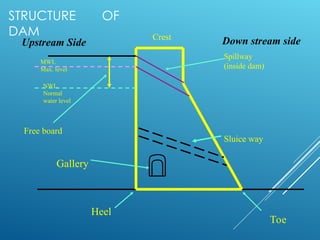
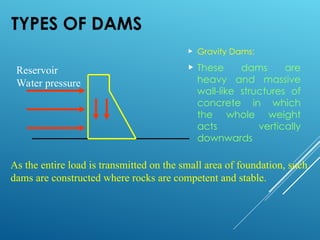
The document provides an overview of dams, highlighting their construction, structure, and purposes such as hydropower, irrigation, and flood control. It describes various types of dams, including gravity, buttress, arch, and earth dams, detailing their specific characteristics and applications. The Bhakra Dam is noted as the highest concrete gravity dam in Asia, emphasizing its significant dimensions and historical construction timeline.