The document discusses key concepts about computers including:
1) It defines data as raw unorganized facts that can be in various forms, while information is data that has been processed into a meaningful form through information processing.
2) It explains that software, including operating systems and application software, controls computer hardware and allows it to perform specific tasks.
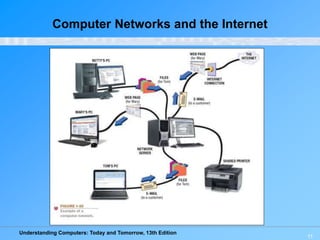
3) It describes computer networks and the internet, where the internet is the world's largest computer network and the World Wide Web allows access to web pages through internet browsers.