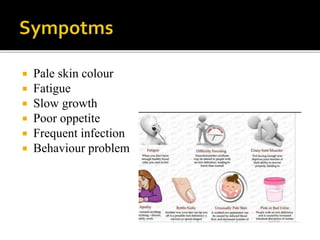
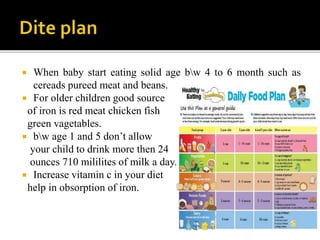
This document discusses iron deficiency anemia (IDA) in children. It defines IDA as a decrease in circulating red blood cells and hemoglobin, impairing oxygen transport. Common causes of IDA in children include premature birth, cow's milk before age 1, and chronic infections. Symptoms include pale skin, fatigue, slow growth, and behavioral problems. The document examines prevalence of IDA based on socioeconomic status, medical history, and anthropometric measures. It provides recommendations to prevent IDA, such as iron supplements and including iron-rich foods in the diet. The conclusion states IDA disproportionately affects young, growth-retarded children and those in food insecure areas.