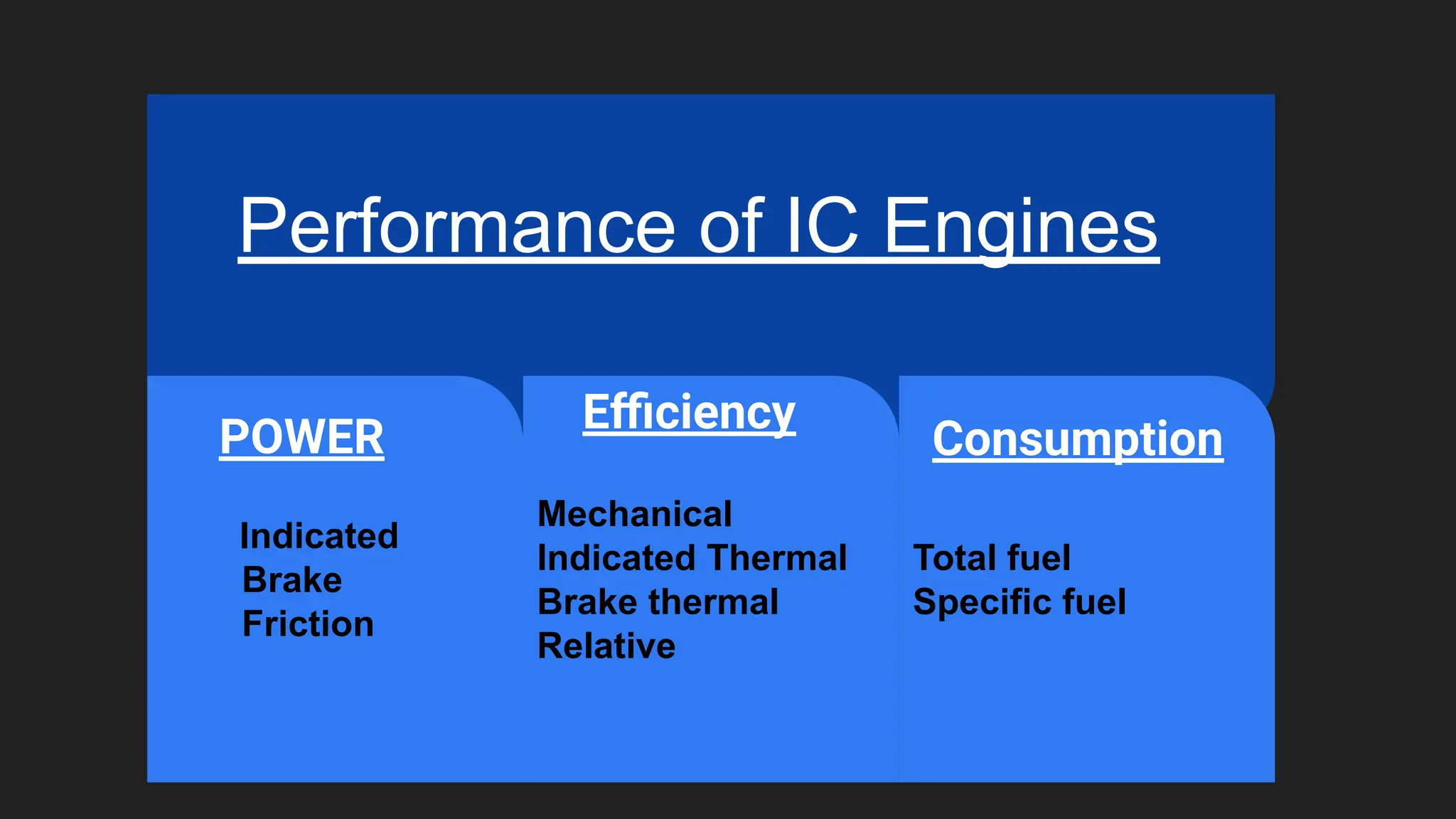
An internal combustion (IC) engine is an engine where fuel combustion occurs internally, and its performance is measured by how efficiently it converts fuel into mechanical work. Key performance indicators include indicated power, brake power, mechanical efficiency, indicated thermal efficiency, and brake thermal efficiency, which assess the engine's power production and losses due to friction. Additionally, relative efficiency is used to compare the efficiencies of various components within a system.