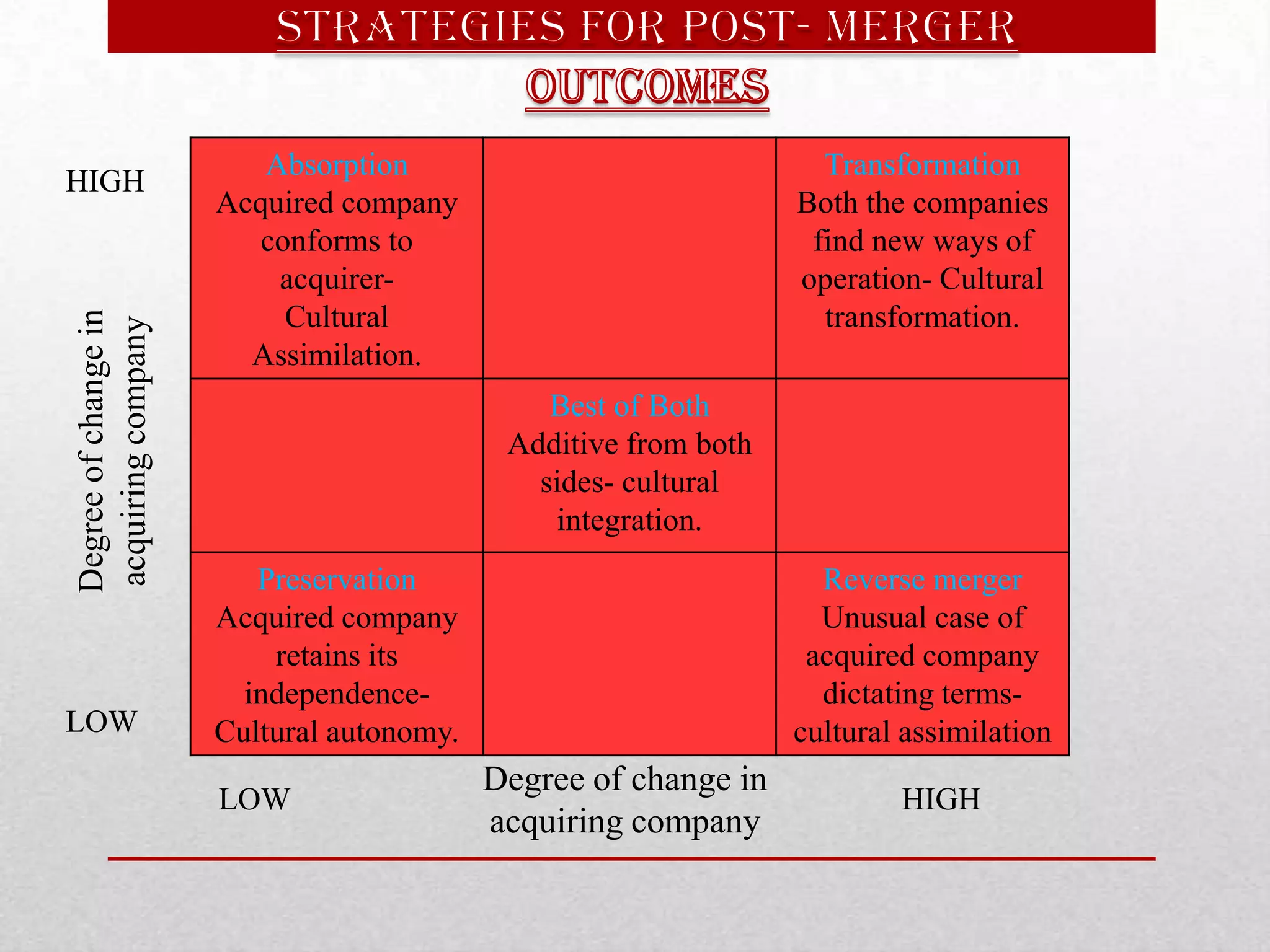
This document discusses different types of mergers including horizontal, vertical, and conglomerate mergers. It also discusses friendly and hostile acquisitions. Mergers allow companies to achieve economies of scale, gain access to new markets and technology, and reduce costs. A successful merger occurs when the net present value of the combined companies is greater than the individual net present values. Challenges in mergers include focusing too much on financials and not people, uncertainty causing low employee morale, and lack of clear leadership and communication during integration. The level of cultural change depends on the acquisition strategy used such as absorption, transformation, best of both, or preservation. Key post-merger integration activities include selecting management teams and boards, assessing culture fit,